Abstract
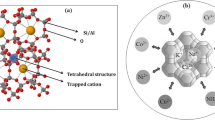
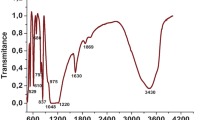
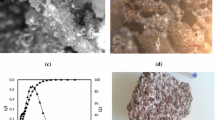
The performance of modified clinoptilolites (zeolites) from two different sources (South Africa and the USA) for the adsorption of Ni2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ from synthetic industrial effluent contaminated with metal concentration levels at 50, 150 and 500 ppm was evaluated. The selectivity of the clinoptilolite for the adsorption of Ni2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ was investigated with mixed feed solutions containing all three ions in equal concentrations and single-component concentrations containing only one of the ions. The homoionic forms of the clinoptilolite were made of Na+, K+ and Ca2+. Batch experiments were then conducted to measure the uptake of metals by the zeolites. The zeolites were characterised using SEM, XRD and BET. The South African clinoptilolite showed a higher surface area and pore volume (17.52m2/g and 0.047cm3/g respectively) than the USA zeolite (12.26m2/g and 0.028cm3/g respectively) for the Na+ homoionic form. According to the equilibrium studies, the selectivity sequence was found to be Pb2+ > Cd2+ > Ni2+, with good fits being obtained using Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isotherms for low metal concentrations. Examples of equilibrium adsorption capacities for RSA and USA clinoptilolite modified with Na+ for Pb were 26.94 mg/g and 27.06 mg/g when RSA-Na+ and USA-Na+ were used respectively. The adsorption was found to depend on the homoionic form of the zeolite and to a lesser extent the source of the zeolite. The selectivity of a particular zeolite for a particular heavy metal can be altered by the homoionic form of the zeolite. Overall, the adsorption capacity of the USA clinoptilolite was higher than the adsorption capacity of the SA clinoptilolite, revealing the potential of clinoptilolite in metal-polluted industrial effluent treatment.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolph MA, Xavier YM, Kriveshini P, Rui K (2012) Phosphine functionalised multiwalled carbon nanotubes: a new adsorbent for the removal of nickel from aqueous solution. J Environ Sci 24(6):1133–1141
Alloway BJ, Ayres DC (1998) Chemical principles of environmental pollution, BJ Alloway and DC Ayres. Water Air Soil Pollut 102(1–2):216–218
Alvarez-Ayuso E, Garcıa-Sánchez A, Querol X (2003) Purification of metal electroplating waste waters using zeolites. Water Res 37(20):4855–4862
Argun ME (2008) Use of clinoptilolite for the removal of nickel ions from water: kinetics and thermodynamics. J Hazard Mater 150(3):587–595
Arshad MN, Sheikh TA, Rahman MM, Asiri AM, Marwani HM, Awual MR (2017) Fabrication of cadmium ionic sensor based on (E)-4-methyl-N′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl) ethylidene) benzenesulfonohydrazide (MPEBSH) by electrochemical approach. J Organomet Chem 827:49–55
Atkins PW (1988) Physical chemistry, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Awual MR (2016) Assessing of lead (III) capturing from contaminated wastewater using ligand doped conjugate adsorbent. Chem Eng J 289:65–73
Awual MR, Hasan MM, Shahat A (2014) Functionalized novel mesoporous adsorbent for selective lead (II) ions monitoring and removal from wastewater. Sensors Actuators B Chem 203:854–863
Alwual MR et al. (2018) Efficient detection and adsorption of Cadmium(11) ions using innovative nanocomposite materials. Chem Eng J 343:118–127
Colella C (1996) Ion exchange equilibria in zeolite minerals. Mineral Deposita 31(6):554–562
Çoruh S (2008) The removal of zinc ions by natural and conditioned clinoptilolites. Desalination 225(1–3):41–57
Ćurković L, Cerjan-Stefanović Š, Filipan T (1997) Metal ion exchange by natural and modified zeolites. Water Res 31(6):1379–1382
Delkash M, Bakhshayesh BE, Kazemian H (2015) Using zeolitic adsorbents to cleanup special wastewater streams: a review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 214:224–241
Erdem E, Karapinar N, Donat R (2004) The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. J Colloid Interface Sci 280(2):309–314
Faghihian H, Marageh MG, Kazemian H (1999) The use of clinoptilolite and its sodium form for removal of radioactive cesium, and strontium from nuclear wastewater and Pb2+, Ni2+, Cd2+, Ba2+ from municipal wastewater. Appl Radiat Isot 50(4):655–660
Febrianto J, Kosasih AN, Sunarso J, Ju YH, Indraswati N, Ismadji S (2009) Equilibrium and kinetic studies in adsorption of heavy metals using biosorbent: a summary of recent studies. J Hazard Mater 162(2–3):616–645
Giles CH, Smith D, Huitson A (1974) A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm. I. Theoretical. J Colloid Interface Sci 47(3):755–765
Godt J, Scheidig F, Grosse-Siestrup C, Esche V, Brandenburg P, Reich A, Groneberg DA (2006) The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health. J Occup Med Toxicol 1(1):22
Günay A, Arslankaya E, Tosun I (2007) Lead removal from aqueous solution by natural and pretreated clinoptilolite: adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 146(1–2):362–371
Inglezakis VJ, Loizidou MM, Grigoropoulou HP (2004) Ion exchange studies on natural and modified zeolites and the concept of exchange site accessibility. J Colloid Interface Sci 275(2):570–576
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) (1997) IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. In: Chromium, Nickel and Welding. World Health Organization, Lyon
Jeon C (2018) Adsorption behavior of cadmium ions from aqueous solution using pen shells. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:57–63
Jewell LL, Kapanji KK Using the molecular sieving properties of clinoptilolite to tailor selectivity for heavy metals removal: a comparison of zeolites from South African and the USA, South African Chemical Engineering Congress, 20–23, September 2009, Somerset Wets, ISBN 978-1-920355-22-0
Kapanji KK (2009) Dissertation (MSc), University of Witwatersrand, 59
Kennedy DA, Tezel FH (2018) Cation exchange modification of clinoptilolite–screening analysis for potential equilibrium and kinetic adsorption separations involving methane, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 262:235–250
Korkuna O, Leboda R, Skubiszewska-Zie BJ, Vrublevs’Ka T, Gun’Ko VM, Ryczkowski J (2006) Structural and physicochemical properties of natural zeolites: clinoptilolite and mordenite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 87(3):243–254
Leofanti G, Padovan M, Tozzola G, Venturelli B (1998) Surface area and pore texture of catalysts. Catal Today 41(1–3):207–219
Marcus Y (1991) Thermodynamics of solvation of ions. Part 5.—Gibbs free energy of hydration at 298.15 K. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 87(18):2995–2999
Medvidović NV, Perić J, Trgo M (2006) Column performance in lead removal from aqueous solutions by fixed bed of natural zeolite–clinoptilolite. Sep Purif Technol 49(3):237–244
Misaelides P (2011) Application of natural zeolites in environmental remediation: a short review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 144(1–3):15–18
Mondale KD, Carland RM, Aplan FF (1995) The comparative ion exchange capacities of natural sedimentary and synthetic zeolites. Miner Eng 8(4–5):535–548
Motsi T, Rowson NA, Simmons MJH (2009) Adsorption of heavy metals from acid mine drainage by natural zeolite. Int J Miner Process 92(1–2):42–48
Ouki SK, Kavannagh M (1997) Performance of natural zeolites for the treatment of mixed metal-contaminated effluents. Waste Manag Res 15(4):383–394
Öztaş NA, Karabakan A, Topal Ö (2008) Removal of Fe (III) ion from aqueous solution by adsorption on raw and treated clinoptilolite samples. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 111(1–3):200–205
Panayotova M, Velikov B (2003) Influence of zeolite transformation in a homoionic form on the removal of some heavy metal ions from wastewater. J Environ Sci Health A 38(3):545–554
Perić J, Trgo M, Medvidović NV (2004) Removal of zinc, copper and lead by natural zeolite—a comparison of adsorption isotherms. Water Res 38(7):1893–1899
Pitcher SK, Slade RCT, Ward NI (2004) Heavy metal removal from motorway stormwater using zeolites. Sci Total Environ 334:161–166
Rodríguez-Iznaga I, Rodríguez-Fuentes G, Petranovskii V (2018) Ammonium modified natural clinoptilolite to remove manganese, cobalt and nickel ions from wastewater: favorable conditions to the modification and selectivity to the cations. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 255:200–210
Semmens MJ, Martin WP (1988) The influence of pretreatment on the capacity and selectivity of clinoptilolite for metal ions. Water Res 22(5):537–542
Shahat A, Awual MR, Khaleque MA, Alam MZ, Naushad M, Chowdhury AS (2015) Large-pore diameter nano-adsorbent and its application for rapid lead (II) detection and removal from aqueous media. Chem Eng J 273:286–295
Shahat A, Hassan MAH, Azzary HME, El-Sharkawy EA, Abdou HM, Awual MR (2018) Novel hierarchical composite adsorbent for selective lead(11) ions capturing from wastewaterr samples. Chem Eng J 332: 377–386
Silbergeld EK, Waalkes M, Rice JM (2000) Lead as a carcinogen: experimental evidence and mechanisms of action. Am J Ind Med 38(3):316–323
Sprynskyy M, Buszewski B, Terzyk AP, Namieśnik J (2006) Study of the selection mechanism of heavy metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Cd2+) adsorption on clinoptilolite. J Colloid Interface Sci 304(1):21–28
Teutli-Sequeira A, Solache-Ríos M, Olguín MT (2009) Influence of Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and NH4+ on the sorption behavior of Cd2+ from aqueous solutions by a Mexican zeolitic material. Hydrometallurgy 97(1–2):46–52
Vasylechko VO, Gryshchouk GV, Zakordonskiy VP, Patsay IO, Vyviurska OA (2013) Sorption of terbium on Transcarpathian clinoptilolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 167:155–161
Wang S, Peng Y (2010) Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 156(1):11–24
Wingenfelder U, Hansen C, Furrer G, Schulin R (2005) Removal of heavy metals from mine waters by natural zeolites. Environ Sci Technol 39(12):4606–4613
Yu LJ, Shukla SS, Dorris KL, Shukla A, Margrave JL (2003) Adsorption of chromium from aqueous solutions by maple sawdust. J Hazard Mater 100(1–3):53–63
Zanin E, Scapinello J, de Oliveira M, Rambo CL, Franscescon F, Freitas L, de Mello JMM, Fiori MA, Oliveira JV, Dal Magro J (2017) Adsorption of heavy metals from wastewater graphic industry using clinoptilolite zeolite as adsorbent. Process Saf Environ Prot 105:194–200
Zhu Z, Li A, Yan L, Liu F, Zhang Q (2007) Preparation and characterization of highly mesoporous spherical activated carbons from divinylbenzene-derived polymer by ZnCl2 activation. J Colloid Interface Sci 316(2):628–634
Acknowledgements
This project received financial support from the University of South Africa, University of the Witwatersrand and NRF South Africa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorimbo, J., Taenzana, B., Muleja, A.A. et al. Adsorption of cadmium, nickel and lead ions: equilibrium, kinetic and selectivity studies on modified clinoptilolites from the USA and RSA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 30962–30978 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2992-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2992-0