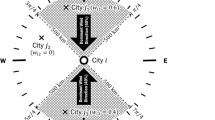
Abstract
Using a dataset encompassing 228 cities in China spanning from 2005 to 2019, this study explores the nonlinear relationship between air quality and housing prices and devises a strategy that incorporates the instrumental variable and machine learning to address the endogeneity issue. Both traditional models and machine learning models find air pollution affects housing prices in a diminishing manner. The negative impact of air pollution on housing prices decreases when the degree of air pollution intensifies. Such a characteristic is more pronounced in Eastern China and cities with fewer land resource constraints and larger populations. Mechanism analysis also reveals that air pollution could affect residents’ perceived air quality and the industrial structure, further contributing to the nonlinear relationship between air quality and housing prices. The further SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) evaluates the importance of air quality in determining housing prices and finds that air quality’s contribution outweighs educational and medical resources. The contribution of air quality also shows a distinct regional disparity and has become increasingly important in recent years. The findings refine the benefit assessment accuracy related to air quality improvement.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Allen T, Murray KA, Zambrana-Torrelio C, Morse SS, Rondinini C, Di Marco M, Breit N, Olival KJ, Daszak P (2017) Global hotspots and correlates of emerging zoonotic diseases. Nature Communications 8(1):1124. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00923-8
Bao R, Liu T (2022) How does government attention matter in air pollution control? Evidence from government annual reports. Resour Conserv Recycl 185:106435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106435
Belkin M, Hsu D, Ma S, Mandal S (2019) Reconciling modern machine-learning practice and the classical bias-variance trade-off. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116(32):15849–15854. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1903070116
Carranza JP, Piumetto MA, Lucca CM, Da Silva E (2022) Mass appraisal as affordable public policy: open data and machine learning for map** urban land values. Land Use Policy 119:106211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2022.106211
Chay KY, Greenstone M (2003) The impact of air pollution on infant mortality: evidence from geographic variation in pollution shocks induced by a recession. Q J Econ 118(3):1121–1167. https://doi.org/10.1162/00335530360698513
Chay KY, Greenstone M (2005) Does air quality matter? Evidence from the Housing Market. J Polit Econ 113(2):376–424. https://doi.org/10.1086/427462
Chen D, Chen S (2017) Particulate air pollution and real estate valuation: evidence from 286 Chinese prefecture-level cities over 2004–2013. Energy Policy 109:884–897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.05.044
Chen S, ** H (2019) Pricing for the clean air: evidence from Chinese housing market. J Clean Prod 206:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.220
Chen S, Oliva P, Zhang P (2022) The effect of air pollution on migration: Evidence from China. J Dev Econ 156:102833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdeveco.2022.102833
Cheng Y, He LY, Huang XF (2021) Development of a high-performance machine learning model to predict ground ozone pollution in typical cities of China. J Environ Manage 299:113670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113670
Darcin M (2014) Association between air quality and quality of life. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(3):1954–1959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2101-3
Dong R, Fisman R, Wang Y, Xu N (2021) Air pollution, affect, and forecasting bias: evidence from Chinese financial analysts. J Financ Econ 139(3):971–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2019.12.004
Dong Z, **a C, Fang K, Zhang W (2022) Effect of the carbon emissions trading policy on the co-benefits of carbon emissions reduction and air pollution control. Energy Policy 165:112998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112998
Fan J, Wu L, Zhang F, Cai H, Wang X, Lu X, **ang Y (2018) Evaluating the effect of air pollution on global and diffuse solar radiation prediction using support vector machine modeling based on sunshine duration and air temperature. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 94:732–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.06.029
Friedman JH (2001) Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Ann Stat 29(5):1189–1232. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1013203451
Fu S, Viard VB, Zhang P (2021) Air pollution and manufacturing firm productivity: nationwide estimates for China. Econ J 131(640):3241–3273. https://doi.org/10.1093/ej/ueab033
Goldstein A, Kapelner A, Bleich J, Pitkin E (2015) Peeking inside the black box: visualizing statistical learning with plots of individual conditional expectation. J Comput Graph Stat 24(1):44–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/10618600.2014.907095
Gui G, Liu F, Sun J, Yang J, Zhou Z, Zhao D (2020) Flight delay prediction based on aviation big data and machine learning. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 69(1):140–150. https://doi.org/10.1109/tvt.2019.2954094
Hammer MS, van Donkelaar A, Li C, Lyapustin A, Sayer AM, Hsu NC, Levy RC, Garay MJ, Kalashnikova OV, Kahn RA, Brauer M, Apte JS, Henze DK, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Ford B (2022) Global Annual PM2.5 Grids from MODIS, MISR and SeaWiFS Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD), 1998–2019, V4.GL.03. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.7927/fx80-4n39
Hao Y, Zheng S (2017) Would environmental pollution affect home prices? An empirical study based on China’s key cities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(31):24545–24561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0073-4
Krzyzanowski M, Cohen A (2008) Update of WHO air quality guidelines. Air Qual Atmos Health 1(1):7–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-008-0008-9
Lan F, Lv J, Chen J, Zhang X, Zhao Z, Pui DYH (2020) Willingness to pay for staying away from haze: evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in **’an. J Environ Manage 262:110301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110301
Leippold M, Wang Q, Zhou W (2022) Machine learning in the Chinese stock market. J Financ Econ 145(2):64–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2021.08.017
Levin IP, Gaeth GJ, Schreiber J, Lauriola M (2002) A new look at framing effects: distribution of effect sizes, individual differences, and independence of types of effects. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process 88(1):411–429. https://doi.org/10.1006/obhd.2001.2983
Liang W, Luo S, Zhao G, Wu H (2020) Predicting hard rock pillar stability using GBDT, XGBoost, and LightGBM algorithms. Mathematics 8(5):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8050765
Lundberg SM, Lee SI (2017) A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Paper presented at the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017):4768–4777.
Maloney KO, Buchanan C, Jepsen RD, Krause KP, Cashman MJ, Gressler BP, Young JA, Schmid M (2022) Explainable machine learning improves interpretability in the predictive modeling of biological stream conditions in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed, USA. J Environ Manag 322:116068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116068
Mehta P, Wang CH, Day AGR, Richardson C, Bukov M, Fisher CK, Schwab DJ (2019) A high-bias, low-variance introduction to Machine Learning for physicists. Phys Rep 810:1–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2019.03.001
Mei Y, Gao L, Zhang J, Wang J (2020) Valuing urban air quality: a hedonic price analysis in Bei**g. Chin Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(2):1373–1385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06874-5
Mo J (2018) Land financing and economic growth: evidence from Chinese counties. China Econ Rev 50:218–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2018.04.011
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, Blondel M, Prettenhofer P, Weiss R, Dubourg V, Vanderplas J, Passos A, Cournapeau D, Brucher M, Perrot M, Duchesnay E (2011) Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. J Machine Learning Res 12:2825–2830
Pierce JR, Aguinis H (2011) The too-much-of-a-good-thing effect in management. J Manag 39(2):313–338. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206311410060
Priyadarshini I, Alkhayyat A, Obaid AJ, Sharma R (2022) Water pollution reduction for sustainable urban development using machine learning techniques. Cities 130:103970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2022.103970
Python A, Bender A, Nandi AK, Hancock PA, Arambepola R, Brandsch J, Lucas TCD (2021) Predicting non-state terrorism worldwide. Sci Adv 7(31):eabg4778. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abg4778
Quan Tran V, Quoc Dang V, Si Ho L (2022) Evaluating compressive strength of concrete made with recycled concrete aggregates using machine learning approach. Constr Build Mater 323:126578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126578
Rao H, Shi X, Rodrigue AK, Feng J, **a Y, Elhoseny M, Yuan X, Gu L (2019) Feature selection based on artificial bee colony and gradient boosting decision tree. Appl Soft Comput 74:634–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.10.036
Ridker RG, Henning JA (1967) The determinants of residential property values with special reference to air pollution. Rev Econ Stat 49(2):246. https://doi.org/10.2307/1928231
Roback J (1982) Wages, rents, and the quality of life. J Polit Econ 90(6):1257–1278. https://doi.org/10.1086/261120
Rosen S (1974) Hedonic prices and implicit markets: product differentiation in pure competition. J Polit Econ 82(1):34–55
Sagi O, Rokach L (2018) Ensemble learning: a survey. WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 8(4):e1249. https://doi.org/10.1002/widm.1249
Shaddick G, Thomas ML, Mudu P, Ruggeri G, Gumy S (2020) Half the world’s population are exposed to increasing air pollution. npj Climate Atmos Sci 3(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-020-0124-2
Tang J, Liang J, Han C, Li Z, Huang H (2019) Crash injury severity analysis using a two-layer stacking framework. Accid Anal Prev 122:226–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aap.2018.10.016
Wang J, Lee CL (2022) The value of air quality in housing markets: a comparative study of housing sale and rental markets in China. Energy Policy 160:112601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112601
Wang J, Wu K, Du Y (2022a) Does air pollution affect urban housing prices? Evidence from 285 Chinese prefecture-level cities. J Clean Prod 370:133480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133480
Wang L, He S, Su S, Li Y, Hu L, Li G (2022b) Urban neighborhood socioeconomic status (SES) inference: a machine learning approach based on semantic and sentimental analysis of online housing advertisements. Habitat Int 124:102572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2022.102572
**u D, Kelly B, Gu S, Karolyi A (2020) Empirical asset pricing via machine learning. The Review of Financial Studies 33(5):2223–2273. https://doi.org/10.1093/rfs/hhaa009
Xue S, Zhang B, Zhao X (2021) Brain drain: the impact of air pollution on firm performance. J Environ Econ Manag 110:102546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2021.102546
Yang Q, Liu G, Gonella F, Chen Y, Liu C, Zhao H, Yang Z (2022) Assessing the temporal-spatial dynamic reduction in ecosystem services caused by air pollution: a near-real-time data perspective. Resour Conserv Recycl 180:106205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2022.106205
Yin P, Brauer M, Cohen AJ, Wang H, Li J, Burnett RT, Stanaway JD, Causey K, Larson S, Godwin W, Frostad J, Marks A, Wang L, Zhou M, Murray CJL (2020) The effect of air pollution on deaths, disease burden, and life expectancy across China and its provinces, 1990–2017: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Planet Health 4(9):e386–e398. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2542-5196(20)30161-3
Zhang C, Zhang X (2022) Evolutionary game analysis of air pollution co-investment in emission reductions by steel enterprises under carbon quota trading mechanism. J Environ Manage 317:115376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115376
Zhang X, Zhang X, Chen X (2017) Happiness in the air: how does a dirty sky affect mental health and subjective well-being? J Environ Econ Manag 85:81–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeem.2017.04.001
Zhang F, Zhou B, Liu L, Liu Y, Fung HH, Lin H, Ratti C (2018a) Measuring human perceptions of a large-scale urban region using machine learning. Landsc Urban Plan 180:148–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.08.020
Zhang X, Chen X, Zhang X (2018b) The impact of exposure to air pollution on cognitive performance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(37):9193–9197. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1809474115
Zhang H, Chen J, Wang Z (2021a) Spatial heterogeneity in spillover effect of air pollution on housing prices: evidence from China. Cities 113:103145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2021.103145
Zhang W, Yu C, Dong Z, Zhuo H (2021b) Ripple effect of the housing purchase restriction policy and the role of investors’ attention. Habitat Int 114:102398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2021.102398
Zheng S, Kahn ME, Liu H (2010) Towards a system of open cities in China: home prices, FDI flows and air quality in 35 major cities. Reg Sci Urban Econ 40(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2009.10.003
Zheng S, Cao J, Kahn ME, Sun C (2013) Real estate valuation and cross-boundary air pollution externalities: evidence from Chinese cities. J Real Estate Finance Econ 48(3):398–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11146-013-9405-4
Zou Y (2019) Air pollution and housing prices across Chinese cities. J Urban Plan Dev 145(4):04019012. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)up.1943-5444.0000517
Acknowledgements
This research is also supported by ZJU-CMZJ Joint Lab on Data Intelligence and Urban Future and China Institute of Urbanization Zhejiang University.
Funding
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 72004199) and Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LQ21G030012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection and analysis were performed by Sheng Pan, Zhiyuan Li, and Ziqing Li. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Weiwen Zhang, Sheng Pan, and Zhaoyingzi Dong. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors agree to participate.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Pan, S., Li, Z. et al. The nonlinear relationship between air quality and housing prices by machine learning. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 114375–114390 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30123-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30123-5