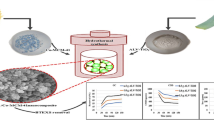
Abstract
VOCs emission reduction in the petroleum and petrochemical industry is a hot and difficult topic at present. The single method may not be able to meet the actual treatment status. Therefore, the adsorption coupled photocatalytic degradation technology was used to remove VOCs. Phosphorus-doped carbon nitride (PCN) and PCN/TiO2 were prepared by hydrothermal synthesis and sol–gel method, and then PCN/TiO2/Zn(OAc)2-ACF composites were prepared by ultrasonic impregnation on zinc acetate modified activated carbon fibers (Zn(OAc)2-ACF). The removal efficiency of n-hexane by composite materials was explored in a self-made reactor, and the factors affecting removal efficiency, removal mechanism, and possible ways of degradation were investigated. The results showed that under the optimum reaction conditions (initial concentration of n-hexane 200 mg/m3, space velocity 1000 h−1, light intensity 24 W, mass fraction of doped PCN 6%, loading twice, calcination temperature 450 °C), PCN/TiO2/Zn(OAc)2-ACF composite has the highest removal efficiency of n-hexane (90.2%). The adsorption capacity of the composites after do** the P element was 215.3 mg/g, which did not enhance the adsorption performance compared with that before do**, but the removal rate of n-hexane was higher. This showed that do** P element was helpful to enhance the photocatalytic activity of the composites.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Note applicable.
References
Abdolahnejad A, Mokhtari M, Ebrahimi AA, Nikaeen M, Shahi MA, Hajizadeh Y (2019) Improved degradation of n-hexane vapours using a hybrid system, a photoreactor packed with TiO2 coated-scoria granules and a multilayer biofilter. J Environ Health Sci Eng 17(2):1017–1027. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00416-4
Bi Y, Sun E, Zhang S, Du F, Wei H, Liu F, Zhao C (2021) Synergistic effect of adsorption and photocatalysis for the degradation of toluene by TiO2 loaded on ACF modified by Zn(CH3COO)2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28(40):57398–57411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14539-5
Brill MH, Li YQ (2016) Calibrating low-scattering samples using Kubelka-Munk model. Color Res Appl 41(4):399–401
Chen P, Chen L, Ge S, Zhang W, Wu M, **ng P, . . ., He Y (2020) Microwave heating preparation of phosphorus doped g-C3N4 and its enhanced performance for photocatalytic H2 evolution in the help of Ag3PO4 nanoparticles. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45(28): 14354-14367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.03.169
Das D, Gaur V, Verma N (2004) Removal of volatile organic compound by activated carbon fiber. Carbon 42(14):2949–2962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2004.07.008
Dobslaw D, Ortlinghaus O (2020) Biological waste air and waste gas treatment: overview, challenges, operational efficiency, and current trends. Sustainability 12(20). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208577
Du X, Bai X, Xu L, Yang L, ** P (2020) Visible-light activation of persulfate by TiO2/g-C3N4 photocatalyst toward efficient degradation of micropollutants. Chem Eng J 384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123245
Fang H-B, Zhang X-H, Wu J, Li N, Zheng Y-Z, Tao X (2018) Fragmented phosphorus-doped graphitic carbon nitride nanoflakes with broad sub-bandgap absorption for highly efficient visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl Catal B Environ 225:397–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.11.080
Fedtke N, Bolt HM (1986) Methodological investigations on the determination of n-hexane metabolites in urine. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 57(2):149–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00381383
Fu J, Xu Q, Low J, Jiang C, Yu J (2019) Ultrathin 2D/2D WO3/g-C3N4 step-scheme H2-production photocatalyst. Appl Catal B Environ 243:556–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.11.011
Gao H, Cao R, Xu X, Zhang S, Yongshun H, Yang H, . . ., Li J (2019) Construction of dual defect mediated Z-scheme photocatalysts for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl Catal B Environ 245: 399-409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.01.004
Geng R, Yin J, Zhou J, Jiao T, Feng Y, Zhang L, . . ., Peng Q (2019) In situ construction of Ag/TiO2/g-C3N4 heterojunction nanocomposite based on hierarchical co-assembly with sustainable hydrogen evolution. Nanomaterials (Basel) 10(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010001
Guo T, Bai Z, Wu C, Zhu T (2008) Influence of relative humidity on the photocatalytic oxidation (PCO) of toluene by TiO2 loaded on activated carbon fibers: PCO rate and intermediates accumulation. Appl Catal B Environ 79(2):171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.09.033
Guo Y, Wen M, Song S, Liu Q, Li G, An T (2022) Enhanced catalytic elimination of typical VOCs over ZnCoOx catalyst derived from in situ pyrolysis of ZnCo bimetallic zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Appl Catal B Environ 308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2022.121212
Hou J, Yang X, Lv X, Huang M, Wang Q, Wang J (2012) Controlled synthesis of TiO2 mesoporous microspheres via chemical vapor deposition. J Alloy Compd 511(1):202–208
Hou C, Liu H, Li Y (2021) The preparation of three-dimensional flower-like TiO2/TiOF2 photocatalyst and its efficient degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride. RSC Adv 11(25):14957–14969. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra01772a
Huang H, Zhou C, Jiao X, Yuan H, Zhao J, He C, . . ., Steele JA (2019) Subsurface defect engineering in single-unit-cell Bi2WO6 monolayers boosts solar-driven photocatalytic performance. ACS Catal 10(2): 1439-1443. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b04789
Humayun M, Fu Q, Zheng Z, Li H, Luo W (2018) Improved visible-light catalytic activities of novel Au/P-doped g-C3N4 photocatalyst for solar fuel production and mechanism. Appl Catal A Gen 568:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2018.10.007
Li Z, Jiang G, Zhang Z, Wu Y, Han Y (2016) Phosphorus-doped g-C3N4 nanosheets coated with square flake-like TiO2: synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic performance in visible light. J Mol Catal A Chem 425:340–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2016.10.020
Li QH, Dong M, Li R, Cui YQ, **e GX, Wang XX, Long YZ (2021) Enhancement of Cr(VI) removal efficiency via adsorption/photocatalysis synergy using electrospun chitosan/g-C3N4/TiO2 nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym 253:117200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117200
Lin C-L, Cheng Y-H, Liu Z-S, Chen J-Y (2012) Adsorption and oxidation of high concentration toluene with activated carbon fibers. J Porous Mater 20(4):883–889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-012-9665-z
Liu ZS, Peng YH, Li WK (2014) Effects of activated carbon fibre-supported metal oxide characteristics on toluene removal. Environ Technol 35(9–12):1499–1507. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.871351
Liu S, Zhu H, Yao W, Chen K, Chen D (2018) One step synthesis of P-doped g-C 3 N 4 with the enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Appl Surf Sci 430:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.108
Long G, Ding J, **e L, Sun R, Chen M, Zhou Y, . . ., Zhao W (2018) Fabrication of mediator-free g-C3N4/Bi2WO6 Z-scheme with enhanced photocatalytic reduction dechlorination performance of 2,4-DCP. Appl Surf Sci 455: 1010-1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.072
Mamaghani AH, Haghighat F, Lee C-S (2017) Photocatalytic oxidation technology for indoor environment air purification: the state-of-the-art. Appl Catal B Environ 203:247–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.10.037
Miyamoto J-i, Kaneko K, Kanoh H (2005) The addition of mesoporosity to activated carbon fibers by a simple reactivation process. Carbon Int J Sponsored Am Carbon Soc 43(4):855–857
Mokhtari M, Hajizadeh Y, Ebrahimi AA, Shahi MA, Jafari N, Abdolahnejad A (2019) Enhanced biodegradation of n-hexane from the air stream using rhamnolipid in a biofilter packed with a mixture of compost, scoria, sugar beet pulp and poplar tree skin. Atmos Pollut Res 10(1):115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2018.06.008
Raja A, Rajasekaran P, Selvakumar K, Ganapathi Raman R, Swaminathan M (2020) Visible active TiO2-CdS-rGO ternary nanocomposite for enhanced photodecomposition of methylene blue. Mater Today Proc 29:1125–1128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.272
Sekar A, Varghese GK, Ravi Varma MK (2019) Analysis of benzene air quality standards, monitoring methods and concentrations in indoor and outdoor environment. Heliyon 5(11):e02918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02918
Shi J-W (2009) Preparation of Fe(III) and Ho(III) co-doped TiO2 films loaded on activated carbon fibers and their photocatalytic activities. Chem Eng J 151(1–3):241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.02.034
Shi J, Zheng J, Wu P, Ji X (2008) Immobilization of TiO2 films on activated carbon fiber and their photocatalytic degradation properties for dye compounds with different molecular size. Catal Commun 9(9):1846–1850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2008.02.018
Sinhamahapatra A, Lee H-Y, Shen S, Mao SS, Yu J-S (2018) H-doped TiO2-x prepared with MgH2 for highly efficient solar-driven hydrogen production. Appl Catal B Environ 237:613–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.06.030
Thanh Truc NT, Pham T-D, Van Thuan D, Son LT, Tran DT, Nguyen MV, . . ., Trang HT (2019) Superior activity of Cu-NiWO4/g-C3N4 Z direct system for photocatalytic decomposition of VOCs in aerosol under visible light. J Alloys Comp 798: 12-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.236
Tian M-J, Liao F, Ke Q-F, Guo Y-J, Guo Y-P (2017) Synergetic effect of titanium dioxide ultralong nanofibers and activated carbon fibers on adsorption and photodegradation of toluene. Chem Eng J 328:962–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.109
Tran Thi VH, Lee BK (2017) Great improvement on tetracycline removal using ZnO rod-activated carbon fiber composite prepared with a facile microwave method. J Hazard Mater 324(Pt B):329–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.066
Wang M, Tan G, Zhang D, Li B, Lv L, Wang Y, . . ., Liu Y (2019) Defect-mediated Z-scheme BiO2-x/Bi2O2.75 photocatalyst for full spectrum solar-driven organic dyes degradation. Appl Catal B Environ 254: 98-112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.04.044
Wei P, Qin D, Chen J, Li Y, Wen M, Ji Y, . . ., An T (2019) Photocatalytic ozonation mechanism of gaseous n-hexane on MOx–TiO2–foam nickel composite (M = Cu, Mn, Ag): unveiling the role of ˙OH and ˙O2−. Environ Sci Nano 6(3): 959-969. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8en01291a
Wen C, Zhang H, Bo Q, Huang T, Lu Z, Lv J, Wang Y (2015) Facile synthesis organic-inorganic heterojunctions of HSbO3/g-C3N4 as efficient visible-light-driven photocatalyst for organic degradation. Chem Eng J 270:405–410
Wu F, Ma Y, Hu YH (2020) Near infrared light-driven photoelectrocatalytic water splitting over P-doped g-C3N4. ACS Appl Energy Mater 3(11):11223–11230. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.0c02148
**e T, Zhang Y, Yao W, Liu Y, Wang H, Wu Z (2019) Synthesis of Bi-deficient monolayered Bi2WO6 nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation. Catal Sci Technol 9(5):1178–1188. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cy02344a
Xu Q, Zhang L, Cheng B, Fan J, Yu J (2020) S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst. Chem 6(7):1543–1559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2020.06.010
Yang C, Miao G, Pi Y, **a Q, Wu J, Li Z, **ao J (2019) Abatement of various types of VOCs by adsorption/catalytic oxidation: a review. Chem Eng J 370:1128–1153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.232
Yi F-Y, Lin X-D, Chen S-X, Wei X-Q (2008) Adsorption of VOC on modified activated carbon fiber. J Porous Mater 16(5):521–526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-008-9228-5
Yu Q, Chen J, Li Y, Wen M, Liu H, Li G, An T (2020) In-situ decoration of metallic Bi on BiOBr with exposed (110) facets and surface oxygen vacancy for enhanced solar light photocatalytic degradation of gaseous n-hexane. Chin J Catal 41(10):1603–1612. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1872-2067(19)63496-0
Zhang X, Xue Z, Li H, Yan L, Yang Y, Wang Y, . . ., Zhang W (2017) Ambient volatile organic compounds pollution in China. J Environ Sci 55: 69-75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.05.036
Zhang X, Zeng Y, Shi W, Tao Z, Liao J, Ai C, . . ., Lin S (2022) S-scheme heterojunction of core–shell biphase (1T-2H)-MoSe2/TiO2 nanorod arrays for enhanced photoelectrocatalytic production of hydrogen peroxide. Chem Eng J 429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131312
Zhao Q, Li Y, Chai X, Xu L, Zhang L, Ning P, . . ., Tian S (2019) Interaction of inhalable volatile organic compounds and pulmonary surfactant: potential hazards of VOCs exposure to lung. J Hazard Mater 369: 512-520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.01.104
Ziemann PJ (2011) Effects of molecular structure on the chemistry of aerosol formation from the OH-radical-initiated oxidation of alkanes and alkenes. Int Rev Phys Chem 30(2):161–195. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144235x.2010.550728
Funding
This research is financially supported by Shandong Natural Science Foundation Project (No. ZR2020MA104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing: HaiDi Wei, EnCheng Sun; methodology: Shuai Zhang, Yuxi Bi, Guoyang Ji; funding support, reviewing: Fang Liu, Ziyan Huang, Chaocheng Zhao.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
EnCheng Sun and HaiDi Wei are co-first authors, and they have made equal contributions to this work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, E., Wei, H., Zhang, S. et al. Adsorption coupling photocatalytic removal of gaseous n-hexane by phosphorus-doped g-C3N4/TiO2/Zn(OAc)2-ACF composites. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 2164–2178 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22382-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22382-5