Abstract
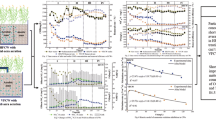
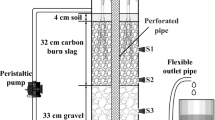
Oxygen and carbon source supply are usually insufficient in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Simultaneous removal of organic pollutants and nitrogen in five batch-operated vertical flow constructed wetlands under different operating conditions was investigated. Alternate aerobic and anaerobic regions were created well with intermittent aeration. Four-month experiments showed that the wetland-applied intermittent aeration combined with step feeding strategy (reactor E) greatly improved the removal of organics, ammonium nitrogen (NH4–N), and total nitrogen (TN) simultaneously, which were 97, 96, and 82 %, respectively. It was much better than non-aerated reactors A and B and outperformed intermittently aerated reactor D without step feeding. Continuous aeration (reactor C) significantly enhanced the organics removal and nitrification, but it limited the TN removal (29 %) seriously as a result of low denitrification level, and the high operation cost remained a question. The effect of plants was confirmed in this study, and the monitoring data showed that the plants could grow normally. Intermittent aeration as well as step feeding had no obvious influence on the growth of wetland plants in this study.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akratos CS, Tsihrintzis VA (2007) Effect of temperature, HRT, vegetation and porous media on removal efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 29(2):173–191
APHA-AWWA-WPCF (2001) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Bodelier P, Libochant AJ, Blom C, Laanbroek H (1996) Dynamics of nitrification and denitrification in root-oxygenated sediments and adaptation of ammonia oxidizing bacteria to low-oxygen or anoxic habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4100–4107
Brisson J, Chazarenc F (2009) Maximizing pollutant removal in constructed wetlands: should we pay more attention to macrophyte species selection? Sci Total Environ 407(13):3923–3930
Burgoon PS, Reddy KR, DeBusk TA (1989) Domestic wastewater treatment using emergent plants cultured in gravel and plastic substrate. In: Hammer DA (ed) Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, pp 536–541
Cui LH, Ouyang Y, Lou Q, Yang F, Chen Y, Zhu W, Luo S (2010) Removal of nutrients from wastewater with Canna indica L. under different vertical-flow constructed wetland conditions. Ecol Eng 36(8):1083–1088
Dong C, Zhu W, Zhao YQ, Gao M (2011) Diurnal fluctuations in root oxygen release rate and dissolved oxygen budget in wetland mesocosm. Desalination 272(1–3):254–258
Hu YS, Zhao YQ, Zhao XH, Kumar JLG (2012) High rate nitrogen removal in an alum sludge-based intermittent aeration constructed wetland. Environ Sci Technol 46:4583–4590
Jia WL, Zhang J, Wu J, **e HJ, Zhang B (2010) Effect of intermittent operation on contaminant removal and plant growth in vertical flow constructed wetlands: a microcosm experiment. Desalination 262(1–3):202–208
Kayser K, Kunst S (2005) Processes in vertical-flow reed beds—nitrification, oxygen transfer and soil clogging. Water Sci Technol 51(9):177–184
Lee Y, Oleszkiewicz JA (2003) Effects of predation and ORP conditions on the performance of nitrifiers in activated sludge systems. Water Res 37(17):4202–4210
Lin YF, **g SR, Wang TW, Lee DY (2002) Effects of macrophytes and external carbon sources on nitrate removal from groundwater in constructed wetlands. Environ Pollut 119(3):413–420
Maltais-Landry G, Maranger R, Brisson J (2009a) Effect of artificial aeration and macrophyte species on nitrogen cycling and gas flux in constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 35(2):221–229
Maltais-Landry G, Maranger R, Brisson J, Chazarenc F (2009b) Nitrogen transformations and retention in planted and artificially aerated constructed wetlands. Water Res 43(2):535–545
Nikolausz M, Kappelmeyer U, Székely A, Rusznyák A, Márialigeti K, Kästner M (2008) Diurnal redox fluctuation and microbial activity in the rhizosphere of wetland plants. Eur J Soil Biol 44(3):324–333
Ong SA, Uchiyama K, Inadama D, Ishida Y, Yamagiwa K (2010) Performance evaluation of laboratory scale up-flow constructed wetlands with different designs and emergent plants. Bioresour Technol 101(19):7239–7244
Ouellet-Plamondon C, Chazarenc F, Comeau Y, Brisson J (2006) Artificial aeration to increase pollutant removal efficiency of constructed wetlands in cold climate. Ecol Eng 27(3):258–264
Saeed T, Sun GZ (2011) Enhanced denitrification and organics removal in hybrid wetland columns: comparative experiments. Bioresour Technol 102(2):967–974
Stefanakis AI, Akratos CS, Tsihrintzis VA (2011) Effect of wastewater step-feeding on removal efficiency of pilot-scale horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol Eng 37(3):431–443
Sundaravadivel M, Vigneswaran S (2001) Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Crit Rev Env Sci Technol 31(4):351–409
Tanner CC, Kadlec RH (2003) Oxygen flux implications of observed nitrogen removal rates in subsurface-flow treatment wetlands. Water Sci Technol 48(5):191–198
Tanner CC, Kadlec RH, Gibbs MM, Sukias JPS, Nguyen ML (2002) Nitrogen processing gradients in subsurface-flow treatment wetlands-influence of wastewater characteristics. Ecol Eng 18(4):499–520
Tee HC, Lim PE, Seng CE, Nawi MAM (2011) Newly developed baffled subsurface-flow constructed wetland for the enhancement of nitrogen removal. Bioresour Technol 104:235–242
Vymazal J (2007) Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 380(1–3):48–65
Vymazal J (2009) The use constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-surface flow for various types of wastewater. Ecol Eng 35(1):1–17
Vymazal J, Kröpfelová L (2009) Removal of organics in constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-surface flow: a review of the field experience. Sci Total Environt 407(13):3911–3922
Wang X, Sun T, Li H, Li Y, Pan J (2010) Nitrogen removal enhanced by shunt distributing wastewater in a subsurface wastewater infiltration system. Ecol Eng 36(10):1433–1438
Wu J, Zhang J, Jia WL, **e H, Gu RR, Li C, Gao BY (2009) Impact of COD/N ratio on nitrous oxide emission from microcosm wetlands and their performance in removing nitrogen from wastewater. Bioresour Technol 100(12):2910–2917
**ong J, Guo G, Mahmood Q, Yue M (2011) Nitrogen removal from secondary effluent by using integrated constructed wetland system. Ecol Eng 37(4):659–662
Yalcuk A, Ugurlu A (2009) Comparison of horizontal and vertical constructed wetland systems for landfill leachate treatment. Bioresour Technol 100(9):2521–2526
Yang L, Chang HT, Huang MNL (2001) Nutrient removal in gravel- and soil-based wetland microcosms with and without vegetation. Ecol Eng 18(1):91–105
Zhao YJ, Liu B, Zhang WG, Ouyang Y, An SQ (2010) Performance of pilot-scale vertical-flow constructed wetlands in responding to variation in influent C/N ratios of simulated urban sewage. Bioresour Technol 101(6):1693–1700
Zhao YJ, Yan C, Li YL, Li JH, Yang M, Nie E, Zheng Z, Luo XZ (2012) Effect of C/N ratios on the performance of earthworm eco-filter for treatment of synthetics domestic sewage. Environ Sci Pollut Res. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-0871-7
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Independent Innovation Foundation of Shandong University (no. 2012JC029), Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Shandong Province (no. JQ201216), the National Water Special Project (no. 2012ZX07203-004), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 50908133).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Hailong Wang
**lin Fan and Shuang Liang equally contributed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, J., Liang, S., Zhang, B. et al. Enhanced organics and nitrogen removal in batch-operated vertical flow constructed wetlands by combination of intermittent aeration and step feeding strategy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20, 2448–2455 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1130-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1130-7