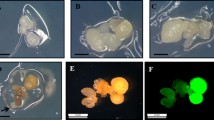
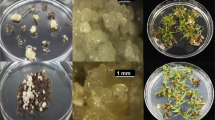
Abstract
A genetic transformation method via secondary somatic embryogenesis was developed for alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Mature somatic embryos of alfalfa were infected by Agrobacterium strain GV3101 containing the binary vector pCAMBIA2301. pCAMBIA2301 harbors the uidA Gus reporter gene and npt II acts as the selectable marker gene. Infected primary embryos were placed on SH2K medium containing plant growth regulators to induce cell dedifferentiation and embryogenesis under 75 mg/L kanamycin selection. The induced calli were transferred to plant medium free of plant growth regulators for embryo formation while maintaining selection. Somatic embryos germinated normally upon transfer to a germination medium. Plants were recovered and grown in a tissue culture room before transfer to a greenhouse. Histochemical analysis showed high levels of GUS activity in secondary somatic embryos and in different organs of plants recovered from secondary somatic embryos. The presence and stable integration of transgenes in recovered plants were confirmed by polymerase chain reaction using transgene-specific primers and Southern blot hybridization using the npt II gene probe. The average transformation efficiency achieved via secondary somatic embryogenesis was 15.2%. The selection for transformation throughout the cell dedifferentiation and embryogenic callus induction phases was very effective, and no regenerated plants escaped the selection procedure. Alfalfa transformation is usually achieved through somatic embryogenesis using different organs of developed plants. Use of somatic embryos as explants for transformation can avoid the plant development phase, providing a faster procedure for introduction of new traits and facilitates further engineering of previously transformed lines.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellucci M, De Marchis F, Arcioni S (2007) Zeolin is a recombinant storage protein that can be used to produce value-added proteins in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 90:85–91
Blaydes DF (1966) Interaction of kinetin and various inhibitors in the growth of soybean tissue. Physiol Plant 9:748–753
Bouton J (2007) The economic benefits of forage improvement in the United States. Euphytica 154:263–270
De Marchis F, Bellucci M, Arcioni S (2008) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of alfalfa. In: Kirti BP (ed) Handbook of new technologies for genetic improvement of legumes. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 29–43
Desgagnes R, Laberge S, Allard G, Khoudi H, Castonguay Y, Lapointe J, Michaud R, Vezina LP (1995) Genetic transformation of commercial breeding lines of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 42:129–140
Du S, Erickson L, Bowley S (1994) Effect of plant genotype on the transformation of cultivated alfalfa (Medicago sativa) by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Rep 13:330–334
Fiore MC, Trabace T, Sunseri F (1997) High frequency of plant regeneration in sunflower from cotyledons via somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Rep 16:295–298
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Han S, Kowalczys K, Latoszek-Green M, Brown DCW (2011) Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of alfalfa through somatic embryogenesis. In: Aslam J, Srivastava PS, Sharma MP (eds) Somatic embryogenesis and genetic transformation in plants. Narosa, New Dehli, pp 219–250
Hood EE, Gelvin SB, Melchersb LS, Hoekema A (1993) New Agrobacterium helper plasmids for gene transfer to plants. Transgenic Res 2:208–218
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the gus gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Koncz C, Schell J (1986) The promoter of TL-DNA gene 5 controls the tissue-specific expression of chimeric genes carried by a novel type of Agobacterium binary vector. Mol Gen Genet 204:383–396
Koprek T, Rangel S, McElroy D, Louwerse JD, Williams-Carrier RE (2001) Transposon-mediated single-copy gene delivery leads to increased transgene expression stability in barley. Plant Physiol 125:1354–1362
Leelavathi S, Sunnichan VG, Kumria R, Vijaykanth GP, Bhatnagar RK, Reddy VS (2004) A simple and rapid Agrobacterium-mediated transformation protocol for cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.): embryogenic calli as a source to generate large numbers of transgenic plants. Plant Cell Rep 22:465–470
Levee V, Garin E, Klimaszewska K, Seguin A (1999) Stable genetic transformation of white pine (Pinus strobus L.) after cocultivation of embryogenic tissues with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Breed 5:429–440
Lodhi MA, Ye GN, Weeden NF, Reisch BI (1994) A simple and efficient method for DNA extraction from grapevine cultivars and Vitis species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 12:6–13
McKersie BD, Brown DCW (1996) Somatic embryogenesis and artificial seeds in forage legumes. Seed Sci Res 6:109–126
McKersie BD, Senaratna T, Bowley S, Brown D, Krochko J, Bewley J (1989) Application of artificial seed technology in the production of hybrid alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 25:1183–1188
Meza TJ, Kamfjord D, Håkelien AM, Evans I, Godager LH, Mandal A, Jakobsen KS, Aalen RB (2001) The frequency of silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana varies highly between progeny of siblings and can be influenced by environmental factors. Transgenic Res 10:53–67
Montague A, Ziauddin A, Lee R, Ainley WM, Strommer J (2007) High-efficiency phosphinothricin-based selection for alfalfa transformation. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 91:29–36
Murashige T, Skoog FA (1962) Revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Namasivayam P (2007) Acquisition of embryogenic competence during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 90:1–8
Ninković S, Miljuš-Djukić J, Nešković M (1995) Genetic transformation of alfalfa somatic embryos and their clonal propagation through repetitive somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 42:255–260
Ninković S, Miljuš-DuKic J, Vinterhalter B, Nešković M (2004) Improved transformation of alfalfa somatic embryos using a superbinary vector. Acta Biol Crac Ser Bot 46:139–143
Radović J, Sokolovic D, Markovic J (2009) Alfalfa-most important perennial forage legume in animal husbandry. Biotech Anim Husbandry 25:465–475
Rosellini D, Capomaccio S, Ferradini N, Sardaro MLS, Nicolia A, Veronesi F (2007) Non-antibiotic efficient selection for alfalfa genetic engineering. Plant Cell Rep 26:1035–1044
Rueb S, Leneman M, Schilperoort RA, Hensgens LAM (1994) Efficient plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis from callus induced on mature rice embryos (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 36:259–264
Samac DA, Austin-Phillips S (2006) Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Agrobacterium protocols. In: Wang K (ed) Methods in molecular biology. Humana, Totowa, pp 301–311
Saunders JW, Bingham ET (1972) Production of alfalfa plants from callus tissue. Plant Sci 12:804–808
Schenk RU, Hildebrandt AC (1972) Medium and techniques for induction and growth of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plant cell cultures. Can J Bot 50:199–204
Shetty K, McKersie BD (1993) Proline, thioproline and potassium mediated stimulation of somatic embryogenesis in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Sci 88:185–193
Sun J, Li W, Zhang H, Zhao J, Yin X, Wang L (2009) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in glandless upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Frontiers Agric China 3:279–283
Taniguchi T, Ohmiya Y, Kurita M, Tsubomura M, Kondo T (2008) Regeneration of transgenic Cryptomeria japonica D. Don after Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of embryogenic tissue. Plant Cell Rep 27:1461–1466
Tian L, Wang H, Wu K, Latoszek-Green M, Hu M, Miki B, Brown D (2002) Efficient recovery of transgenic plants through organogenesis and embryogenesis using a cryptic promoter to drive marker gene expression. Plant Cell Rep 20:1181–1187
Trinh TH, Ratet P, Kondorosi E, Durand P, Kamaté K, Bauer P, Kondorosi A (1998) Rapid and efficient transformation of diploid Medicago truncatula and Medicago sativa ssp. falcata lines improved in somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Rep 17:345–355
Uzelac B, Ninković S, Smigocki A, Budimir S (2007) Origin and development of secondary somatic embryos in transformed embryogenic cultures of Medicago sativa. Biol Plant 51:1–6
Weeks JT, Ye J, Rommens CM (2008) Development of an in planta method for transformation of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Transgenic Res 17:587–597
Zhang BH, Liu F, Liu ZH, Wang HM, Yao CB (2001) Effects of kanamycin on tissue culture and somatic embryogenesis in cotton. Plant Growth Reg 33:137–149
Zhang H, Huang Q, Su J (2010) Development of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) regeneration system and Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation. Agri Sci China 9:170–178
Ziauddin A, Lee RWH, Lo R, Shewen P, Strommer J (2004) Transformation of alfalfa with a bacterial fusion gene, Mannheimia haemolytica A1 leukotoxin50-gfp: Response with Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains LBA4404 and C58. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 79:271–278
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by China Scholarship Council. We thank Susan Sibbald, Sukhminder Sawhney and **nhua Wang for the technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: J. Forster
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Liang, Z., Shan, C. et al. Genetic transformation and full recovery of alfalfa plants via secondary somatic embryogenesis. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 49, 17–23 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-012-9463-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-012-9463-y