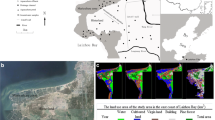
Abstract
Reclamation along coastal zones is a method that has been used to relieve the problems of strained resources and land. Aquaculture, as one of the major man-made activities in reclamation areas, has an environmental impact on coastal waters. The effluents from aquaculture ponds are known to enrich the levels of nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphate. The goals of the present study are to evaluate the environmental impact of mariculture on coastal waters in the east coast of Laizhou Bay, China, and to identify the nitrate sources. Monitoring the concentrations of dissolved nitrogen and phosphate was used to assess their impact on the water quality of coastal waters. A dual isotope (δ15N-NO3 − and δ18O-NO3 −) approach was used to identify the nitrate sources. Higher dissolved nitrogen concentrations (NH4 + and NO3 −) than PO4 3− concentrations associated with enriched δ15N-NO3 − values were observed in the drainage channels, sea cucumber ponds, and groundwater, which indicated that aquaculture activity has more influence on nitrogen nutrients than on phosphate nutrients. In this coastal area with seawater intrusion, nitrogen released from sea cucumber ponds accumulated in nearshore water and migrated in the offshore direction in groundwater currents. This behavior results in nitrogen enrichment in groundwater within the hinterland. Isotopic data indicate that mixing of multiple nitrate sources exists in groundwater, and nitrogen from mariculture is the main source.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson KK, Hooper AB (1983) O2 and H2O are each the source of one O in NO2 produced from NH3 by nitrosomonas: 15N-NMR evidence. FEBS Lett 164(2):236–240. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(83)80292-0
Aravena R, Evans ML, Cherry JA (1993) Stable isotopes of oxygen and nitrogen in sources identification of nitrate from sceptic systems. Ground Water 31:180–186. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.1993.tb01809.x
Barnes RT, Raymond PA (2010) Land-use controls on sources and processing of nitrate in small watersheds: insights from dual isotopic analysis. Ecol Appl 20:1961–1978. doi:10.1890/08-1328.1
Böhlke JK, Eriksen GE, Revesz K (1997) Stable isotope evidence for an atmospheric origin of desert nitrate deposits in northern Chile and southern California, U.S.A. Chem Geol 136(1–2):135–152. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00124-6
Bouwman F, Beusen AHW, Overbeek CC (2013) Hindcasts and future projections of global inland and coastal nitrogen and phosphorus loads due to finfish aquaculture. Rev Fish Sci 21(2):112–156. doi:10.1080/10641262.2013.790340
Burford MA, Williams KC (2001) The fate of nitrogenous waste from shrimp feeding. Aquacult 198:79–93. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(00)00589-5
Burford MA, Costanzo SD, Dennison WC, Jackson CJ, Jones AD et al (2003) A synthesis of dominant ecological processes in intensive shrimp ponds and adjacent coastal environments in NE Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 46:1456–1469. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00282-0
Casciotti KL, Sigman DM, Galanter Hastings M, Böhlke JK, Hilkert A (2002) Measurement of the oxygen isotopic composition of nitrate in seawater and freshwater using the denitrifier method. Anal Chem 74:4905–491. doi:10.1021/ac020113w
Clague JC, Stenger R, Clough TJ (2015) Evaluation of the stable isotope signatures of nitrate to detect denitrification in a shallow groundwater system in New Zealand. Agr Ecosyst Environ 202:188–197. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2015.01.011
Costanzo SD, O’Donohue MJ, Dennison WC, Loneragan NR, Thomas M (2001) A new approach for detecting and map** sewage impacts. Mar Pollut Bull 42:149–156. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00125-9
Costanzo SD, O’ Donohue MJ, Dennison WC (2004) Assessing the influence and distribution of shrimp pond effluent in a tidal mangrove creek in north-east Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 48:514–525. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.09.006
Dähnke K (2008) A nitrate sink in estuaries? An assessment by means of stable nitrate isotopes in the Elbe Estuary. Limnol Oceanogr 53(4):1504–1511. doi:10.4319/lo.2008.53.4.1504
Dierberg FE, Kiattisimkul W (1996) Issues, impacts and implications of shrimp aquaculture in Thailand. Environ Manage 20:649–666
Fogg GE, Rolston DE, Decker DL, Louie DT, Grismer ME (1998) Spatial variation in nitrogen isotope values beneath nitrate contamination source. Groundwater 36(3):418–426. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.1998.tb02812.x
Granger J, Sigman DM, Needoba JA, Harrison PJ (2004) Coupled nitrogen and oxygen isotope fractionation of nitrate during assimilation by cultures of marine phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 49(5):1763–1773. doi:10.4319/lo.2004.49.5.1763
Granger J, Sigman DM, Lehmann MF, Tortell PD (2008) Nitrogen and oxygen isotope fractionation during dissimilatory nitrate reduction by denitrifying bacteria. Limnol Oceanogr 53(6):2533–2545. doi:10.4319/lo.2008.53.6.2533
Herbeck LS, Unger D, Wu Y, Jennerjahn TC (2013) Effluent, nutrient and organic matter export from shrimp and fish ponds causing eutrophication in coastal and back-reef waters of NE Hainan, tropical China. Cont Shelf Res 57:92–104. doi:10.1016/j.csr.2012.05.006
Herbeck LS, Unger D (2013) Pond aquaculture effluents traced along back-reef waters by standard water quality parameters, δ15N in suspended matter and phytoplankton bioassays. Mar Eco Prog Ser 478:71–86. doi:10.3354/meps10170
Hollocher T (1984) Source of the oxygen atoms of nitrate in the oxidation of nitrite by Nitrocacter agilis and evidence against a P-O-N anhydride mechanism in oxidative phosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys 233(2):721–727. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(84)90499-5
Ji DW, Yang JQ, Gao ZH, Jia YG (2007) Eutrophication assessment of the western sea area in the Laizhou Bay during the low water period. Mar Sci Bull 26(1):78–81 (in Chinese)
Kaushal SS, Groffman PM, Band LE (2011) Tracking nonpoint source nitrogen pollution in human-impacted watersheds. Environ Sci Technol 45(19):8225–8232. doi:10.1021/es200779e
Kelly CJ, Keller CK, Evans RD, Orr CH, Smith JL et al (2013) Nitrate-nitrogen and oxygen isotope ratios for identification of nitrate sources and dominant nitrogen cycle processes in a tile-drained dryland agricultural field. Soil Biol Biochem 57:731–738. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.10.017
Kendall C (1998) Tracing nitrogen sources and cycling in catchments. In: Kendall C et al (eds) Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 517–576
Kendall C, Elliott EM, Wankel SD (2007) Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems. In: Michener RH et al (eds) Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science, 2nd edn. Blackwell, Hoboken, pp 375–449
Kumar MS, Burgess S, Luu LT (2004a) Review of nutrient management in freshwater polyculture. J Appl Aquacult 16:17–44. doi:10.1300/J028v16n03_02
Kumar MS, Nguyet NT, Johnson J, Luu LT (2004b) The impact of nutrient concentration (N:P) and manure type on fish polyculture. J Appl Aquacult 16:61–78. doi:10.1300/J028v16n03_04
Li XD, Masuda H, Koba K, Zeng HA (2007) Nitrogen isotope study on nitrate-cotaminated groundwater in the Sichuan Basin, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 178:145–156. doi:10.1007/s11270-006-9186-y
Li RH, Liu SM, Li YW, Zhang GL, Ren JL et al (2014) Nutrient dynamics in tropical rivers, lagoons, and coastal ecosystems of eastern Hainan Island, South China Sea. Biogeosciences 11:481–506. doi:10.5194/bg-11-481-2014
Liu YH, Yang XL, ** Y, Tang XC, Bai YY et al (2011a) Distribution and inter-annual variation of nutrients in Laizhou Bay. Prog Fish Sci 32(4):1–5 (in Chinese)
Liu SM, Li RH, Zhang GL, Wang DR, Du JZ et al (2011b) The impact of anthropogenic activities on nutrient dynamics in the tropical Wenchanghe and Wenjiaohe Estuary and Lagoon system in East Hainan, China. Mar Chem 125:49–68. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2011.02.003
Liu T, Wang F, Michalski G, **a XH, Liu SD (2013) Using 15N, 17O, and 18O to determine nitrate sources in the Yellow River, China. Eviron Sci Technol 47:13412–13421. doi:10.1021/es403357m
Miyake Y, Wada E (1967) The abundance ratio of 15N/14N in marine environments. Rec Oceanographic Works Japan 9:37–53
Páez-Osuna F (2001) The environmental impact of shrimp aquaculture: a global perspective. Environ Pollut 112:229–231. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00111-1
Porubsky WP, Joye SB, Moore WS, Tuncay K, Meile C (2011) Field measurements and modeling of groundwater flow and biogeochemistry at Moses Hammock, a backbarrier island on the Georgia Coast. Biogeochemistry 104:69–90. doi:10.1007/s10533-010-9484-8
Porubsky WP, Weston NB, Moore WS, Ruppel C, Joye SB (2014) Dynamics of submarine groundwater discharge and associated fluxes of dissolved nutrients, carbon, and trace gases to the coastal zone (Okatee River Estuary, South Carolina). Geochim Cosmochim Ac 131:81–97. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2013.12.030
Qu KM, Cui Y, **n FY, Chen MS, Song YL et al (2002) The plane distributions and seasonal variations of nutrients in the East of Laizhou Bay. Oceanic Fisheries Res 22(1):37–46 (in Chinese)
Sigman DM, Casciotti KL, Andreani M, Barford C, Galanter M et al (2001) A bacterial method for the nitrogen isotopic analysis of nitrate in seawater and freshwater. Anal Chem 73(17):4145–4153. doi:10.1021/ac010088e
Sigman DM, Granger J, DiFiore PJ, Lehmann MM, Ho R et al (2005) Coupled nitrogen and oxygen isotope measurements of nitrate along the eastern North Pacific margin. Global Biogeochem Cy 19(4), GB4022. doi:10.1029/2005GB002458
Smith AM, Cave RR (2012) Influence of fresh water, nutrients and DOC in two submarine-groundwater-fed estuaries on the west of Ireland. Sci Total Environ 438:260–270. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.07.094
Suzuki T (2003) Economic and geographic backgrounds of land reclamation in Japanese ports. Mar Pollut Bull 47(1–6):226–229. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00405-8
Thomas Y, Courties C, Helwe YE, Herbland A, Lemonnier H (2010) Spatial and temporal extension of eutrophication associated with shrimp farm wastewater discharges in the New Caledonia Lagoon. Mar Pollut Bull 61:387–398. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.07.005
Vander Zanden MJ, Rasmussen JB (2001) Variation in δ15N and δ13C trophic fractionation: Implications for aquatic food web studies. Limnol Oceanogr 46:2061–2066. doi:10.4319/lo.2001.46.8.2061
Vitoria L, Soler A, Canals À, Otero N (2008) Environmental isotopes (N, S, C, O, D) to determine natural attenuation processes in nitrate contaminated waters: example of Osona (NE Spain). Appl Geochem 23(12):3597–3611. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.07.018
Wankel SD (2006) Nitrogen sources and cycling in the San Francisco Bay Estuary: a nitrate dual isotopic composition approach. Limnol Oceanogr 51(4):1654–1664. doi:10.4319/lo.2006.51.4.1654
Wankel SD, Kendall C, Paytan A (2009) Using nitrate dual isotopic composition (δ15N andδ18O) as a tool for exploring sources and cycling of nitrate in an estuarine system: Elkhorn Slough, California. J Geophys Res 114, G01011. doi:10.1029/2008JG000729
Wada E, Kadonaga T, Matsua S (1975) 15N in nitrogen of naturally occurring substances and global assessment of denitrification from isotopic viewpoint. Geochem J 9:139–148. doi:10.2343/geochemj.9.139
Wexler SK, Hiscock KM, Dennis PF (2011) Catchment-scale quantification of hypothetic denitrification using an isotopic and solute flux approach. Environ Sci Technol 45(9):3967–3973. doi:10.1021/es104322q
Wexler SK, Goodale CL, McGuire KJ, Bailey SW, Groffman PM (2014) Isotopic signals of summer denitrification in a northern hardwood forested catchment. PNAS 116(46):16413–16418. doi:10.1073/pnas.1404321111
Widory D, Petelet-Giraud E, Négrel P, Ladouche B (2005) Tracking the source of nitrate in groundwater using coupled nitrogen and boron isotopes: a synthesis. Environ Sci Technol 39(2):539–548. doi:10.1021/es0493897
Wolff WJ (1997) Development of the conservation of Dutch coastal waters. Aquat Conserv 7(2):165–177
Xue DM, Botte J, De Baets B, Accoe F, Nestler A et al (2009) Present limitations and future prospects of stable isotope methods for nitrate source identification in surface-and groundwater. Water Res 43(5):1159–1170. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.048
Yu DY (2005) Breeding techniques of sea cucumber. China Ocean Press, Bei**g
Zhang XL, Gu DQ, Feng AP, Sui YZ (2008) Biogeochemical circulation and management countermeasures of N and P in coastal wetlands of southern Laizhou Bay. Chinese J Eco-Agri 16(5):1127–1133 (in Chinese)
Zhang XL, Liu LJ, Li PY, Li P (2014) Evaluation of coastal wetland degradation in China. Mar Sci Bull 33(1):112–119 (in Chinese)
Zhao L, Wei H, Feng SZ (2002) Annual cycle and budgets of nutrients in the Bohai Sea. Chinese J Envi Sci 23(1):78–81 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Basic Research Program (2013CB430403) of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hailong Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, P., Xu, S. The impact of mariculture on nutrient dynamics and identification of the nitrate sources in coastal waters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 1300–1311 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5363-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5363-0