Abstract
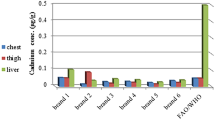
Quail meat is an emerging source of high-quality animal protein. Quails are exposed to a wide range of xenobiotics such as heavy metals. In this study, residual concentrations of four toxic metals, of significant public health importance, including cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), arsenic (As), and nickel (Ni), were determined in edible tissues of quails. In addition, metal loads were measured in water, feed, and litter samples collected from same quail farms as possible sources for quail exposure to heavy metals. The possible use of metallothionein (MT) and heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) as molecular biomarkers of exposure to heavy metals was further investigated. Furthermore, the dietary intake and the potential risk assessment of the examined heavy metals among children and adults were calculated. The edible tissues of quails contained high concentrations of four heavy metals (contents (ppm/ww) ranging from 0.02 to 0.32 in Cd, 0.05 to 1.96 in Pb, 0.002 to 0.32 in As, and 1.17 to 3.94 in Ni), which corresponded to the high contents of these metals in the feeds, water, and litter. MT and Hsp70 mRNA expressions showed positive correlations with the concentrations of heavy metals in tissues indicating the possibility to use these proteins as biomarkers for quail’s exposure to toxic metals. Dietary intake of quail meat and risk assessment revealed potential risks especially for children after prolonged exposure to the examined metals. Thus, legislations should be established and continuous screening of metal residues should be adopted in order to reduce the toxic metal concentrations in feeds and drinking water for quails. Reduction of exposure to heavy metals subsequently would lead to minimization of exposure of such toxicants through consumption of quail meat.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Arab AAK (2001) Heavy metal contents in Egyptian meat and the role of detergent washing on their levels. Food Chem Toxicol 39(6):593–599
Ahmed AM, Hamed DM, Elsharawy NT (2017) Evaluation of some heavy metals residues in batteries and deep litter rearing systems in Japanese quail meat and offal in Egypt. Vet World 10(2):262–269
Ajumobi OO, Tsofo A, Yango M, Aworh MK, Anagbogu IN, Mohammed A, Umar-Tsafe N, Mohammed S, Abdullahi M, Davis L, Idris S, Poggensee G, Nguku P, Gitta SNP (2014) High concentration of blood lead levels among young children in Bagega community, Zamfara—Nigeria and the potential risk factor. Pan Afr Med J 18:1–14
Bortey-Sam N, Nakayama SM, Ikenaka Y, Akoto O, Baidoo E, Yohannes YB, Mizukawa H, Ishizuka M (2015) Human health risks from metals and metalloid via consumption of food animals near gold mines in Tarkwa, Ghana: estimation of the daily intakes and target hazard quotients (THQs). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 111:160–167
Chen SS, Lin YW, Kao YM, Shih YC (2013) Trace elements and heavy metals in poultry and livestock meat in Taiwan. Food Add Contam: Part B 6(4):231–236
Cobbett C, Goldsbrough P (2002) Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: role of heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 53:159–182
Cui Y, Zhu Y, Zhai R, Huang Y, Qiu Y, Liang J (2005) Exposure to metal mixtures and human health impacts in a contaminated area in Nanning, China. Environ Int 31:784–790
Darwish WS, Ikenaka Y, El-Ghareeb WR, Ishizuka M (2010) High expression of the mRNA of cytochrome P450 and phase II enzymes in the lung and kidney tissues of cattle. Animal 4(12):2023–2029.
Darwish WS, Ikenaka Y, Nakayama S, Ishizuka M (2014) The effect of copper on the mRNA expression profile of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes in cultured rat H4-II-E cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 158(2):243–248
Darwish WS, Hussein MA, El-Desoky KI, Ikenaka Y, Nakayama S, Mizukawa H, Ishizuka M (2015) Incidence and public health risk assessment of toxic metal residues (cadmium and lead) in Egyptian cattle and sheep meats. Int Food Res J 22(4):1719–1726
Darwish WS, Ikenaka Y, Nakayama SM, Mizukawa H, Ishizuka M (2016) Constitutive effects of lead on aryl hydrocarbon receptor gene battery and protection by β-carotene and ascorbic acid in human HepG2 cells. J Food Sci 81(1):T275–T281
European Commission (EC) (2006) Commission regulation (EC) no 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuff. Off J Eur Union, 2006
Feng H, Gao Y, Zhao L, Wei Y, Li Y, Wei W, Wu Y, Sun D (2013) Biomarkers of renal toxicity caused by exposure to arsenic in drinking water. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 35:495–501
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (2003) Animal production and health paper: good practices in planning and management of integrated commercial poultry production in South Asia. Rome, 2003. http://www.fao.org/3/a-y4991e.pdf accessed on 07122017
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (2013) Current worldwide annual meat consumption per capita, livestock and fish primary equivalent. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization (FAO/WHO) (2010) Summary and conclusions of the seventy-third meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives, Geneva, 8–17 June 2010. Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Geneva, World Health Organization (JECFA/73/SC; http://www.who.int/entity/foodsafety/publications/chem/summary73
Hu Y, Zhang W, Chen G, Cheng H, Tao S (2017) Public health risk of trace metals in fresh chicken meat products on the food markets of a major production region in southern China. Environ Pollut 234:667–676
Ishii C, Nakayama SMM, Ikenaka Y, Nakata H, Saito K, Watanabe Y, Mizukawa H, Tanabe S, Nomiyama K, Hayashi T, Ishizuka M (2017) Lead exposure in raptors from Japan and source identification using Pb stable isotope ratios. Chemosphere 186:367–373
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Al-Mamun MH, Islam KN, Ibrahim M, Masunaga S (2014) Arsenic and lead in foods: a potential threat to human health in Bangladesh. Food Add Contam: Part A 31(12):1982–1992
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Al-Mamun MH, Masunaga S (2015) Assessment of trace metals in foodstuffs grown around the vicinity of industries in Bangladesh. J Food Compos Anal 42:8–15
Jarup L, Akesson A (2009) Review: current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238:201–208
Kalisinska E, Salicki W, Myslek P, Kavetska KM, Jackowski A (2004) Using the mallard to biomonitor heavy metal contamination of wetlands in North-Western Poland. Sci Tot Environ 320:145–161
Kar I, Mukhopadhayay SK, Patra AK, Pradhan S (2017) Bioaccumulation of selected heavy metals and histopathological and hematobiochemical alterations in backyard chickens reared in an industrial area, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0799-z
Kehrig HA, Hauser-Davis RA, Seixas TG, Fillmann G (2015) Trace-elements, methylmercury and metallothionein levels in Magellanic penguin (Spheniscus magellanicus) found stranded on the southern Brazilian coast. Mar Pollut Bull 96(1–2):450–455
Komsta-Szumska E, Chmielnicka J (1983) Effect of zinc, cadmium or copper on mercury distribution in rat tissues. Toxicol Lett 17:349–354
Kumar P, Prasad Y, Patra AK, Swarup D (2007) Levels of cadmium and lead in tissues of freshwater fish (Clarias batrachus L.) and chicken in western UP (India). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79(4):396–400
Lin HJ, Sunge T, Cheng CY, Guo HR (2013) Arsenic levels in drinking water and mortality of liver cancer in Taiwan. J Hazard Mater 263:1132–1138
Loutfy N, Fuerhacker M, Tundo P, Raccanelli S, El Dien AG, Ahmed MT (2006) Dietary intake of dioxins and dioxin-like PCBs, due to the consumption of dairy products, fish/seafood and meat from Ismailia city, Egypt. Sci Tot Environ 370:1–8
Maia AR, Soler-Rodriguez F, Pérez-López M (2017) Concentration of 12 metals and metalloids in the blood of white stork (Ciconia ciconia): basal values and influence of age and gender. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 73(4):522–532
Mariam I, Iqbal S, Nagra SA (2004) Distribution of some trace and macrominerals in beef, mutton and poultry. Int J Agric Biol 5:816–820
Maxfield LF, Fraize CD, Coffin JM (2005) Relationship between retroviral DNA-integration-site selection and host cell transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(5):1436–1441
Mehaisen GMK, Ibrahim RM, Desoky AA, Safaa HM, El-Sayed OA, Abass AO (2017) The importance of propolis in alleviating the negative physiological effects of heat stress in quail chicks. PLoS One 12(10):e0186907
Ogbomida ET, Nakayama SMM, Bortey-Sam N, Oroszlany B, Tongo I, Enuneku AA, Ozekeke O, Ainerua MO, Fasipe IP, Ezemonye LI, Mizukawa H, Ikenaka Y, Ishizuka M (2018) Accumulation patterns and risk assessment of metals and metalloid in muscle and offal of free-range chickens, cattle and goat in Benin City, Nigeria. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 151:98–108
OIE: World Organization for Animal Health (2017) Terrestrial Animal Health Code: summary analysis of slaughter methods and the associated animal welfare issues; 1:7.5.9 (http://www.oie.int/index.php?id=169&L=0&htmfile=chapitre_aw_slaughter.htm)
Renner R (2009) Out of plumb: when water treatment causes lead contamination. Environ Health Perspect 117:A542–A547
Shaheen N, Ahmed MK, Islam MS, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M, Tukun AB, Islam S, Abu Torab MA, Rahim AT (2016) Health risk assessment of trace elements via dietary intake of 'non-piscine protein source' foodstuffs (meat, milk and egg) in Bangladesh. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(8):7794–7806
Shi L, Cao H, Luo J, Liu P, Wang T, Hu G, Zhang C (2017) Effects of molybdenum and cadmium on the oxidative damage and kidney apoptosis in duck. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 145:24–31
Sigrist M, Hilbe N, Brusa L, Campagnoli D, Beldoménico H (2016) Total arsenic in selected food samples from Argentina: estimation of their contribution to inorganic arsenic dietary. Food Chem 210:96–101
Tekin-Ozan S (2008) Determination of heavy metal levels in water, sediment and tissues of tench (Tinca tinca L., 1758) from Beyşehir Lake (Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 145(1–3):295–302
Tukaj S, Bisewska J, Roeske K, Tukaj Z (2011) Time- and dose-dependent induction of Hsp70 in Lemna minor exposed to different environmental stressors. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 87:226–230
Uluozlu OD, Tuzen M, Mendil D, Soylak M (2009) Assessment of trace element contents of chicken products from Turkey. J Hazard Mater 163(2–3):982–987
United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) (1989) Risk assessment guidance for superfund, vol 1. EPA/540/1-89/002. Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, US EPA, Washington, DC
United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) (1991) Quantification of toxicologic effects for nickel. Prepared by the office of health and environmental assessment, environmental criteria and assessment office, Cincinnati, OH for the office of water, office of science and technology, Washington, DC
United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) (2010) Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS). Cadmium (CASRN-7440-43-9) http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst/0141.html
Villar TC, Elaine J, Kaligayahan P, Flavier ME (2005) Lead and cadmium levels in edible internal organs and blood of poultry chicken. J Appl Sci 5(7):1250–1253
Xu J, Sheng L, Yan Z, Hong L (2014) Blood lead and cadmium levels of children: a case study in Changchun, Jilin Province, China. The West Indian Med J 63:29–33
Yabe J, Nakayama MMS, Ikenaka Y, Muzandu K, Choongo K, Mainda G, Mabeta M, Ishizuka M, Umemura T (2013) Metal distribution in tissues of free-range chickens near a lead–zinc mine in Kabwe. Zambia Environ Toxicol Chem 32(1):189–192
Yabe J, Nakayama SM, Ikenaka Y, Yohannes YB, Bortey-Sam N, Oroszlany B, Muzandu K, Choongo K, Kabalo AN, Ntapisha J, Mweene A, Umemura T, Ishizuka M (2015) Lead poisoning in children from townships in the vicinity of a lead-zinc mine in Kabwe, Zambia. Chemosphere 119C:941–947
Yang D, Chen Y, Gunn JM, Belzile N (2008) Selenium and mercury in organisms: interactions and mechanisms. Environ Rev 16:71–92
Young RA (2005) Toxicity profiles: toxicity summary for cadmium, Risk Assessment Information System. University of Tennessee (rais.ornl.Gov/tox/profiles/cadmium.html)
Zhuang P, Zou H, Shu W (2009) Biotransfer of heavy metals along a soil-plant-insect-chicken food chain: field study. J Environ Sci (China) 21(6):849–853
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by grant provided from Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University to departments of Food control, Veterinary Hygiene, and Educational Veterinary Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Darwish, W.S., Atia, A.S., Khedr, M.H.E. et al. Metal contamination in quail meat: residues, sources, molecular biomarkers, and human health risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 20106–20115 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2182-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2182-0