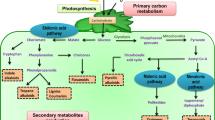
Abstract
The reactive electrophilic species (RES), typically the molecules bearing α,β-unsaturated carbonyl group, are widespread in living organisms and notoriously known for their damaging effects. Many of the mycotoxins released from phytopathogenic fungi are RES and their contamination to cereals threatens food safety worldwide. However, due to their high reactivity, RES are also used by host organisms to synthesize specific metabolites. The evolutionary conserved glyoxalase (GLX) system scavenges the cytotoxic α-oxoaldehydes that bear RES groups, which cause host disorders and diseases. In cotton, a specialized enzyme derived from glyoxalase I (GLXI) through gene duplications and named as specialized GLXI (SPG), acts as a distinct type of aromatase in the gossypol pathway to transform the RES intermediates into the phenolic products. In this review, we briefly introduce the research progress in understanding the RES, especially the RES-type mycotoxins, the GLX system and SPG, and discuss their application potential in detoxification and synthetic biology.
Similar content being viewed by others
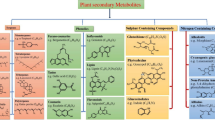
References
Aldini, G., Vistoli, G., Stefek, M., Chondrogianni, N., Grune, T., Sereikaite, J., Sadowska- Bartosz, I., and Bartosz, G. (2013). Molecular strategies to prevent, inhibit, and degrade advanced glycoxidation and advanced lipoxidation end products. Free Rad Res 47, 93–137.
Alvarez Viveros, M.F., Inostroza-Blancheteau, C., Timmermann, T., González, M., and Arce-Johnson, P. (2013). Overexpression of GlyI and GlyII genes in transgenic tomato (Solanum lycopersicum Mill.) plants confers salt tolerance by decreasing oxidative stress. Mol Biol Rep 40, 3281–3290.
Arunachalam, C., and Doohan, F.M. (2013). Trichothecene toxicity in eukaryotes: cellular and molecular mechanisms in plants and animals. Toxicol Lett 217, 149–158.
Ben Taheur, F., Kouidhi, B., Al Qurashi, Y.M.A., Ben Salah-Abbès, J., and Chaieb, K. (2019). Biotechnology of mycotoxins detoxification using microorganisms and enzymes. Toxicon 160, 12–22.
Cameron, A.D., Ridderström, M., Olin, B., Kavarana, M.J., Creighton, D. J., and Mannervik, B. (1999). Reaction mechanism of glyoxalase I explored by an X-ray crystallographic analysis of the human enzyme in complex with a transition state analogue. Biochemistry 38, 13480–13490.
Dave, A., and Graham, I.A. (2012). Oxylipin signaling: A distinct role for the jasmonic acid precursor cis-(+)-12-oxo-phytodienoic acid (cis-OPDA). Front Plant Sci 3, 42.
de Lorenzo, V., Prather, K.L., Chen, G.Q., O'Day, E., von Kameke, C., Oyarzún, D.A., Hosta- Rigau, L., Alsafar, H., Cao, C., Ji, W., et al. (2018). The power of synthetic biology for bioproduction, remediation and pollution control. EMBO Rep 19, e45658.
Dick, R.A., Kwak, M.K., Sutter, T.R., and Kensler, T.W. (2001). Antioxidative function and substrate specificity of NAD(P)H- dependent alkenal/one oxidoreductases. A new role for leukotriene B4 12-hydroxydehydrogenase/15-oxoprostaglandin 13-reductase. J Biol Chem 276, 40803–40810.
Farmer, E.E., and Davoine, C. (2007). Reactive electrophile species. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10, 380–386.
Hovatta, I., Tennant, R.S., Helton, R., Marr, R.A., Singer, O., Redwine, J. M., Ellison, J.A., Schadt, E.E., Verma, I.M., Lockhart, D.J., et al. (2005). Glyoxalase 1 and glutathione reductase 1 regulate anxiety in mice. Nature 438, 662–666.
Huang, J.Q., Fang, X., Tian, X., Chen, P., Lin, J.L., Guo, X.X., Li, J.X., Fan, Z., Song, W.M., Chen, F.Y., et al. (2020). Aromatization of natural products by a specialized detoxification enzyme. Nat Chem Biol 16, 250–256.
Hussein, H.S., and Brasel, J.M. (2001). Toxicity, metabolism, and impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. Toxicology 167, 101–134.
Kang, Y., Feng, H., Zhang, J., Chen, S., Valverde, B.E., and Qiang, S. (2017). TeA is a key virulence factor for Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissler infection of its host. Plant Physiol Biochem 115, 73–82.
Kolb, N.S., Hunsaker, L.A., and Vander J.D.L. (1994). Aldose reductasecatalyzed reduction of acrolein: Implications in cyclophosphamide toxicity. Mol Pharmacol 45, 797–801.
Kuhla, B., Boeck, K., Lüth, H.J., Schmidt, A., Weigle, B., Schmitz, M., Ogunlade, V., Münch, G., and Arendt, T. (2006). Age-dependent changes of glyoxalase I expression in human brain. Neurobiol Aging 27, 815–822.
Lee, C., and Park, C. (2017). Bacterial responses to glyoxal and methylglyoxal: Reactive electrophilic species. Int J Mol Sci 18, 169.
Li, P., Su, R., Yin, R., Lai, D., Wang, M., Liu, Y., and Zhou, L. (2020). Detoxification of mycotoxins through biotransformation. Toxins 12, 121.
Li, W., Lybrand, D.B., Zhou, F., Last, R.L., and Pichersky, E. (2019). Pyrethrin biosynthesis: The cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase CYP82Q3 converts jasmolone to pyrethrolone. Plant Physiol 181, 934–944.
Luo, D., Callari, R., Hamberger, B., Wubshet, S.G., Nielsen, M.T., Andersen-Ranberg, J., Hallström, B.M., Cozzi, F., Heider, H., Lindberg Møller, B., et al. (2016). Oxidation and cyclization of casbene in the biosynthesis of Euphorbia factors from mature seeds of Euphorbia lathyris L.. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, E5082–E5089.
Lv, N., Hao, S., Luo, C., Abukiwan, A., Hao, Y., Gai, F., Huang, W., Huang, L., **ao, X., Eichmüller, S.B., et al. (2018). miR-137 inhibits melanoma cell proliferation through downregulation of GLO1. Sci China Life Sci 61, 541–549.
Mano, J., Belles-Boix, E., Babiychuk, E., Inzé, D., Torii, Y., Hiraoka, E., Takimoto, K., Slooten, L., Asada, K., and Kushnir, S. (2005). Protection against photooxidative injury of tobacco leaves by 2-alkenal reductase. Detoxication of lipid peroxide-derived reactive carbonyls. Plant Physiol 139, 1773–1783.
McCormick, S.P., Stanley, A.M., Stover, N.A., and Alexander, N.J. (2011). Trichothecenes: from simple to complex mycotoxins. Toxins 3, 802–814.
Peng, Z., Cheng, H., Sun, G., Pan, Z., Wang, X., Geng, X., He, S., and Du, X. (2020). Expression patterns and functional divergence of homologous genes accompanied by polyploidization in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Sci China Life Sci https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-1618-7.
Rabbani, N., and Thornalley, P.J. (2014). The critical role of methylglyoxal and glyoxalase 1 in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 63, 50–52.
Racker, E. (1951). The mechanism of action of glyoxalase. J Biol Chem 190, 685–696.
Richard, J.L. (2007). Some major mycotoxins and their mycotoxicoses—An overview. Int J Food Microbiol 119, 3–10.
Riechers, D.E., Kreuz, K., and Zhang, Q. (2010). Detoxification without intoxication: herbicide safeners activate plant defense gene expression. Plant Physiol 153, 3–13.
Sankaranarayanan, S., Jamshed, M., Kumar, A., Skori, L., Scandola, S., Wang, T., Spiegel, D., and Samuel, M.A. (2017). Glyoxalase goes green: The expanding roles of glyoxalase in plants. Int J Mol Sci 18, 898.
Sankaranarayanan, S., Jamshed, M., and Samuel, M.A. (2015). Degradation of glyoxalase I in Brassica napus stigma leads to self-incompatibility response. Nat Plants 1, 15185.
Scheckhuber, C.Q., Mack, S.J., Strobel, I., Ricciardi, F., Gispert, S., and Osiewacz, H.D. (2010). Modulation of the glyoxalase system in the aging model Podospora anserina: effects on growth and lifespan. Aging 2, 969–980.
Shang, Y., Ma, Y., Zhou, Y., Zhang, H., Duan, L., Chen, H., Zeng, J., Zhou, Q., Wang, S., Gu, W., et al. (2014). Biosynthesis, regulation, and domestication of bitterness in cucumber. Science 346, 1084–1088.
Simpson, P.J., Tantitadapitak, C., Reed, A.M., Mather, O.C., Bunce, C.M., White, S.A., and Ride, J.P. (2009). Characterization of two novel aldoketo reductases from Arabidopsis: Expression patterns, broad substrate specificity, and an open active-site structure suggest a role in toxicant metabolism following stress. J Mol Biol 392, 465–480.
Streit, E., Naehrer, K., Rodrigues, I., and Schatzmayr, G. (2013). Mycotoxin occurrence in feed and feed raw materials worldwide: Long-term analysis with special focus on Europe and Asia. J Sci Food Agric 93, 2892–2899.
Taki, N., Sasaki-Sekimoto, Y., Obayashi, T., Kikuta, A., Kobayashi, K., Ainai, T., Yagi, K., Sakurai, N., Suzuki, H., Masuda, T., et al. (2005). 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid triggers expression of a distinct set of genes and plays a role in wound-induced gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139, 1268–1283.
Thornalley, P.J. (1990). The glyoxalase system: new developments towards functional characterization of a metabolic pathway fundamental to biological life. Biochem J 269, 1–11.
Thornalley, P.J. (2003). Glyoxalase I—structure, function and a critical role in the enzymatic defence against glycation. Biochem Soc Trans 31, 1343–1348.
Tian, X., Fang, X., Huang, J.Q., Wang, L.J., Mao, Y.B., and Chen, X.Y. (2019). A gossypol biosynthetic intermediate disturbs plant defence response. Phil Trans R Soc B 374, 20180319.
Tian, X., Ruan, J., Huang, J., Fang, X., Mao, Y., Wang, L., Chen, X., and Yang, C. (2016a). Gossypol: phytoalexin of cotton. Sci China Life Sci 59, 122–129.
Tian, X., Ruan, J.X., Huang, J.Q., Yang, C.Q., Fang, X., Chen, Z.W., Hong, H., Wang, L.J., Mao, Y.B., Lu, S., et al. (2018). Characterization of gossypol biosynthetic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, E5410–E5418.
Tian, Y., Tan, Y., Liu, N., Liao, Y., Sun, C., Wang, S., and Wu, A. (2016b). Functional agents to biologically control deoxynivalenol contamination in cereal grains. Front Microbiol 7, 395.
Wang, K., Huang, G., and Zhu, Y. (2016). Transposable elements play an important role during cotton genome evolution and fiber cell development. Sci China Life Sci 59, 112–121.
Weng, J.K., Philippe, R.N., and Noel, J.P. (2012). The rise of chemodiversity in plants. Science 336, 1667–1670.
**a, Y., Huang, G., and Zhu, Y. (2019). Sustainable plant disease control: biotic information flow and behavior manipulation. Sci China Life Sci 62, 1710–1713.
Yamauchi, Y., Hasegawa, A., Taninaka, A., Mizutani, M., and Sugimoto, Y. (2011). NADPH-dependent reductases involved in the detoxification of reactive carbonyls in plants. J Biol Chem 286, 6999–7009.
Zhou, Y., Ma, Y., Zeng, J., Duan, L., Xue, X., Wang, H., Lin, T., Liu, Z., Zeng, K., Zhong, Y., et al. (2016). Convergence and divergence of bitterness biosynthesis and regulation in Cucurbitaceae. Nat Plants 2, 16183.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31690092, 31788103 to X. Chen and 31872666 to X. Fang), the Ministry of Agriculture of China (2016ZX08010002-005 to X. Shangguan), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (QYZDY-SSW-SMC026 and 153D31KYSB20160074 to X. Chen) and the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (2019QNRC001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, JQ., Lin, JL., Guo, XX. et al. RES transformation for biosynthesis and detoxification. Sci. China Life Sci. 63, 1297–1302 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1729-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1729-5