Abstract
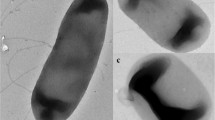
A new strain SWH-15 was successfully isolated after initial electrokinetic remediation experiment using the same saline soil sampled from Shengli Oilfield, China. Four methods (morphological and biochemical characteristics, whole-cell fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) analysis, 16S rRNA sequence analysis and DNA G + C content and DNA–DNA hybridization analysis) were used to identify the taxonomic status of SWH-15 and confirmed that SWH-15 was a novel species of the Bacillus (B.) cereus group. Then, we assessed the degrading ability of the novel strain SWH-15 to crude oil through a microcosm experiment with four treatments, including control (CK), bioremediation using SWH-15 (Bio), electrokinetic remediation (EK), and combined bioremediation and electrokinetic remediation (Bio + EK). The results showed that the Bio + EK combined remediation treatment was more effective than the CK, Bio, and EK treatments in degrading crude oil contaminants. Bioaugmentation, by addition of the strain SWH-15 had synergistic effect with EK in Bio + EK treatment. Bacterial community analysis showed that electrokinetic remediation alone significantly altered the bacterial community of the saline soil. The addition of the strain SWH-15 alone had a weak effect on the bacterial community. However, the strain SWH-15 boosted the growth of other bacterial species in the metabolic network and weakened the impact of electrical field on the whole bacterial community structure in the Bio + EK treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adiguzel A, Ozkan H, Baris O, Inan K, Gulluce M, Sahin F (2009) Identification and characterization of thermophilic bacteria isolated from hot springs in Turkey. J Microbiol Meth 79:321–328
Barba S, Villaseñor J, Rodrigo MA, Cañizares P (2017) Effect of the polarity reversal frequency in the electrokinetic-biological remediation of oxyfluorfen polluted soil. Chemosphere 177:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.002
Bento FM, Camargo FAO, Okeke BC, Frankenberger WT (2005) Comparative bioremediation of soils contaminated with diesel oil by natural attenuation, biostimulation and bioaugmentation. Bioresour Technol 96:1049–1055
Cecchin I, Reddy KR, Thomé A, Tessaro EF, Schnaid F (2017) Nanobioremediation: integration of nanoparticles and bioremediation for sustainable remediation of chlorinated organic contaminants in soils. Int Biodeter Biodegr 119:419–428
Dai Y, Li N, Zhao Q, **e S (2015) Bioremediation using Novosphingobium strain DY4 for 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-contaminated soil and impact on microbial community structure. Biodegradation 26:161–170
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Ehrhardt CJ, Chu V, Brown T, Simmons TL, Swan BK, Bannan J, Robertson JM (2010) Use of fatty acid methyl ester profiles for discrimination of Bacillus cereus T-strain spores grown on different media. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:1902–1912
El-Helow ER (2001) Identification and molecular characterization of a novel Bacillus strain capable of degrading Tween-80. FEMS Microbiol Lett 196:119–122
Farias BCS, Hissa DC, Nascimento CTM et al (2018) Cyclic lipopeptide signature as fingerprinting for the screening of halotolerant Bacillus strains towards microbial enhanced oil recovery. Appl Microbiol Biot 102:1179–1190
Gao YC, Wang JN, Guo SH, Hu YL, Li TT, Mao R, Zeng DH (2015) Effects of salinization and crude oil contamination on soil bacterial community structure in the Yellow River Delta region, China. Appl Soil Ecol 86:165–173
Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn TG (2004) Taxonomic outline of the prokaryotes. Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, second edn. Springer, New York
Gerhardt P, Murray R, Wood WA et al (1994) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC
Gholami-Shiri J, Mowla D, Dehghani S, Setoodeh P (2017) Exploitation of novel synthetic bacterial consortia for biodegradation of oily-sludge TPH of Iran gas and oil refineries. J Environ Chem Eng 5:2964–2975
Gill RT, Harbottle MJ, Smith JW et al (2014) Electrokinetic-enhanced bioremediation of organic contaminants: a review of processes and environmental applications. Chemosphere 107:31–42
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA et al (2007) DNA–DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
Granum P (2007) Bacillus cereus. In: Doyle M, Beuchat L (eds) Food microbiology: fundamentals and frontiers, 3rd edn. ASM Press, Washington, DC
Guinebretiere MH, Auger S, Galleron N, Contzen M, de Sarrau B, de Buyser ML, Lamberet G, Fagerlund A, Granum PE, Lereclus D, de Vos P, Nguyen-The C, Sorokin A (2013) Bacillus cytotoxicus sp. nov. is a novel thermotolerant species of the Bacillus cereus group occasionally associated with food poisoning. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:31–40
Guo S, Fan R, Li T, Hartog N, Li F, Yang X (2014) Synergistic effects of bioremediation and electrokinetics in the remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 109:226–233
Harbottle MJ, Lear G, Sills GC, Thompson IP (2009) Enhanced biodegradation of pentachlorophenol in unsaturated soil using reversed field electrokinetics. J Environ Manag 90:1893–1900
Kim SH, Han HY, Lee YJ, Kim CW, Yang JW (2010) Effect of electrokinetic remediation on indigenous microbial activity and community within diesel contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 408:3162–3168
Kwon GH, Lee HA, Park JY, Kim JS, Lim J, Park CS, Kwon DY, Kim YS, Kim JH (2009) Development of a RAPD-PCR method for identification of Bacillus species isolated from Cheonggukjang. Int J Food Microbiol 129:282–287
Lear G, Harbottle MJ, van der Gast CJ, Jackman SA, Knowles CJ, Sills G, Thompson IP (2004) The effect of electrokinetics on soil microbial communities. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1751–1760
Lear G, Harbottle MJ, Sills G, Knowles CJ, Semple KT, Thompson IP (2007) Impact of electrokinetic remediation on microbial communities within PCP contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 146:139–146
Li F, Guo S, Hartog N (2012) Electrokinetics-enhanced biodegradation of heavy polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil around iron and steel industries. Electrochim Acta 85:228–234
Li T, Deng X, Wang J, Chen Y, He L, Sun Y, Song C, Zhou Z (2014) Biodegradation of nitrobenzene in a lysogeny broth medium by a novel halophilic bacterium Bacillus licheniformis. Mar Pollut Bull 89:384–389
Li T, Wang Y, Guo S, Li X, Xu Y, Wang Y, Li X (2016) Effect of polarity-reversal on electrokinetic enhanced bioremediation of pyrene contaminated soil. Electrochim Acta 187:567–575
Lima AT, Hofmann A, Reynolds D, Ptacek CJ, van Cappellen P, Ottosen LM, Pamukcu S, Alshawabekh A, O'Carroll DM, Riis C, Cox E, Gent DB, Landis R, Wang J, Chowdhury AIA, Secord EL, Sanchez-Hachair A (2017) Environmental electrokinetics for a sustainable subsurface. Chemosphere 181:122–133
Liu Y, Lai Q, Göker M, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Wang M, Sun Y, Wang L, Shao Z (2015) Genomic insights into the taxonomic status of the bacillus cereus group. Sci Rep 5:14082
Luo Q, Wang H, Zhang X, Fan X, Qian Y (2006) In situ bioelectrokinetic remediation of phenol-contaminated soil by use of an electrode matrix and a rotational operation mode. Chemosphere 64:415–422
MIDI (2005) Sherlock microbial identification system operating manual, version 6.0. Newark DE: MIDI Inc.
Qin QL, **e BB, Zhang XY, Chen XL, Zhou BC, Zhou J, Oren A, Zhang YZ (2014) A proposed genus boundary for the prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J Bacteriol 196:2210–2215
Saimmai A, Kaewrueng J, Maneerat S (2012) Used lubricating oil degradation and biosurfactant production by SC-9 consortia obtained from oil-contaminated soil. Ann Microbiol 62:1757–1767
Schloss PD, Gevers D, Westcott SL (2011) Reducing the effects of PCR amplification and sequencing artifacts on 16S rRNA-based studies. PLoS One 6:e27310
Shieh WY, Jean WD, Lin YT (2003) Marinobacter lutaoensis sp. nov., a thermotolerant marine bacterium isolated from a coastal hot spring in Lutao, Taiwan. Can J Microbiol 9:244–252
Shinagawa K (1990) Analytical methods for Bacillus cereus and other Bacillus species. Int J Food Microbiol 10:125–141
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M et al (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tindall BJ, Rosselló-Mora R, Busse HJ et al (2010) Notes on the characterization of prokaryote strains for taxonomic purposes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:249–266
US EPA Method 3540c (1996) Soxhlet extraction. United States Environmental Protection Agency, SW-846 manual. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/3540c.pdf
US EPA Method 8015b (1996) Nonhalogenated organics using GC/FID, revision 2, United States Environmental Protection Agency, SW-846 manual. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC https://archive.epa.gov/epawaste/hazard/testmethods/web/pdf/method%208015b,%20revision%202%20-%201996.pdf
Varjani SJ (2017) Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Bioresour Technol 223:277–286
Varjani SJ, Upasani VN (2017) A new look on factors affecting microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants. Int Biodeter Biodegr 120:71–83
Varjani SJ, Rana DP, Jain AK, Bateja S, Upasani VN (2015) Synergistic ex-situ biodegradation of crude oil by halotolerant bacterial consortium of indigenous strains isolated from on shore sites of Gujarat, India. Int Biodeter Biodegr 103:116–124
Wang W, Sun M (2009) Phylogenetic relationships between Bacillus species and related genera inferred from 16S rDNA sequences. Braz J Microbiol 40:505–521
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naïve bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wick LY, Mattle PA, Wattiau P, Harms H (2004) Electrokinetic transport of PAH-degrading bacteria in model aquifers and soil. Environ Sci Technol 38:4596–4602
Wick LY, Shi L, Harms H (2007) Electro-bioremediation of hydrophobic organic soil-contaminants: a review of fundamental interactions. Electrochim Acta 52:3441–3448
Wick LY, Buchholz F, Fetzer I, Kleinsteuber S, Härtig C, Shi L, Miltner A, Harms H, Pucci GN (2010) Responses of soil microbial communities to weak electric fields. Sci Total Environ 408:4886–4893
Yuan Y, Guo S, Li F, Wu B, Yang X, Li X (2016) Coupling electrokinetics with microbial biodegradation enhances the removal of cycloparaffinic hydrocarbons in soils. J Hazard Mater 320:591–601
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Key Research and Development Plan of Shandong Province (No. 2017GSF17118; No. 2017GSF217005), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41601331), and Taishan Scholars Project (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Yc., Guo, Sh., Wang, Jn. et al. Novel Bacillus cereus strain from electrokinetically remediated saline soil towards the remediation of crude oil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 26351–26360 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2495-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2495-z