Abstract
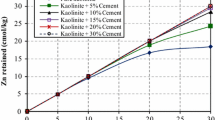
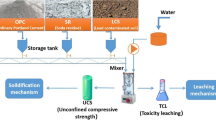
The focus of the present study was on the applicability of superfine zeolite (SZ) and polypropylene fibers in improving the geo-environmental parameters as well as the durability of cement-based stabilized/solidified low plasticity clay containing different dosages of Pb. The leaching data revealed that while adding a low range (≤ 7.5%) of sole cement even in the severely polluted soils could fully eliminate the Pb bioavailability, the metal retention capacity might portray a marked sensitivity to the acid-washing process. A major reduction was also observed in the mechanical/leaching performance of those samples after undergoing the wetting–drying (w-d) cycle, especially at a high proportion of Pb, which could weaken the cementation bonding dramatically; hence, much more cement was needed to pass the required stabilization/solidification (S/S) standards. Besides, the micro level tests indicated that the application of SZ (with 25% cement replacement) would alleviate the Pb declining impact on the S/S reactions and modify the porous network of soil. As a result, the specimens amended by cement-SZ (CSZ) were more functional (~ 1.4 times) in immobilizing the toxic ions than the cement alone was. However, the CSZ admixture might not perfectly restrain the w-d forces/deteriorations. Such a potential drawback was found to be solvable by the insertion of fiber, in which case, an enhancement in the ductility and the metal capsulation could be also manifested. In fact, the CSZ/fiber treatment could form a well-intertwined matrix, showing high success rates in stabilizing/solidifying the contaminated soils alongside a significant decrease (~ 2-folds) in the quantity of needed amount of cement to give the S/S satisfactory operation under the harsh environmental conditions.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that they have not need research data support with this submission. Also, the authors are sure that all data and materials as well as software application or custom code support their published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Abdi MR, Ghalandarzadeh A, Shafiei-Chafi L (2022) Optimization of lime and fiber content for improvement of clays with different plasticity using response surface method (RSM). Transp Geotech 32:100685
Akbari HR, Sharafi H, Goodarzi AR (2021) Effect of polypropylene fiber and nano-zeolite on stabilized soft soil under wet-dry cycles. Geotext Geomembr 49(6):1470–1482
Aldaood A, Khalil A, Bouasker M, Muzahim AM (2021) Experimental study on the mechanical behavior of cemented soil reinforced with straw fiber. Geotech Geol Eng 39:2985–3001
ASTM (2006) Annual book of ASTM standards. vol. 04.08. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia
Awual MR, Hasan MM, Rahman MM, Asiri AM (2019) Novel composite material for selective copper (II) detection and removal from aqueous media. J Mol Liq 283:772–780
Boz A, Sezer A, Özdemir T, Hızal GE, Dolmacı ÖA (2018) Mechanical properties of lime-treated clay reinforced with different types of randomly distributed fibers. Arab J Geosci 11:1–14
Cao X, Wang W, Ma R, Sun S, Lin J (2019) Solidification/stabilization of Pb2+ and Zn2+ in the sludge incineration residue-based magnesium potassium phosphate cement: physical and chemical mechanisms and competition between coexisting ions. Environ Pollut 253:171–180
Chen Q, Lv G, Jiang X, Zhao X, Kong L (2019) Stabilization of heavy metals in municipal solid waste circulating fluidized bed incineration fly ash by fusion-hydrothermal method. Waste Dispos Sustain Energy 1(4):251–259
Chen W, Wang F, Li Z, Li Q (2020) A comprehensive evaluation of the treatment of lead in MSWI fly ash by the combined cement solidification and phosphate stabilization process. Waste Manage 114:107–114
Chen Y, Chen F, Zhou F, Lu M, Hou H, Li J, ... Wang T (2022) Early solidification/stabilization mechanism of heavy metals (Pb, Cr and Zn) in Shell coal gasification fly ash based geopolymer. Sci Total Environ 802, 149905
Chiu AC, Akesseh R, Moumouni IM, **ao Y (2019) Laboratory assessment of rice husk ash (RHA) in the solidification/stabilization of heavy metal contaminated slurry. J Hazard Mater 371:62–71
Choobbasti AJ, Samakoosh MA, Kutanaei SS (2019) Mechanical properties soil stabilized with nano calcium carbonate and reinforced with carpet waste fibers. Constr Build Mater 211:1094–1104
Contessi S, Calgaro L, Dalconi MC, Bonetto A, Bellotto MP, Ferrari G, ... Artioli G (2020) Stabilization of lead contaminated soil with traditional and alternative binders. J Hazard Mater 382, 120990
Cuisinier O, Masrouri F, Mehenni A (2020) Alteration of the hydromechanical performances of a stabilized compacted soil exposed to successive wetting-drying cycles. J Mater Civ Eng 32(11):04020349
Dong Y, Liu F, Qiao X, Zhou L, Bi W (2018) Effects of acid mine drainage on calcareous soil characteristics and Lolium perenne L. germination. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(12):2742
Du YJ, Wei ML, Reddy KR, Liu ZP, ** F (2014) Effect of acid rain pH on leaching behavior of cement stabilized lead-contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 271:131–140
Du YJ, Bo YL, ** F, Liu CY (2016) Durability of reactive magnesia-activated slag-stabilized low plasticity clay subjected to drying-wetting cycle. Eur J Environ Civ Eng 20:215–230
Emmanuel E, Yong LL, Anggraini V, Pasbakhsh P (2020) Can halloysite nanotubes be used to remediate zinc and lead-contaminated marine clay? A solidification/stabilization approach. Appl Clay Sci 186:105441
EN-12457-4, (2002) Characterisation of waste. Leaching. Compliance test for leaching of granular waste materials and sludges- Part 4: One Stage batch test at a liquid to solid ratio of 10 l/kg for materials with particle size below 10 mm (without or with size reduction). European Committee for Standardization, Brussels
Ge S, Jiang W, Zheng L, **e X, Pan Y (2021) Green remediation of high-lead contaminated soil by stabilization/solidification with insoluble humin: long-term leaching and mechanical characteristics. J Clean Prod 324:129184
Goodarzi AR, Movahedrad M (2017) Stabilization/solidification of zinc-contaminated kaolin clay using ground granulated blast-furnace slag and different types of activators. Appl Geochem 81:155–165
He L, Wang Z, Gu WB (2021) Evolution of freeze-thaw properties of cement-lime solidified contaminated soil. Environ Technol Innov 21:101189
Helson O, Eslami J, Beaucour AL, Noumowe A, Gotteland P (2018) Durability of soil mix material subjected to wetting/drying cycles and external sulfate attacks. Constr Build Mater 192:416–428
Jafarpour P, Moayed RZ, Kordnaeij A (2020) Yield stress for zeolite-cement grouted sand. Constr Build Mater 247:1–12
Jalali J, Noorzad R (2021) Discrete fiber reinforcement efficiency in the mechanical properties and wet-dry performance of fat clay treated with industrial sewage sludge ash. Constr Build Mater 284:122739
Kim SH, Chung H, Jeong S, Nam K (2021) Identification of pH-dependent removal mechanisms of lead and arsenic by basic oxygen furnace slag: relative contribution of precipitation and adsorption. J Clean Prod 279:123451
Li W, Yi Y (2019) Stabilization/solidification of lead-and zinc-contaminated soils using MgO and CO2. J CO2 Util 33:215–221
Liu J, Zha F, Xu L, Kang B, Yang C, Feng Q, ... Zhang J (2020a) Strength and microstructure characteristics of cement-soda residue solidified/stabilized zinc contaminated soil subjected to freezing-thawing cycles. Cold Reg Sci Technol 172, 102992
Liu W, Li W, Sun X (2020b) Investigation of drying-wetting durability of cement-stabilised clayey soil. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Ground Improvement 175(2):139–149
Liu Y, Pang H, Wang X, Yu S, Chen Z, Zhang P, ... Wang X (2021) Zeolitic imidazolate framework-based nanomaterials for the capture of heavy metal ions and radionuclides: a review. Chem Eng J 406 127139
Luo Z, Zhi T, Liu L, Mi J, Zhang M, Tian C, ... Mu Y (2022) Solidification/stabilization of chromium slag in red mud-based geopolymer. Constr Build Mater 316 125813
Mola-Abasi H, Semsani SN, Saberian M, Khajeh A, Li J, Harandi M (2020) Evaluation of the long-term performance of stabilized sandy soil using binary mixtures: a micro-and macro-level approach. J Clean Prod 267:122209
Napia C, Sinsiri T, Jaturapitakkul C, Chindaprasirt P (2012) Leaching of heavy metals from solidified waste using Portland cement and zeolite as a binder. Waste Manage 32(7):1459–1467
Ng YCH, **ao H, Armediaz Y, Pan Y, Lee FH (2020) Effect of short fibre reinforcement on the yielding behaviour of cement-admixed clay. Soils Found 60(2):439–453
Nosrati SA, Negahdar A, Negahdar H (2021) Stabilizing the clayey sand contaminated with heavy metals by zeolite and rice husk ash absorbents. Arab J Geosci 14(18):1–15
Ok YS, Yang JE, Zhang YS, Kim SJ, Chung DY (2007) Heavy metal adsorption by a formulated zeolite-Portland cement mixture. J Hazard Mater 147(1–2):91–96
Ouhadi VR, Yong RN, Deiranlou M (2021) Enhancement of cement-based solidification/stabilization of a lead-contaminated smectite clay. J Hazard Mater 403:123969
Pu S, Zhu Z, Song W, Wang H, Huo W, Zhang J (2021) A novel acidic phosphoric-based geopolymer binder for lead solidification/stabilization. J Hazard Mater 415:125659
Reddy VA, Solanki CH, Kumar S, Reddy KR, Du YJ (2020) Stabilization/solidification of zinc-and lead-contaminated soil using limestone calcined clay cement (LC3): an environmentally friendly alternative. Sustainability 12(9):3725
Roshan K, Choobbasti AJ, Kutanaei SS (2020) Evaluation of the impact of fiber reinforcement on the durability of lignosulfonate stabilized clayey sand under wet-dry condition. Transportation Geotechnics 23:100359
Rudžionis Ž, Adhikary SK, Manhanga FC, Ashish DK, Ivanauskas R, Stelmokaitis G, Navickas AA (2021) Natural zeolite powder in cementitious composites and its application as heavy metal absorbents. J Build Eng 43:103085
Salem A, Sene RA (2011) Removal of lead from solution by combination of natural zeolite–kaolin–bentonite as a new low-cost adsorbent. Chem Eng J 174(2–3):619–628
Szajerski P (2021) Solidification of radioactive waste in lignite slag and bismuth oxide filled elastomer matrices: release mechanism, immobilization efficiency, long term radiation stability and aging. Chem Eng J 404:126495
Tran KQ, Satomi T, Takahashi H (2019) Tensile behaviors of natural fiber and cement reinforced soil subjected to direct tensile test. J Build Eng 24:1–10
UK Environment Agency (2016) The environmental permitting (England and Wales) regulations. No. 1154, http://www.legislation.gov.uk/id/ukdsi/2016/9780111150184. Accessed 17 Jan 2022
Vakili AH, Ghasemi J, Selamat MR, Salimi M, Farhadi MS (2018) Internal erosional behaviour of dispersive clay stabilized with lignosulfonate and reinforced with polypropylene fiber. Constr Build Mater 193:405–415
Venkatesh N, Ali D, Pillai RJ, Heera Lal M (2021) Strength and durability characteristic of lime stabilized Black Cotton soil. In Problematic Soils and Geoenvironmental Concerns, Springer, Singapore, p 739–750
Wang F, Xu J, Yin H, Zhang Y, Pan H, Wang L (2021) Sustainable stabilization/solidification of the Pb, Zn, and Cd contaminated soil by red mud-derived binders. Environ Pollut 284:117178
Wang F, Zhang Y, Shen Z, Pan H, Xu J, Al-Tabbaa A (2019) GMCs stabilized/solidified Pb/Zn contaminated soil under different curing temperature: leachability and durability. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(26):26963–26971
Wang H, Ju C, Zhou M, Chen J, Dong Y, Hou H (2022) Sustainable and efficient stabilization/solidification of Pb, Cr, and Cd in lead-zinc tailings by using highly reactive pozzolanic solid waste. J Environ Manage 306:114473
Wen J, Yan C, **ng L, Wang Q, Yuan L, Hu X (2021) Simultaneous immobilization of As and Cd in a mining site soil using HDTMA-modified zeolite. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(8):9935–9945
Xuan Z, Jun Z (2021) Influence of zeolite addition on mechanical performance and shrinkage of high strength engineered cementitious composites. J Build Eng 36:1–11
Yan X, An J, Yin Y, Gao C, Wang B, Wei S (2022) Heavy metals uptake andtranslocation of typical wetland plants and their ecological effects on the coastal soil of a contaminated bay in Northeast China. Science of the Total Environment 803:149871
Yang L, Wen T, Wang L, Miki T, Bai H, Lu X, Nagasaka, T, (2019) Thestability of the compounds formed in the process of removal Pb (II), Cu (II) and Cd (II) by steelmaking slag in an acidic aqueous solution. J Environ Manag 231:41–48
Yang T, Xue Y, Liu X, Zhang Z (2022) Solidification/stabilization and separation/extraction treatments of environmental hazardous components in electrolytic manganese residue: a review. Process Saf Environ Prot 157:509–526
Zamulina IV, Gorovtsov AV, Minkina TM, Mandzhieva SS, Bauer TV, Burachevskaya MV (2021) The influence of long-term Zn and Cu contamination in Spolic Technosols on water-soluble organic matter and soil biological activity. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111471
Zha F, Liu C, Kang B, Yang X, Zhou Y, Yang C (2021) Acid rain leaching behavior of Zn-contaminated soils solidified/stabilized using cement-soda residue. Chemosphere 281:130916
Zha F, Wang H, Xu L, Yang C, Kang B, Chu C, ... Tan X (2020) Initial feasibility study in adsorption capacity and mechanism of soda residue on lead (II)-contaminated soil in solidification/stabilization technology. Environ Earth Sci 79, 1-12
Zhang H, Zhao Y, Hou D, Hao H (2022a) Cementitious binders modified with halloysite nanotubes for enhanced lead immobilization. Powder Technol 395:149–157
Zhang Y, Ong YJ, Yi Y (2022b) Comparison between CaO-and MgO-activated ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBS) for stabilization/solidification of Zn-contaminated clay slurry. Chemosphere 286:131860
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by MR, ARG, and SHL. The final draft of the manuscript was written by ARG, and all authors commented on previous drafts of the manuscript. The corresponding author ensures that all listed authors have approved the manuscript before submission, including the names and order of authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies on animals and human subjects. The authors confirm that all the research meets ethical guidelines and adheres to the legal requirements of the study country.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that this manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data and material in any form.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kitae Baek
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rozbahani, M., Goodarzi, A.R. & Lajevardi, S.H. Coupling effect of superfine zeolite and fiber on enhancing the long-term performance of stabilized/solidified Pb-contaminated clayey soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 4203–4218 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22453-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22453-7