Abstract
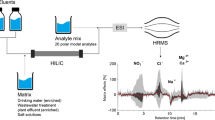
Theoretical papers and environmental applications of hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) have been published for a wide range of analytes, but to our knowledge, no study focused on acidic herbicides (e.g., triketones, phenoxy acids, sulfonylurea, and acidic metabolites of chloroacetanilides). Matrix effects are the main obstacle to natural sample analysis by liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (MS) via an electrospray ionization (ESI) interface. Therefore, we paid particular attention on limiting interference by (i) adapting the emerging HILIC technique, which is generally considered more sensitive than conventional reversed phase liquid chromatography and (ii) optimizing the solid phase extraction (SPE) step using a design of experiment. A rapid and reliable off line SPE-HILIC-ESI-MS/MS method was thus developed for the quantification of acidic herbicides in fresh water, with limits of quantifications (LOQs) ranging from 5 to 22 ng L−1. Then, the analysis of freshwater samples highlighted the robustness of the method, and the importance of the chloroacetanilides metabolites among the studied analytes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpert AJ (1990) Hydrophilic-interaction chromatography for the separation of peptides, nucleic acids and other polar compounds. J Chromatogr A 499:177–196
Assoumani A, Lissalde S, Margoum C, Mazzella N, Coquery M (2013) In situ application of stir bar sorptive extraction as a passive sampling technique for the monitoring of agricultural pesticides in surface waters. Sci Total Environ 463–464:829–835
Balinova A (1996) Ion-pairing mechanism in the solid-phase extraction and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of acidic herbicides in water. J Chromatogr A 728(1–2):319–324
Carabias-Martinez R, Rodriguez-Gonzalo E, Herrero-Hernández E, Hernández-Méndez J (2004a) Simultaneous determination of phenyl- and sulfonylurea herbicides in water by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography with UV diode array or mass spectrometric detection. Anal Chim Acta 517(1–2):71–79
Carabias-Martinez R, Rodriguez-Gonzalo E, Revilla-Ruiz P (2004b) Determination of weakly acidic endocrine-disrupting compounds by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with post-column base addition. J Chromatogr A 1056(1–2):131–138
Chirita R-I, West C, Finaru A-L, Elfakir C (2010) Approach to hydrophilic interaction chromatography column selection: Application to neurotransmitters analysis. J Chromatogr A 1217(18):3091–3104
Chirita R-I, West C, Zubrzycki S, Finaru A-L, Elfakir C (2011) Investigations on the chromatographic behaviour of zwitterionic stationary phases used in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218(35):5939–5963
Dagnac T, Jeannot R, Mouvet C, Baran N (2002) Determination of oxanilic and sulfonic acid metabolites of acetochlor in soils by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 957(1):69–77
Dias NC, Poole CF (2002) Mechanistic study of the sorption properties of Oasis® HLB and its use in solid-phase extraction. Chromatographia 56(5–6):269–275
Esparza X, Moyano E, Galceran MT (2009) Analysis of chlormequat and mepiquat by hydrophilic interaction chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry in food samples. J Chromatogr A 1216(20):4402–4406
Freitas LG, Götz CW, Ruff M, Singer HP, Müller SR (2004) Quantification of the new triketone herbicides, sulcotrione and mesotrione, and other important herbicides and metabolites, at the ng/l level in surface waters using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1028(2):277–286
Fung N, Ikesaki T (1991) Determination of nine acidic herbicides in water and soil by gas chromatograpy using an electron-capture detector. J Chromatogr A 537:385–395
Guo Y, Gaiki S (2005) Retention behavior of small polar compounds on polar stationary phases in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1074(1–2):71–80
Heaton J, Gray N, Cowan DA, Plumb RS, Legido-Quigley C, Smith NW (2011) Comparison of reversed-phase and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography for the separation of ephedrines. Journal of Chromatography A (0)
Kalkhoff SJ, Kolpin DW, Thurman EM, Ferrer I, Barcelo D (1998) Degradation of chloroacetanilide herbicides: The prevalence of sulfonic and oxanilic acid metabolites in Iowa groundwaters and surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 32(11):1738–1740
Karlsson G, Winge S, Sandberg H (2005) Separation of monosaccharides by hydrophilic interaction chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection. J Chromatogr A 1092(2):246–249
Kebarle P, Tang L (1993) From ions in solution to ions in the gas phase: The mechanism of electrospray mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 65(22):972A–986A
Li R, Zhang Y, Lee CC, Lu R, Huang Y (2010) Development and validation of a hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatographic method for determination of aromatic amines in environmental water. J Chromatogr A 1217(11):1799–1805
Lissalde S, Mazzella N, Fauvelle V, Delmas F, Mazellier P, Legube B (2011) Liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry method for thirty-three pesticides in natural water and comparison of performance between classical solid phase extraction and passive sampling approaches. J Chromatogr A 1218(11):1492–1502
Liu M, Chen EX, Ji R, Semin D (2008) Stability-indicating hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography method for highly polar and basic compounds. J Chromatogr A 1188(2):255–263
Mitchell CR, Bao Y, Benz NJ, Zhang S (2009) Comparison of the sensitivity of evaporative universal detectors and LC/MS in the HILIC and the reversed-phase HPLC modes. J Chromatogr B 877(32):4133–4139
Nguyen HP, Schug KA (2008) The advantages of ESI-MS detection in conjunction with HILIC mode separations: Fundamentals and applications. J Sep Sci 31(9):1465–1480
Öllers S, Singer HP, Fässler P, Müller SR (2001) Simultaneous quantification of neutral and acidic pharmaceuticals and pesticides at the low-ng/l level in surface and waste water. J Chromatogr A 911(2):225–234
Pichon V, Cau Dit Coumes C, Chen L, Guenu S, Hennion MC (1996) Simple removal of humic and fulvic acid interferences using polymeric sorbents for the simultaneous solid-phase extraction of polar acidic, neutral and basic pesticides. J Chromatogr A 737(1):25–33
Qin F, Zhao YY, Sawyer MB, Li X-F (2008) Column-switching reversed phase–hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of free estrogens and their conjugates in river water. Anal Chim Acta 627(1):91–98
Quintana JB, Rodil R, Muniategui-Lorenzo S, López-Mahía P, Prada-Rodríguez D (2007) Multiresidue analysis of acidic and polar organic contaminants in water samples by stir-bar sorptive extraction–liquid desorption–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1174(1–2):27–39
Rodil R, Quintana JB, López-Mahía P, Muniategui-Lorenzo S, Prada-Rodríguez D (2009) Multi-residue analytical method for the determination of emerging pollutants in water by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1216(14):2958–2969
Roubeix V, Fauvelle V, Tison-Rosebery J, Mazzella N, Coste M, Delmas F (2012) Assessing the impact of chloroacetanilide herbicides and their metabolites on periphyton in the Leyre River (SW France) via short term growth inhibition tests on autochthonous diatoms. J Environ Monit 14(6):1655–1663
Steen R, Hogenboom AC, Leonards PEG, Peerboom RAL, Cofino WP, Brinkman UAT (1999) Ultra-trace-level determination of polar pesticides and their transformation products in surface and estuarine water samples using column liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 857(1–2):157–166
Taylor PJ (2005) Matrix effects: the Achilles heel of quantitative high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray–tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Biochem 38(4):328–334
Tran ATK, Hyne RV, Doble P (2007) Determination of commonly used polar herbicides in agricultural drainage waters in Australia by HPLC. Chemosphere 67(5):944–953
Vikingsson S, Kronstrand R, Josefsson M (2008) Retention of opioids and their glucuronides on a combined zwitterion and hydrophilic interaction stationary phase. J Chromatogr A 1187(1–2):46–52
Wells MJM, Yu LZ (2000) Solid-phase extraction of acidic herbicides. J Chromatogr A 885(1–2):237–250
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Region Aquitaine, FEDER, and the ANR RIPOST and ANR Potomac for their financial support and Muriel Bonnet and Maryse Boudigues for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fauvelle, V., Mazzella, N., Morin, S. et al. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry for acidic herbicides and metabolites analysis in fresh water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 3988–3996 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2876-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2876-x