Abstract
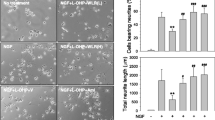
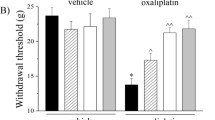
Oxaliplatin (L-OHP) is a platinum-based anticancer agent used to treat various types of cancer. It frequently causes acute and chronic peripheral neuropathies, such as cold allodynia and mechanical hyperalgesia. Nin**’yoeito (NYT) is a formula used in traditional Japanese Kampo medicine to improve recovery from diseases and other medical disorders. We previously reported that treatment with a boiling-water extract of NYT prevented L-OHP-induced damage to neurite-like outgrowths from differentiated PC12 cells. The objectives of the present study were to evaluate the in vivo effects of NYT on L-OHP-induced neuropathic pain in mice and identify the active ingredients in NYT. Treatment with NYT extract significantly ameliorated both cold allodynia and mechanical hyperalgesia induced by L-OHP. While L-OHP treatment suppressed neurite outgrowths from primary dorsal root ganglion cells in vitro, NYT extract blocked this suppression in a concentration-dependent manner. Among the herbal components of NYT, the extract of ginseng (Panax ginseng roots) showed a protective effect against neurite damage induced by L-OHP, and one of its active ingredients was identified as ginsenoside Rg3. Ginseng extract partially relieved L-OHP-induced neuropathic pain in mice. Our results suggest that NYT could be an attractive agent for treating L-OHP-induced neuropathic pain, and that the active ingredient of NYT may be ginseng.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grothey A, Goldberg RM (2004) A review of oxaliplatin and its clinical use in colorectal cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother 5:2159–2170
Qvortrup C, Yilmaz M, Ogreid D, Berglund A, Balteskard L, Ploen J, Fokstuen T, Starkhammar H, Sorbye H, Tveit K, Pfeiffer P (2008) Chronomodulated capecitabine in combination with short-time oxaliplatin: a Nordic phase II study of second-line therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer after failure to irinotecan and 5-flourouracil. Ann Oncol 19:1154–1159
Gourgou-Bourgade S, Bascoul-Mollevi C, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouche O, Guimbaud R, Becouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Boige V, Berille J, Conroy T (2013) Impact of FOLFIRINOX compared with gemcitabine on quality of life in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer: results from the PRODIGE 4/ACCORD 11 randomized trial. J Clin Oncology 31:23–29
Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, Iveson T, Nicolson M, Coxon F, Middleton G, Daniel F, Oates J, Norman AR, Upper Gastrointestinal Clinical Studies Group of the National Cancer Research Institute of the United Kingdom (2008) Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N Engl J Med 358:36–46
Yamada Y, Takahari D, Matsumoto H, Baba H, Nakamura M, Yoshida K, Yoshida M, Iwamoto S, Shimada K, Komatsu Y, Sasaki Y, Satoh T, Takahashi K, Mishima H, Muro K, Watanabe M, Sakata Y, Morita S, Shimada Y, Sugihara K (2013) Leucovorin, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin plus bevacizumab versus S-1 and oxaliplatin plus bevacizumab in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (SOFT): an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14:1278–1286
Pasetto LM, D’Andrea MR, Rossi E, Monfardini S (2006) Oxaliplatin-related neurotoxicity: how and why? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 59:159–168
Carozzi VA, Canta A, Chiorazzi A, Cavaletti G (2014) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: what do we know about mechanisms? Neurosci Lett 596:90–107
Bensky D, Clavey S, Stöger E (2004) Chinese herbal medicine—materia medica, 3rd edn. Eastland, Seattle
Suzuki T, Yamamoto A, Ohsawa M, Motoo Y, Mizukami H, Makino T (2015) Nin**’yoeito and ginseng extract prevent oxaliplatin-induced neurodegeneration in PC12 cells. J Nat Med 69:531–537
The Society of Japanese Pharmacopoeia (2016) The Japanese pharmacopoeia seventeenth edition (JPXVII). Yakuji-Nippo, Tokyo
Gao S, Kushida H, Makino T (2017) Ginsenosides, ingredients of the root of Panax ginseng, are not substrates but inhibitors of sodium-glucose transporter 1. J Nat Med 71:131–138
Ohsawa M, Otake S, Murakami T, Yamamoto S, Makino T, Ono H (2014) Gabapentin prevents oxaliplatin-induced mechanical hyperalgesia in mice. J Pharmacol Sci 125:292–299
Suzuki T, Miyamoto K, Yokoyama N, Sugi M, Kagioka A, Kitao Y, Adachi T, Ohsawa M, Mizukami H, Makino T (2016) Processed aconite root and its active ingredient neoline may alleviate oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathic pain. J Ethnopharmacol 186:44–52
Dixon WJ (1980) Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 20:441–462
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63
Ushio S, Egashira N, Sada H, Kawashiri T, Shirahama M, Masuguchi K, Oishi R (2012) Gosha**kigan reduces oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy without affecting anti-tumour efficacy in rodents. Eur J Cancer 48:1407–1413
Kitamura R, Andoh T, Fushimi H, Komatsu K, Shibahara N, Kuraishi Y (2013) Involvement of descending monoaminergic systems in antiallodynic effect of gosha**kigan in oxaliplatin-treated mice. J Tradit Med 30:183–189
Mizuno K, Kono T, Suzuki Y, Miyagi C, Omiya Y, Miyano K, Kase Y, Uezono Y (2014) Gosha**kigan, a traditional Japanese medicine, prevents oxaliplatin-induced acute peripheral neuropathy by suppressing functional alteration of TRP channels in rat. J Pharmacol Sci 125:91–98
Mizuno K, Shibata K, Komatsu R, Omiya Y, Kase Y, Koizumi S (2016) An effective therapeutic approach for oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy using a combination therapy with gosha**kigan and bushi. Cancer Biol Ther 17:1206–1212
Kato Y, Tateai Y, Ohkubo M, Saito Y, Amagai SY, Kimura YS, Iimura N, Okada M, Matsumoto A, Mano Y, Hirosawa I, Ohuchi K, Tajima M, Asahi M, Kotaki H, Yamada H (2014) Gosha-**ki-gan reduced oxaliplatin-induced hypersensitivity to cold sensation and its effect would be related to suppression of the expression of TRPM8 and TRPA1 in rats. Anticancer Drugs 25:39–43
Oki E, Emi Y, Kojima H, Higashijima J, Kato T, Miyake Y, Kon M, Ogata Y, Takahashi K, Ishida H, Saeki H, Sakaguchi Y, Yamanaka T, Kono T, Tomita N, Baba H, Shirabe K, Kakeji Y, Maehara Y (2015) Preventive effect of gosha**kigan on peripheral neurotoxicity of FOLFOX therapy (GENIUS trial): a placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized phase III study. Int J Clin Oncol 20:767–775
Ahn BS, Kim SK, Kim HN, Lee JH, Lee JH, Hwang DS, Bae H, Min BI, Kim SK (2014) Gyejigachulbu-tang relieves oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic cold and mechanical hypersensitivity in rats via the suppression of spinal glial activation. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2014:436482
Deng B, Jia L, Pan L, Song A, Wang Y, Tan H, **ang Q, Yu L, Ke D (2016) Wen-Luo-Tong prevents glial activation and nociceptive sensitization in a rat model of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2016:3629489
Andoh T, Mizoguchi S, Kuraishi Y (2017) Shakuyakukanzoto attenuates oxaliplatin-induced cold dysesthesia by inhibiting the expression of transient receptor potential melastatin 8 in mice. J Tradit Complement Med 7:30–33
Gauchan P, Andoh T, Kato A, Sasaki A, Kuraishi Y (2009) Effects of the prostaglandin E1 analog limaprost on mechanical hyperalgesia caused by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. J Pharm Sci 109:469–472
Pang H, Wang HL, Fu L, Su CY (2001) Pharmacokinetic studies of 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 in human volunteers. Acta Pharma Sin 36:170–173
Kim C, Lee JH, Kim W, Li D, Kim Y, Lee K, Kim SK (2016) The suppressive effects of cinnamomi cortex and its phytocompound coumarin on oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic cold allodynia in rats. Molecules 21:E1253
Di Cesare Mannelli L, Pacini A, Micheli L, Femia AP, Maresca M, Zanardelli M, Vannacci A, Gallo E, Bilia AR, Caderni G, Firenzuoli F, Mugelli A, Ghelardini C (2017) Astragali radix: could it be an adjuvant for oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy? Sci Rep 7:42021
Wang CZ, Yuan CS (2008) Potential role of ginseng in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Am J Chin Med 36:1019–1028
Qi F, Li A, Inagaki Y, Gao J, Li J, Kokudo N, Li XK, Tang W (2010) Chinese herbal medicines as adjuvant treatment during chemo- or radio-therapy for cancer. Biosci Trend 4:297–307
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) C #16K09267 (2016), and the Kidani Memorial Trust (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, T., Yamamoto, A., Ohsawa, M. et al. Effect of nin**’yoeito and ginseng extracts on oxaliplatin-induced neuropathies in mice. J Nat Med 71, 757–764 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-017-1113-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-017-1113-6