Abstract
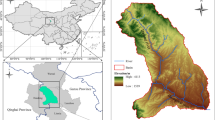
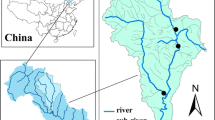
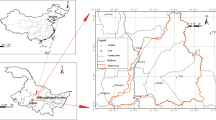
Excessive nitrogen (N) discharge from agriculture causes widespread problems in aquatic ecosystems. Knowledge of spatiotemporal patterns and source attribution of N pollution is critical for nutrient management programs but is poorly studied in headwaters with various small water bodies and mini-point pollution sources. Taking a typical small watershed in the low mountains of Southeastern China as an example, N pollution and source attribution were studied for a multipond system around a village using the Hydrological Simulation Program-Fortran (HSPF) model. The results exhibited distinctive spatio-seasonal variations with an overall seriousness rank for the three indicators: total nitrogen (TN) > nitrate/nitrite nitrogen (NOx −-N) > ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), according to the Chinese Surface Water Quality Standard. TN pollution was severe for the entire watershed, while NOx −-N pollution was significant for ponds and ditches far from the village, and the NH3-N concentrations were acceptable except for the ponds near the village in summer. Although food and cash crop production accounted for the largest source of N loads, we discovered that mini-point pollution sources, including animal feeding operations, rural residential sewage, and waste, together contributed as high as 47% of the TN and NH3-N loads in ponds and ditches. So, apart from eco-fertilizer programs and concentrated animal feeding operations, the importance of environmental awareness building for resource management is highlighted for small farmers in headwater agricultural watersheds. As a first attempt to incorporate multipond systems into the process-based modeling of nonpoint source (NPS) pollution, this work can inform other hydro-environmental studies on scattered and small water bodies. The results are also useful to water quality improvement for entire river basins.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander RB, Boyer EW, Smith RA, Schwarz GE, Moore RB (2007) The role of headwater streams in downstream water quality. J Am Water Resour As 43(1):41–59
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration—guidelines for computing crop water requirements—FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56. FAO, Rome 300(9):D05109
Armstrong A, Stedman RC, Bishop JA, Sullivan PJ (2012) What’s a stream without water? Disproportionality in headwater regions impacting water quality. Environ Manag 1:1–12
Asian Development Bank (2011) Nonpoint source pollution control in catchment areas. Technical Assistance Report, http://www.adb.org/projects/documents/nonpoint-source-pollution-control-catchment-areas. Accessed 1 Oct 2017
Bicknell B, Imhoff J, Kittle J, Jobes T, Donigian A (2005) Hydrological Simulation Program-FORTRAN: HSPF version 12.2 user's manual. AQUA TERRA Consultants, Mountain View, California
Butcher JB, Johnson TE, Nover D, Sarkar S (2014) Incorporating the effects of increased atmospheric CO2 in watershed model projections of climate change impacts. J Hydrol 513:322–334
Chen M, Chen J, Sun F (2010) Estimating nutrient releases from agriculture in China: an extended substance flow analysis framework and a modeling tool. Sci Total Environ 408(21):5123–5136
Chen M, Sun F, Shindo J (2016) China’s agricultural nitrogen flows in 2011: environmental assessment and management scenarios. Resour Conserv Recy 111:10–27
Chen W, Duan W, He B, Chen W (2017) Water quality modeling for typical rural watershed based on the WASP model in Mountain Mao Region, upper Taihu Basin. Journal of Lake Science 29:836–847 (in Chinese)
Administration CEP (2002) Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis method. China Environmental Science Press, Bei**g (in Chinese)
Administration CM (2004) Specifications for surface meteorological observation. China Meteorological Press, Bei**g (in Chinese)
Denk TR, Mohn J, Decock C, Lewicka-Szczebak D, Harris E, Butterbach-Bahl K, Kiese R, Wolf B (2017) The nitrogen cycle: a review of isotope effects and isotope modeling approaches. Soil Biol Biochem 105:121–137
Ding X, Shen Z, Hong Q, Yang Z, Wu X, Liu R (2010) Development and test of the export coefficient model in the upper reach of the Yangtze River. J Hydrol 383(3):233–244
Dodds WK, Oakes RM (2008) Headwater influences on downstream water quality. Environ Manag 41(3):367–377
Doherty J (2015) Calibration and uncertainty analysis for complex environmental models. Watermark Numerical Computing, Brisbane, Australia
Donigian AS (2002) Watershed model calibration and validation: the HSPF experience. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, National TMDL Science and Policy 8:44–73
Duda PB, Hummel PR, Donigian AS, Imhoff JC (2012) BASINS/HSPF: model use, calibration, and validation. T ASABE 55(4):1523–1547
Filoso S, Vallino J, Hopkinson C, Rastetter E, Claessens L (2004) Modeling nitrogen transport in the Ipswich River basin, Massachusetts, using a Hydrological Simulation Program in FORTRAN (HSPF). J Am Water Resour As 40(5):1365–1384
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai Z, Freney JR, Martinelli LA, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320(5878):889–892
Hamon RW, Weiss LL, Wilson WT (1954) Insolation as an empirical function of daily sunshine duration. Mon Weather Rev 82(6):141–146
Hashemi F, Olesen JE, Dalgaard T, Børgesen CD (2016) Review of scenario analyses to reduce agricultural nitrogen and phosphorus loading to the aquatic environment. Sci Total Environ 573:608–626
Hayashi S, Murakami S, KQ X, Watanabe M (2015) Simulation of the reduction of runoff and sediment load resulting from the Gain for Green Program in the Jialingjiang catchment, upper region of the Yangtze River, China. J Environ Manag 149:126–137
He M, Hogue TS (2012) Integrating hydrologic modeling and land use projections for evaluation of hydrologic response and regional water supply impacts in semi-arid environments. Environ Earth Sci 65(6):1671–1685
Jeon JH, Yoon CG, Donigian AS, Jung KW (2007) Development of the HSPF-Paddy model to estimate watershed pollutant loads in paddy farming regions. Agr water Manage 90(1):75–86
Johnes PJ (1996) Evaluation and management of the impact of land use change on the nitrogen and phosphorus load delivered to surface waters: the export coefficient modelling approach. J Hydrol 183(3–4):323–349
Lam QD, Schmalz B, Fohrer N (2010) Modelling point and diffuse source pollution of nitrate in a rural lowland catchment using the SWAT model. Agr water Manage 97(2):317–325
Lassaletta L, García-Gómez H, Gimeno BS, Rovira JV (2010) Headwater streams: neglected ecosystems in the EU Water Framework Directive. Implications for nitrogen pollution control. Environ Sci Pol 13(5):423–433
Li H, Zhang W, Zhang F, Li L (2010) Analysis of the changes in chemical fertilizer use and efficiency of the main grain crops in China. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science 16(5):1136–1143 (in Chinese)
Li H, Zhu G, Chen W, Gao R, Yu Z, Nie X, Diao Y, Li X (2013) Current situation of good water quality reservoirs in hilly region of south-east China: protection practices of Tianmuhu Reservoir. Journal of Lake Science 25:775–784 (in Chinese)
Li X, Liu C, Liu X, Yu J, Liu X (2014) Sources and processes affecting nitrate in a dam-controlled subtropical river, Southwest China. Aquat Geochem 20(5):483–500
Li Z, Liu H, Luo C, Li Y, Li H, Pan J, Jiang X, Zhou Q, **ong Z (2015) Simulation of runoff and nutrient export from a typical small watershed in China using the Hydrological Simulation Program-Fortran. Environ Sci Pollut R 22(10):7954–7966
Lim SL, Lee LH, TY W (2016) Sustainability of using composting and vermicomposting technologies for organic solid waste biotransformation: recent overview, greenhouse gases emissions and economic analysis. J Clean Prod 111:262–278
Liu B, Liu H, Zhang B, Bi J (2013) Modeling nutrient release in the Tai Lake Basin of China: source identification and policy implications. Environ Manag 51(3):724–737
Liu Y, Fu Q, Yin C (2009) Phosphorus sorption and sedimentation in a multipond system within a headstream agricultural watershed. Water Qual Res J Can 44(3):243–252
Liu Z, Tong STY (2011) Using HSPF to model the hydrologic and water quality impacts of riparian land-use change in a small watershed. J Environ Inform 17(1):1–14
Lu J, Gong D, Shen Y, Liu M, Chen D (2013) An inversed Bayesian modeling approach for estimating nitrogen export coefficients and uncertainty assessment in an agricultural watershed in eastern China. Agr Water Manage 116:79–88
Luo P, He B, Chaffe PLB, Nover D, Takara K, Rozainy MMR (2013) Statistical analysis and estimation of annual suspended sediments of major rivers in Japan. Environ Sci-Proc Imp 15(5): 1052-1061
Luo P, He B, Takara K, Razafindrabe BH, Nover D, Yamashiki Y (2011) Spatiotemporal trend analysis of recent river water quality conditions in Japan. J Environ Monitor 13(10): 2819-2829
Ma X, Li Y, Zhang M, Zheng F, Du S (2011) Assessment and analysis of non-point source nitrogen and phosphorus loads in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of Hubei Province, China. Sci Total Environ 412:154–161
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV (1970) River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I-A discussion of principles. J Hydrol 10(3):282–290
Nestler A, Berglund M, Accoe F, Duta S, Xue D, Boeckx P, Taylor P (2011) Isotopes for improved management of nitrate pollution in aqueous resources: review of surface water field studies. Environ Sci Pollut R 18(4):519–533
Ongley ED, Zhang X, Yu T (2010) Current status of agricultural and rural non-point source pollution assessment in China. Environ Pollut 158(5):1159–1168
Ouyang Y, Leininger TD, Moran M (2015) Estimating effects of reforestation on nitrogen and phosphorus load reductions in the Lower Yazoo River Watershed, Mississippi. Ecol Eng 75:449–456
Qiang F, Yin C, Shan B (2006) Phosphorus sorption capacities in a headstream landscape—the pond chain structure. J Environ Sci-China 18(5):1004–1011
Rasmussen JJ, McKnight US, Loinaz MC, Thomsen NI, Olsson ME, Bjerg PL, Binning PJ, Kronvang B (2013) A catchment scale evaluation of multiple stressor effects in headwater streams. Sci Total Environ 442:420–431
Ribarova I, Ninov P, Cooper D (2008) Modeling nutrient pollution during a first flood event using HSPF software: Iskar River case study, Bulgaria. Ecol Model 211(1):241–246
Robertson GP, Vitousek PM (2009) Nitrogen in agriculture: balancing the cost of an essential resource. Annu Rev Environ Resour 34:97–125
Shen Z, Qiu J, Hong Q, Chen L (2014) Simulation of spatial and temporal distributions of non-point source pollution load in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Sci Total Environ 493:138–146
Tang T, Reed P, Wagener T, Van WK (2006) Comparing sensitivity analysis methods to advance lumped watershed model identification and evaluation. Hydrol Earth Syst Sc Discussions 3(6):3333–3395
Verhoeven JT, Arheimer B, Yin C, Hefting MM (2006) Regional and global concerns over wetlands and water quality. Trends Ecol Evol 21(2):96–103
Wang M, Lu B, Wang J, Zhang H, Guo L, Lin H (2016) Using dual isotopes and a Bayesian isotope mixing model to evaluate nitrate sources of surface water in a drinking water source watershed, East China. Water 8(8):355
Wang X (2005) Diffuse pollution from livestock production in China. Chin J Geochem 24(2):189–193
Wang X, Hao F, Cheng H, Yang S, Zhang X, Bu Q (2011) Estimating non-point source pollutant loads for the large-scale basin of the Yangtze River in China. Environ Earth Sci 63(5):1079–1092
Wang Y, Liu N, Wang J (2015) Study on atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus in Taihu Lake. Environmental Science and Management 40(5):103–105 (in Chinese)
Wellen C, Kamran-Disfani AR, Arhonditsis GB (2015) Evaluation of the current state of distributed watershed nutrient water quality modeling. Environ Sci Technol 49(6):3278–3290
Wischmeier W, Smith D (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses. Agricultural handbook 537. Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture
Yang X, Fang S (2015) Practices, perceptions, and implications of fertilizer use in East-Central China. Ambio 44(7):647–652
Yang Y, Wang L (2010) A review of modeling tools for implementation of the EU water framework directive in handling diffuse water pollution. Water Resour Manag 24(9):1819–1843
Yin C, Shan B, Mao Z (2006) Sustainable water management by using wetlands in catchments with intensive land use. In: Wetlands and natural resource management, ecological studies, vol 190. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Yin C, Zhao M, ** W, Lan Z (1993) A multi-pond system as a protective zone for the management of lakes in China. Hydrobiologia 251(1):321–329
Zhang Y, Zhou M, Wu X (1986) Soil records of Jurong Country in Jiangsu Province. Soil Survey Office of Jurong County, Zhenjiang Department of Agriculture (in Chinese)
Zhu T, Liu X (2003) Concise manual on agricultural fertilization techniques. Golden Shield Press, Bei**g (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This study was sponsored by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2017M611938), Postdoctoral Research Funding Programs of Jiangsu Province (No. 1601038B), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41471460 and 41130750), and Science and Technology Service Network Initiative of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KFJ-SW-STS-174). We would like to thank Meng H, Wu Q, Wang W, Yang C, Zhao K, Wu H, Wu Y, Zhang X, Zhang H, Liu X, and Li Y for their field work. We also appreciate the editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., He, B., Nover, D. et al. Spatiotemporal patterns and source attribution of nitrogen pollution in a typical headwater agricultural watershed in Southeastern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 2756–2773 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0685-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0685-8