Abstract
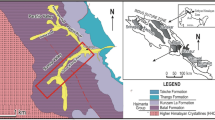
Se-rich black rock series of the Middle and Late Permian system is widely distributed in Enshi Prefecture with an exposed area of 850 km2, among which the unique Yutangba black rock series independent selenium deposit with industrial mining significance in the world is produced. However, the source and metallogenic mechanisms of Se are still controversial. In general, terrestrial weathering and submarine hydrothermal processes are the main source end members of Si and Se, and the related siliceous rocks record the deposition process of Si and Se from different sources. The study of lithofacies and paleogeography shows that western Hubei belongs to the near east–west turn of the Yangzi platform in the Middle and Late Permian and becomes an inter-platform basin with nearly north–south direction. Therefore, the comparative study of the Yutangba deposit and the selenium-rich black rock series in the northern Shadi with high selenium content is expected to reveal the provenance evolution of the two sections in space, and further restrict the Se mineralization mechanism in the Enshi basin. From the element geochemistry study, the black rock series in two study areas may have formed in a transitional position of either the continental margin or continental slope, in the process of sedimentary, more terrigenous clastic materials entered. They are rich in lithophile elements V and Cr. δU > 1.0, U/Th and V/(V + Ni) ratio indicate that the Se-rich strata of black rock series in the Enshi areas occurred in an anoxic reducing environment and formed in an environment between the ocean basin and the continental margin. From Si–O isotope geochemistry, the original Si source of the study area is thought to relate to a volcanic eruption, which leads to the enrichment of Si in the seawater. The determined values of S isotope in the black rock series of the two study areas both show the characteristics related to organic reduction/biogenic.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alan DH, Samuel MS (1970) Oxygen-18 studies of recent planktonic foraminifera-comparisons of phenotypes and of test parts. Science 170(3953):69–71
Arthur MA, Sageman BB (1994) Marine shales: depositional mechanism and environments of ancient deposits. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 22:499–551
Boström K, Peterson MNA (1969) The origin of aluminum-poor ferromanganoan sediments of high heat flow on the East Pacific Rise. Marine Geol 7:427–447
Boström K, Kraaemer T, Gartner S (1973) Provenance and accumulation rates of opaline silica, Al, Ti, Fe, Mn, Cu, Ni and Co in Pacific Pelagic sediments. Chem Geol 11(2):123–148
Chaussidon M, Lorand JP (1990) Sulphur isotope composition of orogenic spinel iherzolite massifs from Ariege (North-Eastern Pyrenees, France): an ion microprobe study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:2835–2846
Clayton RN (1986) High temperature isotope effects in the early solar system. Rev Mineral 16:129–139
Clayton RN, Mayeda TK (1963) The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxide silicates for isotopic analysis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 27:43–52
Clayton PJ, Halikas JA, Maurice WL (1972) The depression of widowhood. Br J Psychiatry 120:71–78
Dill H (1986) Metallopetrogenesis of Early paleozoic graptolite shales from the Graafenthal Horst (Northern Bavaria-Federal Republic of Germany). Econ Geol 81(4):889–903
Douthitt CB (1982) The geochemistry of the stable isotopes of silicon. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 39(5):1179–1186
Fan HF, Wen HJ, Ling HW, Yu WX (2005) Determination of trace selenium in geological samples by Hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry-a comparative experiment of two different dissolution methods. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem 24(3):200–203 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Feng CX (2004) The enriching-mechanism of Se of Cambrian and Permian silicalite formation in the peripheral margins of Yangtze Block: taking Yutangba and Ziyang Se-rich areas as an example. Ph. D. Dissertation. Guiyang: Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Science (in Chinese with English abstract)
Feng CX, Liu JJ, Liu S, Hu RZ (2002) The geochemistry and petrogenesis of siliceous rocks of Se diggings in Yutangba. Acta Sedimentol Sin 20(4):727–732 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Feng CX, Liu JJ, Hu RZ, Liu S (2004) Geochemistry of the Yutangba Se deposit in western Hubei Province China. Chin J Geochem 23(3):255–264
Feng CX, Jiajun L, Shen L, Ruizhong H, Guoxiang C (2009) Petropetrogenesis and sedimentary environment of the cherts from Yutangba, western Hubei Province: evidence from silicon, oxygen, carbon and sulfur isotopic composition. Acta Petrol Sin 25(5):1253–1259 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Francois R (1988) Carbon and oxygen isotope variations in Precambrian cherts. Geochem Cosmochim Acta 52(6):1473–1478
Frimmel HE (2005) Archean atmospheric evolution: evidence from the Witwatersand gold fields, South Africa. Earth Sci Rev 70:1–46
Girty GH, Rdige DL, Knaack C, Johnson D, Al-Riyami RK (1996) Provenance and depositional setting of Paleozoic chert and argillite, Sierra Nevada California. J Sediment Res 66(1):107–118
Hubei Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (1990) Hubei Provincial Regional Geology-Special Geological Report of the Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources of the People's Republic of China, I. Regional Geology No. 20. Geological Publishing House, pp 1–644
Hou KJ, Li YH, Wan DF (2007) Constraints on the Archean atomospheric oxygen and sulfur cycle from mass-independent sulfur records from Anshan-Benxi BIFs, Liaoning province China. Sci China (Series D) 50(10):1471–1478
Huang JQ, Chen BW (1987) The evolution of the Tethys in China and adjacent regions. Geological Publishing House, Bei**g, pp 1–109 (in Chinese)
Jiang SY, Zhao HX, Cheng YQ, Yang T, Tang JH, Ling HF (2007) Trace and rare earth element geochemistry of phosphate nodules from the lower Cambrian black shale sequence in the Mufu mountain of Nan**g, Jiangsu Province China. Chem Geol 244(3–4):584–604
Jones B, Manning DAC (1994) Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of paleoredox conditions in ancient mudstones. Chem Geol 111:111–129
Knauth LP, Epstein S (1976) Hydrogen and oxygen isotope rations in nodular and bedded cherts. Geochem Cosmochim Acta 40(9):1095–1108
Knauth LP, Lowe DR (1978) Oxygen isotope geochemistry of cherts from the Onverwacht Group (3.4 billion years), Transvaal, south Africa, with implications for secular variations in the isotopic composition of cherts. Earth Planet Science Lett 41(2):209–222
Li SR, Gao ZM (1995) REE characteristtic of black series of the lower Cambrian Niutitang formation in Hunan-Guizhou provinces, China-with a discussion on the REE patterns in marine hydrothermal sediments. Acta Mineral Sin 15(2):225–322 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu JJ, Feng CX, Li ZM, Wang JP, Liu SR, Zhou GF (2005) The research of significance and discovery of Secondary native selenium in the Yutangba Se deposit, western Hubei. Geosciences 19(4):531–537 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu JJ, Cao Y, Carranza EJM, Feng CX, Zhai DG, Wang JP, Li JX (2014) Characterization of secondary native selenium in the Yutangba Se Deposit, western Hubei. China Resour Geol 64(3):271–281
Murray RW (1994) Chemical criteria to identify the depositional environment of chert: general principles and application. Sed Geol 90(3–4):213–232
Murray RW, Ten Brink MRB, Jone DL, Gerlach DC, RussIII GP (1990) Rare earth elements as indicators of different marine depositional environments of chert and shale. Geology 18(3):268–271
Niu ZJ, Xu AW, Duan QF, Fu TA (2000) Original and enrichment of Se in Permian strata in the north part of Jianshi Hubei. Reg Geol China 19(4):396–401 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Peng J, **a WJ, Yi HS (1995) Silicon and oxygen isotopic compositions and origin analysis of Late Precambrian bedded cherts in western Hunan. Geol Rev 41(1):34–41 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Peng J, **a WJ, Yi HS (1999) Geochemical characteristics and depositional environments of the Late Precambrian environments of the Late Precambrian bedded siliceous rocks in western Hunan. Sediment Facies Palaeogeogr 19(2):29–37 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Qi L, Hu J, Gregoire DC (2000) Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Talanta 51(3):507–513
Rimmer SM (2004) Geochemical paleoredox indicators in Devonian-Mississippian black shales, central Appalachian Basin (USA). Chem Geol 206:373–391
Robert NC, Toshilo KM (1986) Oxygen isotopes in Shergotty (in Shergotty Consortium and SNC meteorites). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 50(6):979–982
Rollinson HR (1993) Using geochemical data: evaluation presentation and interpretation. Longman, Harlow, p 352
Rona PA (1978) Criteria for recognition of hydrothermal mineral deposits in ocean crust. Econ Geol 73:135–160
Shi XB, Wong MZ, Luo H, Xu LL, Gong ZY, Zhao XS, Duan XF (2016) Sequence stratigraphy of Middle Permian Gufeng formation from Se-rich area in Enshi, Southwestern Hubei. Geol Miner Resour South China 32(1):1–9
Song TR, Ding TP (1989) The trying application of silicon isotope of silication to analyzing sedimentary faces. Chin Sci Bull 34(18):1408–1411 (in Chinese)
Sugisaki R, Yamamoto K, Adachi M (1982) Triassic bedded cherts in central Japan are not pelagic. Nature 298:644–647
Sun SS, McDonough W (1989) Chemical and isotopic-systematics of oceanic basalts: implication for Inantie composition and processes. In: Saunders AI, Norry MJ (eds) Magmatism in ocean basins. Geological Society London, Special Publications, London, vol 42, pp 313–345
Tian SP, Zhu YN, Wang QL, Zhu HJ (2007) The metallogenic condition and its prognosis of Se deposit in east Enshi state of Hubei Province. Geol Chem Miner 39(3):141–149 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ti** D, Shaoyong J, Defang W, Li YH, Li JC, Song HB, Liu ZJ, Yao XM (1994) Silicon isotopic geochemistry. Geological Publishing House, Bei**g, pp 1–102
Tong Li (1992) The Statistical characteristics of the abundance of chemical elements in the earth’s crust. Geol Prospect 28(10):1–7 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wignall PB (1994) Black shales. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Wignall PB (2001) Large igneous provinces and mass extinctions. Earth Sci Rev 53(1–2):1–33
Wilde SA, Middleton MF, Evans BJ (1996) Terrane accretion in the southwestern Yilgarn Craton: evidence from a deep seismic crustal profile. Precambr Res 78:179–196
Yamamoto K (1987) Geochemical characteristics and depositional environments of cherts and associated rocks in the Franciscan and Shimanto terranes. Sed Geol 52:65–108
Yao LB (2002) Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Yutangba Selenium Deposit. PhD thesis of Institute Geochimstry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese)
Yao LB, Gao ZM, Yang ZS, Long HB (2002) Genesis of selenium rich siliceous rocks in Yutangba Selenium Deposit. Sci China 32(10):54–63 (in Chinese)
Yu RY (1993) Preliminary analysis on the geological characteristics and origin of the Shuanghe Se ore beds Hubei Hubei. Geology 7(1):50–56 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu T, Yang ZF, Wang R, Zeng QL, Hou WL (2018) Characteristics and sources of soil Se and other elements in typical high Se soil area of Enshi. Soil 50(6):1119–1125 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao ZH (1993) Controlling factors of geochemical characteristics of Eu. J Nan**g Univ (Geoscience) 5(3):271–280 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng X, Qian HD, Wu XM (2006) Geochemical and genetic characteristics of Se ore deposit in Shuanghe, Enshi Hubei Province. Geol China Univ 12(1):83–92 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou SQ, Huang GZ (2010) Characteristics and geostructure significance of the late Permian intracontinental Chasmic basin in southwest of Hubei. Resour Environ Eng 24(2):130–133 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgements
The research is supported by the General Project of Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2020JM-423). We are grateful for the assistance in the Field of Professor Jianming Zhu of China University of Geosciences (Bei**g) and Youqiang Qi, an associate researcher of the Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences. We also acknowledge the help of the State Key Laboratory of Ore Deposit Geochemistry, Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences for assistance with the geochemical work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, C., Liu, S. & Coulson, I.M. Lithological and Si–O–S isotope geochemistry: constraints on the origin and genetic environment of the selenium (Se)-rich siliceous rocks in Enshi, Hubei Province, China. Acta Geochim 40, 89–105 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-020-00442-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-020-00442-2