Abstract
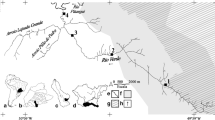
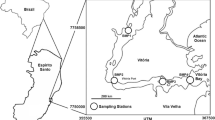
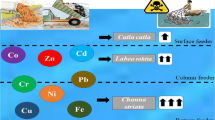
In this research, diatoms as the first step and fishes as the last step of the food chain were compared as toxic metal accumulation bioindicator in an A-class wetland in Turkey. Bioaccumulations of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) were determined in liver, gill and muscle tissues of two commercially consumed fish species Carassius gibelio and Cyprinus carpio and in frustules of epiphytic diatom communities living on submerged macrophytes. Samples were collected seasonally from the Gala Lake, which is among the best stopover habitats of birds migrating between Europe and Africa, considering the paddy harvest period that is a major stress factor for the ecosystem. Also, potential human health risks associated with the consumption of fishes and consumption — dermal contact of diatoms were evaluated both for summer — before paddy harvest (BPH) and autumn — after paddy harvest (APH) periods. As a result of this research, the investigated toxic metal concentrations were increased significantly in diatoms in the APH period, while less significant exchanges were recorded in fishes. The bioaccumulations of PTEs were ranked as follows: Zn > Mn > Se > Cu > B > Cr > Ni > As > Pb > Cd for C. gibelio; Zn > Mn > Se > Cu > B > Cr > As > Ni > Pb > Cd for C. carpio; and Mn > Zn > Se > Pb > B > Ni > Cr > Cu > As > Cd for diatom frustules. Although the HI values in diatoms detected in the APH period were statistically significantly higher (about 1000 times; p < 0.05) than detected in the BPH period, they were less than the limit of 1 in both seasons. However, the HI coefficients of fishes were quite higher than the limit (an average of 23.59 for C. gibelio and 19.18 for C. carpio), which means quite high probable non-carcinogenic health risks for humans. Furthermore, the CR coefficients of Cr, Ni and As in muscle tissues of fishes were considerably higher than the limit of 10−4, which reflects a significant carcinogenic health risk for consumers. The data showed that although the fishes at the top of the food chain bioaccumulate the PTEs in their tissues much higher than the diatoms at the bottom of the food chain, the diatoms are much more sensitive to changes in the environmental conditions than the fishes and they are more effective biological tools as toxic metal accumulation bioindicators.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data analysed during this research are included in this published article.
References
Amankwaa G, Yin X, Zhang L, Huang W, Cao Y, Ni X, Gyimah E (2021) Spatial distribution and eco-environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from a Crater Lake (Bosomtwe/Bosumtwi). Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(15):19367–19380
Atıcı T, Tokatlı C, Çiçek A (2016) Non – silica algae of Seydisuyu Stream Basin (Eskişehir, Turkey). Biodivers Conserv 9(3):84–90
Atıcı T, Tokatlı C, Çiçek A (2018) Diatoms of Seydisuyu Stream Basin (Turkey) and assessment of water quality by statistical and biological approaches. Sigma J Eng Natural Sci 36(1):271–288
ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry) (2012a) Toxicological profile for arsenic. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Atlanta.
ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry) (2012b) Toxicological profile for chromium. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Atlanta.
Aydın GB, Çamur BE (2021) The aquatic ecosystem evaluation of Gala Lake National Park by the hypothetical potential bio-ecological risk analysis. Rev Hydrobiol 14(1–2):25–40
Batur E, Maktav D (2019) Assessment of surface water quality by using satellite images fusion based on PCA method in the Lake Gala, Turkey. IEEE Trans Geosci Rem Sens 57:2983–2989
Bhowmick S, Pramanik S, Singh P, Mondal P, Chatterjee D, Nriagu J (2018) Arsenic in groundwater of West Bengal, India: a review of human health risks and assessment of possible intervention options. Sci Total Environ 612:148–169
Billah MM, Kamal AHM, Idris MH, Ismail J (2017) Mangrove macroalgae as biomonitors of heavy metal contamination in a tropical estuary. Malaysia Water Air Soil Pollut 228:347
Bonanno G, Orlando-Bonaca M (2018) Trace elements in Mediterranean seagrasses and macroalgae: a review. Sci Total Environ 618:1152–1159
Caçador I, Costa JL, Duarte B, Silva G, Medeiros JP, Azeda C, Castro N, Freitas J, Pedro S, Almeida PR, Cabral H, Costa MJ (2012) Macroinvertebrates and fishes as biomonitors of heavy metal concentration in the Seixal Bay (Tagus estuary): which species perform better? Ecol Indic 19:184–190
Chakraborty S, Bhattacharya T, Singh G, Maity JP (2014) Benthic macroalgae as biological indicators of heavy metal pollution in the marine environments: a biomonitoring approach for pollution assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 100:61–68
Chiarelli R, Roccheri M (2014) Marine invertebrates as bioindicators of heavy metal pollution. Open J Meta 4:93–106
Chien LC, Hung TC, Choang KY, Yeh CY, Meng PJ, Shieh MJ, Han BC (2002) Daily intake of TBT, Cu, Zn, Cd and As for fishermen in Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 285(1–3):177–185
Chua EM, Flint N, Wilson SP, Vink S (2018) Potential for biomonitoring metals and metalloids using fish condition and tissue analysis in an agricultural and coal mining region. Chemosphere 202:598–608
Çetin T, Solak CN, Yılmaz E (2021) Testing the performance of European diatom indices for evaluating the ecological status in the Kızılırmak basin, Turkey: flowing waters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:43567–43578
Çiçek A, Köse E, Emiroğlu Ö, Tokatlı C, Başkurt S, Sülün Ş (2014) Boron and arsenic levels in water, sediment and tissues of Carassius gibelio (Bloch, 1782) in a dam lake. Pol J Environ Stud 23(5):1843–1848
Çulha ST, Yabanlı M, Baki B, Yozukmaz A (2016) Heavy metals in tissues of scorpionfish (Scorpaena porcus) caught from Black Sea (Turkey) and potential risks to human health. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(20):20882–20892
Duan P, Khan S, Ali N, Shereen MA, Siddique R, Ali B, Iqbal HMN, Nabi G, Sajjad W, Bilal M (2020) Biotransformation fate and sustainable mitigation of a potentially toxic element of mercury from environmental matrices. Arab J Chem 13(9):6949–6965
Elipek BÇ, Arslan N, Kirgiz T, Öterler B, Güher H, Özkan N (2010) Analysis of benthic macroinvertebrates in relation to environmental variables of Lake Gala, a National Park of Turkey. Turk J Fish Aquat Sc 10:235–243
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (1998) METHOD 3051, microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils, and oils.
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2001) METHOD 200.7, determination of metals and trace elements in water and wastes by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2004) Risk assessment guidance for superfund, Volume1. Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E).
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) (2019) Regional screening levels (RSLs) –equations.
European Committee for Standardization (2014) Water quality - guidance standard for the routine sampling and preparation of benthic diatoms from rivers and lakes. European Standard EN, 13946, Brussels.
Erkmen B, Kolankaya D (2006) Determination of organochlorine pesticide residues in water, sediment, and fish samples from the Meriç Delta. Turkey Int J Environ Anal Chem 86(1–2):161–169
Farias DR, Hurd CL, Eriksen RS, Macleod CK (2018) Macrophytes as bioindicators of heavy metal pollution in estuarine and coastal environments. Mar Pollut Bull 128:175–184
GDFA (General Directorate of Fisheries and Aquaculture) (2018) Fisheries statistics. Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture and Livestock.
Georgieva E, Antal L, Stoyanova S, Arnaudova D, Velcheva I, Iliev I, Vasileva T, Bivolarski V, Mitkovska V, Chassovnikarova T, Todorova B, Uzochukwu IE, Nyeste K, Yancheva V (2022) Biomarkers for pollution in caged mussels from three reservoirs in Bulgaria: a pilot study. Heliyon 8:e09069
Georgieva E, Yancheva V, Stoyanova S, Velcheva I, Iliev I, Vasileva T, Bivolarski V, Petkova E, László B, Nyeste K, Antal L (2021) Which is more toxic? Evaluation of the short-term toxic effects of chlorpyrifos and cypermethrin on selected biomarkers in common carp (Cyprinus carpio, Linnaeus 1758). Toxics 9:125
Güher H, Erdoğan S, Kırgız T, Elipek BÇ (2011) The dynamics of zooplankton in national park of Lake Gala (Edirne-Turkey). Acta Zool Bulg 63(2):157–168
Hu C, Yang X, Dong J, Zhang X (2018) Heavy metal concentrations and chemical fractions in sediment from Swan Lagoon, China: their relation to the physiochemical properties of sediment. Chemosphere 209:848–856
Hu C, Yang X, Gao L, Zhang P, Li W, Dong J, Li C, Zhang X (2019) Comparative analysis of heavy metal accumulation and bioindication in three seagrasses: which species is more suitable as a bioindicator? Sci Total Environ 669:41–48
Interreg-IPA CBC (2018) Ecosystem recourses Lake Gala. The project “Measures for conservation and restoration of natural heritage in Bourgas and Enez”. CB005.1.12.115.
Islam MS (2021) Preliminary assessment of trace elements in surface and deep waters of an urban river (Korotoa) in Bangladesh and associated health risk. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12541-5
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Raknuzzaman M, Al-Mamun MH, Islam MK (2015) Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: a preliminary assessment of an urban river in a develo** country. Ecol Indic 48:281–292
Jolly YN, Rakib MRJ, Islam MS, Akther S, Idris AM (2021) Phoungthong K (2021) Potential toxic elements in sediment and fishes of an important fish breeding river in Bangladesh: a preliminary study for ecological and health risks assessment. Toxin Rev. https://doi.org/10.1080/155695431965624
Javed M, Usmani N (2016) Accumulation of heavy metals and human health risk assessment via the consumption of freshwater fish Mastacembelus armatus inhabiting, thermal power plant effluent loaded canal. Springer Plus, 5:776. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2471-3
Köse E, Emiroğlu Ö, Çiçek A, Aksu S, Başkurt S, Tokatlı C, Şahin M, Uğurluoğlu A (2020) Assessment of ecologic quality in terms of heavy metal concentrations in sediment and fish on Sakarya River and dam lakes, Turkey. Soil Sediment Contam: Int J 29(3):292–303
Lin Z, Li J, Luan Y, Dai W (2020) Application of algae for heavy metal adsorption: a 20-year meta-analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110089
Marella TK, Saxena A, Tiwari A (2020) Diatom mediated heavy metal remediation: a review. Bioresour Technol 305:123068
Mehmood R, Imran U, Ullah A, Ullman JL, Weidhaas J (2020) Health risks associated with accumulation of heavy metals in fish of Keenjhar Lake. Pakistan Environ Sci Pollut Res 1:11
Mutlu E, Uncumusaoğlu AA (2018) Analysis of spatial and temporal water pollution patterns in Terzi Pond (Kastamonu/Turkey) by using multivariate statistical methods. Fresenius Environ Bull 27(5):2900–2912
Nyeste K, Dobrocsi P, Czeglédi I, Czédli H, Harangi S, Baranyai E, Simon E, Nagy SA, Antal L (2019) Age and diet-specific trace element accumulation patterns in different tissues of chub (Squalius cephalus): juveniles are useful bioindicators of recent pollution. Ecol Indic 101:1–10
Öterler B (2017) Community structure, temporal and spatial changes of epiphytic algae on three different submerged macrophytes in a shallow lake. Pol J Environ Stud 26(5):2147–2158
Plessl C, Otachi EO, Körner W, Avenantoldewage A, Jirsa F (2017) Fish as bioindicators for trace element pollution from two contrasting lakes in the Eastern Rift Valley, Kenya: spatial and temporal aspects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19767–19776
Rizwan K, Rahdar A, Bilal M, Iqbal HMN (2022) MXene-based electrochemical and biosensing platforms to detect toxic elements and pesticides pollutants from environmental matrices. Chemosphere 291:132820
Rovira J, Mari M, Schuhmavher M, Nadal M, Domingo JL (2011) Monitoring environmental pollutants in the vicinity of a cement plant: a temporal study. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:372–384
Sharma P, Iqbal HMN, Chandra R (2021) Evaluation of pollution parameters and toxic elements in wastewater of pulp and industries in India: a case study. Case Studies Chem Environ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2021.100163
Solak CN, Peszek L, Yilmaz E, Ergül HA, Kayal M, Ekmekçi F, Várbíró G, Yüce AM, Canli O, Binici MS, Ács E (2020) Use of diatoms in monitoring the Sakarya river basin. Turkey Water 12(3):703
Tang W, Cui J, Shan B, Wang C, Zhang W (2014) Heavy metal accumulation by periphyton is related to eutrophication in the Hai River Basin. Northern China Plosone 9(1):e86458
Tokatlı C (2015) Assessment of the water quality in the Meriç River: as an element of the ecosystem in the Thrace Region of Turkey. Pol J Environ Stud 24(5):2205–2211
Tokatlı C (2017) Bio – ecological and statistical risk assessment of toxic metals in sediments of a worldwide important wetland: Gala Lake National Park (Turkey). Arch Environ Prot 43(1):34–47
Tokatlı C (2018) Essential and toxic element bioaccumulations in fishes of Gala and Siğirci Lakes (Meriç River Delta, Turkey). Acta Aliment 47(4):470–478
Tokatlı C (2021) Health risk assessment of toxic metals in surface and groundwater resources of a significant agriculture and industry zone in Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 80:156
Tokatlı C, Baştatlı Y (2016) Trace and toxic element levels in river sediments. Pol J Environ Stud 25(4):1715–1720
Tokatlı C, İslam S (2022) Spatial–temporal variations and bio-geo-ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of A class wetland in Turkey. Arab J Geosci 15:121
Tokatlı C, Köse E, Uğurluoğlu A, Çiçek A, Emiroğlu Ö (2014) Use of geographic information system (GIS) to evaluate the water quality of Gala Lake (Edirne). Sigma J Eng Natural Sci 32:490–501
Tokatlı C, Mutlu E, Arslan N (2021) Assessment of the potentially toxic element contamination in water of Şehriban Stream (Black Sea Region, Turkey) by using statistical and ecological indicators. Water Environ Res https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1576.
Tokatlı C, Solak CN, Yılmaz E, Atıcı T, Dayıoğlu H (2020) A research on epipelic diatoms of Meriç and Tunca Rivers and application of biological diatom index for water quality assessment. Aquat Sci Eng 35(1):19–26
Tokatlı C, Ustaoğlu F (2020) Health risk assessment of toxicants in Meriç River Delta Wetland, Thrace Region. Turkey Environ Earth Sci 79:426
Tokatlı C, Ustaoğlu F (2021) Evaluation of toxic metal accumulations in Meriç Delta Fish: possible human health risks. Act Aqua Tr 17(1):136–145
Tokatlı C, Varol M (2021) Variations, health risks, pollution status and possible sources of dissolved toxic metal(loid)s in stagnant water bodies located in an intensive agricultural region of turkey. Environ Res 201:111571
Töre Y, Ustaoğlu F, Tepe Y, Kalipci E (2021) Levels of toxic metals in edible fish species of the Tigris River (Turkey); threat to public health. Ecol Indic 123:107361
TFC (Turkish Food Codex) (2002) Communique on the determination of maximum levels of certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture and Livestock.
Ustaoğlu F, Aydın H (2020) Health risk assessment of dissolved heavy metals in surface water in a subtropical rivers basin system of Giresun (north-eastern Turkey). Desalin Water Treat 194:222–234
Ustaoğlu F, İslam S, Tokatlı C (2022) Ecological and probabilistic human health hazard assessment of heavy metal in sera lake nature park sediments (Trabzon, Turkey). Arab J Geosci 15:597
Ustaoğlu F, Tepe Y, Taş B (2020) Assessment of stream quality and health risk in a subtropical Turkey River System: a combined approach using statistical analysis and water quality index. Ecol Indic 113:105815
Varol M (2020) Spatio-temporal changes in surface water quality and sediment phosphorus content of a large reservoir in Turkey. Environ Pollut 259:113860
Varol M, Kaya GK, Sünbül MR (2019) Evaluation of health risks from exposure to arsenic and heavy metals through consumption of ten fish species. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(32):33311–33320
Varol M, Tokatlı C (2021) Impact of paddy fields on water quality of Gala Lake (Turkey): an important migratory bird stopover habitat. Environ Pollut 287:117640
Varol M, Ustaoğlu F, Tokatlı C (2022) Ecological risks and controlling factors of trace elements in sediments of dam lakes in the Black Sea Region (Turkey). Environ Res 205:112478
Wei X, Han L, Gao B, Zhou H, Lu J, Wan X (2016) Distribution, bioavailability, and potential risk assessment of the metals in tributary sediments of Three Gorges Reservoir: the impact of water impoundment. Ecol Indic 61:667
Yüksel B, Ustaoğlu F, Tokatlı C, İslam S (2022) Ecotoxicological risk assessment for sediments of Cavuşlu Stream in Giresun, Turkey: association between garbage disposal facility and metallic accumulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:17223–17240
Zhou Q, Zhang J, Fu J, Shi J, Jiang G (2008) Biomonitoring: an appealing tool for assessment of metal pollution in the aquatic ecosystem. Anal Chim Acta 606:135–150
Funding
This investigation was financially supported by the Trakya University (project number: 2019/127).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cem Tokatli established the idea of the research, obtained all the data, assessed the obtained data and prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The author has given his consent to publish this research article.
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Alexandros Stefanakis
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tokatli, C. Comparisons of diatoms and fishes as toxic metal bioindicator: a case study of an A-class wetland in northwest Turkey under effect of an intensive paddy cultivation stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 87231–87244 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21903-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21903-6