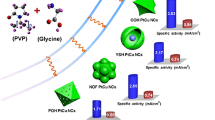
Abstract
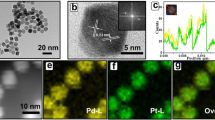
In this paper, we reported a solvothermal method for the synthesis of octahedral Pt–Cu bimetallic alloy nanocrystals (NCs) with tunable composition. Inspired by the result from our previous exploration on octahedral Pt–Cu alloy NCs that Cu contents can be tuned from 10 % to 50 %, we further tuned the Cu portion from 50 % to 75 % by simply introducing n-butylamine in the reaction system. It is believed that n-butylamine plays a key role in breaking through a thermodynamic constraint in the formation of Pt–Cu alloy nanocrystals (NCs). The synergistic effect of underpotential deposition-like Cu reduction and the different complexion abilities of amine group of n-butylamine with two metal species effectively tuned the reduction kinetics, by which each reduced Pt atom is able to catalyze reduction of more Cu atoms and be fully covered with 12 Cu atoms in the Pt–Cu alloy crystal, while Cu precursor is not able to be reduced solely and bind solely with Cu atoms, resulting in the successful tuning of Cu composition from 50 % to 75 %. In addition, we investigated the electro-catalytic activity of Pt–Cu bimetallic alloy NCs with different composition in electro-oxidation of methanol. The as-prepared PtCu3 NCs exhibit excellent electro-catalytic performance and stability in comparison with commercial Pt black and other compositional Pt–Cu alloy NCs.
摘要
由于不同金属之间氧化还原电势、原子半径和电负性的不同,设计和制备形貌和合金成分可控双金属合金纳米晶仍具挑战。在金属欠电位沉积(UPD)诱导Cu的还原合成了Cu比例可达50 %的八面体Pt-Cu合金纳米晶的基础上,引入**丁胺,通过其与金属的配位作用调节了Pt和Cu前驱物的还原速度,进一步将Cu的比例提高到75 %。与UPD单原子层沉积类似,在该反应中每个被还原的Pt原子均有能力催化Cu原子的还原并键合最多12个Cu原子(密堆积结构),而铜前驱物不能在Cu原子表面上直接还原,使得纳米晶体中Cu的比例最高达到75 %。此外,性能研究表明PtCu3纳米晶体表现出最高的电催化活性和稳定性。.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tian N, Zhou ZY, Sun SG et al (2007) Synthesis of tetrahexahedral platinum nanocrystals with high-index facets and high electro-oxidation activity. Science 316:732–735
Huang XQ, Zhao ZP, Fan JM et al (2011) Amine-assisted synthesis of concave polyhedral platinum nanocrystals having 411 high-index facets. J Am Chem Soc 133:4718–4721
**a BY, Wu HB, Yan Y et al (2013) Ultrathin and ultralong single-crystal platinum nanowire assemblies with highly stable electrocatalytic activity. J Am Chem Soc 135:9480–9485
**a BY, Wu HB, Wang X et al (2013) Highly concave platinum nanoframes with high-index facets and enhanced electrocatalytic properties. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:12337–12340
Zhang L, Chen DQ, Jiang ZY et al (2012) Facile syntheses and enhanced electrocatalytic activities of Pt nanocrystals with hkk high-index surfaces. Nano Res 5:181–189
Wu Y, Cai SF, Wang DS et al (2012) Syntheses of water-soluble octahedral, truncated octahedral, and cubic Pt–Ni nanocrystals and their structure-activity study in model hydrogenation reactions. J Am Chem Soc 134:8975–8981
Xu XL, Zhang X, Sun H et al (2014) Synthesis of Pt–Ni alloy nanocrystals with high-index facets and enhanced electrocatalytic properties. Angew Chem Int Ed 126:12730–12735
Wu JB, Gross A, Yang H (2011) Shape and composition-controlled platinum alloy nanocrystals using carbon monoxide as reducing agent. Nano Lett 11:798–802
Saleem F, Zhang ZC, Xu B et al (2013) Ultrathin Pt–Cu nanosheets and nanocones. J Am Chem Soc 135:18304–18307
**a BY, Wu HB, Wang X et al (2012) One-pot synthesis of cubic PtCu3 nanocages with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for the methanol oxidation reaction. J Am Chem Soc 134:13934–13937
Yang HZ, Zhang J, Sun K et al (2010) Enhancing by weakening: electrooxidation of methanol on Pt3Co and Pt nanocubes. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:6848–6851
Xu Y, Hou SX, Liu Y et al (2012) Facile one-step room-temperature synthesis of Pt3Ni nanoparticle networks with improved electro-catalytic properties. Chem Commun 48:2665–2667
Chen S, Su HY, Wang YC et al (2014) Size-controlled synthesis of platinum-copper hierarchical trigonal bipyramid nanoframes. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:108–113
Lee YW, Ko AR, Han SB et al (2011) Synthesis of octahedral Pt–Pd alloy nanoparticles for improved catalytic activity and stability in methanol electrooxidation. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:5569–5572
Huang XQ, Zhu EB, Chen Y et al (2013) A facile strategy to Pt3Ni nanocrystals with highly porous features as an enhanced oxygen reduction reaction catalyst. Adv Mater 25:2974–2979
Huang XQ, Li YJ, Chen Y et al (2013) Plasmonic and catalytic AuPd nanowheels for the efficient conversion of light into chemical energy. Angew Chem Int Ed 125:6179–6183
Xu D, Bliznakov S, Liu ZP et al (2010) Composition-dependent electrocatalytic activity of Pt–Cu nanocube catalysts for formic acid oxidation. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:1282–1285
Choi S, **e SF, Shao MH et al (2014) Controlling the size and composition of nanosized Pt–Ni octahedra to optimize their catalytic activities toward the oxygen reduction reaction. ChemSusChem 7:1476–1483
Chen QL, Zhang JW, Jia YY et al (2014) Wet chemical synthesis of intermetallic Pt3Zn nanocrystals via weak reduction reaction together with UPD process and their excellent electrocatalytic performances. Nanoscale 6:7019–7024
Zhang JW, Zhang L, **e SF et al (2011) Synthesis of concave palladium nanocubes with high-index surfaces and high electrocatalytic activities. Chem Eur J 17:9915–9919
Zhang JW, Hou CP, Huang H et al (2013) Surfactant-concentration-dependent shape evolution of Au–Pd alloy nanocrystals from rhombic dodecahedron to trisoctahedron and hexoctahedron. Small 9:538–544
Zhang L, Zhang JW, Kuang Q et al (2011) Cu2+-assisted synthesis of hexoctahedral Au–Pd alloy nanocrystals with high-index facets. J Am Chem Soc 133:17114–17117
Yu NF, Tian N, Zhou ZY et al (2014) Electrochemical synthesis of tetrahexahedral rhodium nanocrystals with extraordinarily high surface energy and high electrocatalytic activity. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:5097–5101
Li CC, Sun L, Sun YQ et al (2013) One-pot controllable synthesis of Au@Ag heterogeneous nanorods with highly tunable plasmonic absorption. Chem Mater 25:2580–2590
Kang SW, Lee YW, Park YS et al (2013) One-pot synthesis of trimetallic Au@PdPt core–shell nanoparticles with high catalytic performance. ACS Nano 7:7945–7955
Park YS, Lee YW, Kang SW et al (2014) One-pot synthesis of Au@Pd core-shell nanocrystals with multiple high- and low-index facets and their high electrocatalytic performance. Nanoscale 6:9798–9805
Yoon JS, Baik HS, Lee SM et al (2014) One-pot synthesis of ultralong coaxial Au@Pt nanocables with numerous highly catalytically active perpendicular twinning boundaries and Au@Pt core–shell bead structures. Nanoscale 6:6434–6439
Kim YN, Lee YW, Kim MJ et al (2014) One-pot synthesis and electrocatalytic properties of Pd@Pt core-shell nanocrystals with tailored morphologies. Chem Eur J 20:7901–7905
Oezaslan M, Strasser P (2011) Activity of dealloyed PtCo3 and PtCu3 nanoparticle electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell. J Power Sources 196:5240–5249
Oezaslan M, Hasche F, Strasser P (2012) PtCu3, PtCu, Pt3Cu alloy nanoparticle electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline and acidic media. J Electrochem Soc 159:B444–B454
Jayasayee K, Rob van veen JA, Manivasagam TG et al (2012) Oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity and durability of carbon supported PtM (Co, Ni, Cu) alloys: influence of particle size and non-noble metals. Appl Catal B Environ 111–112:515–526
Huang XQ, Li YJ, Li YJ et al (2012) Synthesis of PtPd bimetal nanocrystals with controllable shape, composition, and their tunable catalytic properties. Nano Lett 12:4265–4270
Jiang YQ, Jia YY, Zhang JW et al (2013) Underpotential deposition-induced synthesis of composition-tunable Pt–Cu nanocrystals and their catalytic properties. Chem Eur J 19:3119–3124
Denton AR, Ashcroft NW (1991) Vegard’s law. Phys Rev A 43:3161–3164
Yang HZ, Dai L, Xu D et al (2010) Electrooxidation of methanol and formic acid on PtCu nanoparticles. Eletrochim Acta 55:8000–8004
Wu JB, Zhang JL, Peng ZM et al (2010) Truncated octahedral Pt3Ni oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysts. J Am Chem Soc 132:4984–4985
Choi S, Choi R, Han SW et al (2011) Shape-controlled synthesis of Pt3Co nanocrystals with high electrocatalytic activity toward oxygen reduction. Chem Eur J 17:12280–12284
Lim BK, Jiang MJ, Camargo PHC et al (2009) Pd–Pt bimetallic nanodendrites with high activity for oxygen reduction. Science 324:1302–1305
Kakade BA, Tamaki T, Ohashi H et al (2012) Highly active bimetallic PdPt and CoPt nanocrystals for methanol electro-oxidation. J Phys Chem C 116:7464–7470
Huang HJ, Sun DP, Wang X (2012) PtCo alloy nanoparticles supported on graphene nanosheets with high performance for methanol oxidation. Chin Sci Bull 57:3071–3079
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CBA00508 and 2015CB932301), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21131005, 21333008, and J1310024) and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (2014J01058).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Cao, Z., Chen, Q. et al. Synthesis of composition-tunable octahedral Pt–Cu alloy nanocrystals by controlling reduction kinetics of metal precursors. Sci. Bull. 60, 1002–1008 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-015-0781-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-015-0781-4