Summary
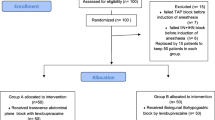
To evaluate the anesthetic effect of ultrasound-guided (USG) ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve (II/IHN) block combined with genital branch of genitofemoral nerve (GFN) block in the elderly undergoing inguinal hernia repair, 54 old patients (aged 60–96years, ASA I–III) with indirect hernia were enrolled and scheduled for unilateral tension-free herniorrhaphy. Patients were grouped randomly to receive either USG II/IHN plus GFN block (Group G) or USG II/IHN block alone (Group I). The intraoperative visual analogue scale (VAS) scores were recorded at skin incision, at spermatic cord/round ligament traction and at sac ligation. The resting and dynamic VAS scores were recorded postoperatively. The requirements of extra sedatives and analgesics for intra- and postoperative analgesia were assessed. Occurrence of complications of the block, postoperative nausea and vomiting and femoral nerve palsy was also reported. Both groups showed similar sensory block. When stretching spermatic cord/round ligament, the patients in group G had significantly lower VAS scores than in group I. And group G used much fewer adjuvant sedatives and analgesics to achieve adequate anaesthesia. In addition, group G was presented with better intraoperative anaesthesia and lower postoperative dynamic VAS scores at all time points tested. No significant difference was found in the postoperative requirement of rescue medication. Both groups showed no complications related to the block and group G reported no femoral nerve palsy. The addition of GFN block to II/IHN block improves the quality of perioperative anesthesia and analgesia in the elderly and reduces the consumption of extra sedatives and analgesics during the surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chlebny T, Zelga P, Pryt M, et al. Safe and uncomplicated inguinal hernia surgery in the elderly-message from anesthesiologists to general surgeons. Pol Przegl Chir, 2017,89(2):5–10
Mei W, Tian YK, Huang YG. Development and prospect of regional anesthesia: complying with the times and develo** the application of visualized technique in local anesthesia. J Clin Anesthesiol (Chinese), 2017,33 (10):941–943
Li Y, Su YL, Yuan Q, et al. Comparison of three nerve block methods in inguinal tension-free hernioplasty of the elders. Chin J Neuromed (Chinese), 2015,14(9):945–949
Stav A, Reytman L, Stav MY, et al. Transversus Abdominis Plane Versus Ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric Nerve Blocks for Analgesia Following Open Inguinal Herniorrhaphy. Rambam Maimonides Med J, 2016,7(3): 1–9
Casati A, Danelli G, Baciarello M, et al. A prospective, randomized comparison between ultrasoundand nerve stimulation guidance for multiple injection axillary brachial plexus block. Anesthesiology, 2007,106(5):992–996
Yang M, Fang H, Zhang FX, et al. Effect of dexmedetomidine combined with ropivacaine forilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerve block under sevoflurane anesthesia. J Clin Anesthesiol (Chinese), 2017,33(9):872–874
Yaster M, Maxwell LG. Pediatric regional anesthesia. Anesthesiology, 1989,70(2):324–338
Dario B, Philip P. In: Dnnilo J, Philip P, eds. Regional Nerve Blocks in Anesthesia and Pain Therapy: Traditional and Ultrasound-Guided Techniques. 4 ed. Heidelberg New York Dordrecht London: Springer, 2015:707–715
Sasaoka N, Kawaquchi M, Yoshitani K, et al. Evaluation of genitofemoral nerve block, in addition to ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerve block, during inguinal hernia repair in children. Br J Anaesth, 2005,94(2):243–246
Rosemar A, Angeras U, Rosengren A. Body mass index and groin hernia: a 34-year follow-up study in Swedish men. Ann Surg, 2008,247(6):1064–1068
Wirtschafter ZT, Bentley JP. Hernias as a Collagen Maturation Defect. Ann Surg, 1964,160(5):852–859
Read RC. Attenuation of the rectus sheath in inguinal herniation. Am J Surg, 1970,120(5):610–614
Strom C, Rasmussen LS, Sieber FE. Should general anaesthesia be avoided in the elderly? Anaesthesia, 2014,69(Suppl 1):35–44
van Schoor AN, Boon JM, Bosenberg AT, et al. Anatomical considerations of the pediatric ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve block. Paediatr Anaesth, 2005,15(5):371–377
Weintraud M, Marhofer P, Bosenberg A, et al. Ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric blocks in children: where do we administer the local anesthetic without direct visualization? Anesth Analg, 2008,106(1):89–93
Starling JR, Harms BA. Diagnosis and treatment of genitofemoral and ilioinguinal neuralgia. World J Surg, 1989,13(5):586–591
Starling JR, Harms BA, Schroeder ME, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of genitofemoral and ilioinguinal entrapment neuralgia. Surgery, 1987,102(4):581–586
Peng PW, Narouze S. Ultrasound-guided interventional procedures in pain medicine: a review of anatomy, sonoanatomy, and procedures: part I: nonaxial structures. Reg Anesth Pain Med, 2009,34(5):458–474
Rab M, Ebmer AJ, Dellon AL. Anatomic variability of the ilioinguinal and genitofemoral nerve: implications for the treatment of groin pain. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2001,108(6):1618–1623
Shandling B, Steward DJ. Regional analgesia for postoperative pain in pediatric outpatient surgery. J Pediatr Surg, 1980,15(4):477–480
Frassanito L, Zanfini BA, Pitoni S, et al. Ultrasound-guided genitofemoral nerve block for inguinal hernia repair in the male adult: a randomized controlled pilot study. Minerva Anestesiol, 2018,84(2):189–195
Wipfli M, Birkhauser F, Luyet C, et al, Ultrasound-guided spermatic cord block for scrotal surgery. BrJ Anaesth, 2011,106(2):255–259
Shanthanna H. Successful treatment of genitofemoral neuralgia using ultrasound guided injection: a case report and short review of literature. Case Rep Anesthesiol, 2014,4:e371703
Peng PW, Tumber PS. Ultrasound-guided interventional procedures for patients with chronic pelvic pain - a description of techniques and review of literature. Pain Physician, 2008,11(2):215–224
Terkawi AS, Romdhane K. Ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency ablation of the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve for treatment of intractable orchalgia. Saudi J Anaesth, 2014,8(2):294–298
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this study.
This work is supported by grants from Hubei Province Health and Family Planning Scientific Research Project (No. WJ2019F01).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., **a, W., Peng, Xh. et al. Evaluation of Ultrasound-guided Genitofemoral Nerve Block Combined with Ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric Nerve Block during Inguinal Hernia Repair in the Elderly. CURR MED SCI 39, 794–799 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-019-2107-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-019-2107-2