Abstract
Introduction
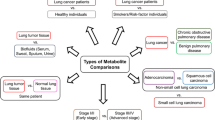
Metabolomics has emerged as a powerful method to provide insight into cancer progression, including separating patients into low- and high-risk groups for overall (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). However, survival prediction based mainly on metabolites obtained from biofluids remains elusive.
Objectives
This proof-of-concept study evaluates metabolites as biomarkers obtained directly from tumor core biopsies along with covariates age, sex, pathological stage at diagnosis (I/II vs. III/VI), histological subtype, and treatment vs. no treatment to risk stratify lung cancer patients in terms of OS and PFS.
Methods
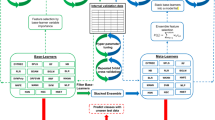
Tumor core biopsy samples obtained during routine lung cancer patient care at the University of Louisville Hospital and Norton Hospital were evaluated with high-resolution 2DLC-MS/MS, and the data were analyzed by Kaplan–Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazards regression. A linear equation was developed to stratify patients into low and high risk groups based on log-transformed intensities of key metabolites. Sparse partial least squares discriminant analysis (SPLS-DA) was performed to predict OS and PFS events.
Results
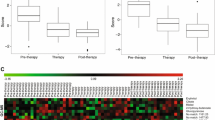
Univariable Cox proportional hazards regression model coefficients divided by the standard errors were used as weight coefficients multiplied by log-transformed metabolite intensity, then summed to generate a risk score for each patient. Risk scores based on 10 metabolites for OS and 5 metabolites for PFS were significant predictors of survival. Risk scores were validated with SPLS-DA classification model (AUROC 0.868 for OS and AUROC 0.755 for PFS, when combined with covariates).
Conclusion
Metabolomic analysis of lung tumor core biopsies has the potential to differentiate patients into low- and high-risk groups based on OS and PFS events and probability.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Datasets used are in [Metabolomics Workbench (MetWB), RRID:SCR_013794, www.metabolomicsworkbench.org] (Study ST001527).
Abbreviations
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PC1:
-
First principal component
- PC2:
-
Second principal component
- PC3:
-
Third principal component
- PFS:
-
Progression free survival
- PLS-DA:
-
Partial least squares discriminant analysis
- SPLS-DA:
-
Sparse partial least squares discriminant analysis
References
Abusalamah, H., Reel, J. M., & Lupfer, C. R. (2020). Pyruvate affects inflammatory responses of macrophages during influenza A virus infection. Virus Research, 286, 198088.
Anantharaju, P. G., Reddy, B. D., Padukudru, M. A., Kumari Chitturi, C. M., Vimalambike, M. G., & Madhunapantula, S. V. (2017). Naturally occurring benzoic acid derivatives retard cancer cell growth by inhibiting histone deacetylases (HDAC). Cancer Biology & Therapy, 18, 492–504.
Bamji-Stocke, S., van Berkel, V., Miller, D. M., & Frieboes, H. B. (2018). A review of metabolism-associated biomarkers in lung cancer diagnosis and treatment. Metabolomics, 14, 81.
Berker, Y., Vandergrift, L. A., Wagner, I., Su, L., Kurth, J., Schuler, A., Dinges, S. S., Habbel, P., Nowak, J., Mark, E., Aryee, M. J., Christiani, D. C., & Cheng, L. L. (2019). Magnetic resonance spectroscopy-based metabolomic biomarkers for ty**, staging, and survival estimation of early-stage human lung cancer. Science and Reports, 9, 10319.
Cascino, A., Muscaritoli, M., Cangiano, C., Conversano, L., Laviano, A., Ariemma, S., Meguid, M. M., & Rossi Fanelli, F. (1995). Plasma amino acid imbalance in patients with lung and breast cancer. Anticancer Research, 15, 507–510.
Collino, S., Martin, F. P., & Rezzi, S. (2013). Clinical metabolomics paves the way towards future healthcare strategies. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 75, 619–629.
Cooke, J. P., & Ghebremariam, Y. T. (2008). Endothelial nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and angiogenesis. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine, 18, 247–253.
Dercle, L., Fronheiser, M., Lu, L., Du, S., Hayes, W., Leung, D. K., Roy, A., Wilkerson, J., Guo, P., Fojo, A. T., Schwartz, L. H., & Zhao, B. (2020). Identification of non-small cell lung cancer sensitive to systemic cancer therapies using radiomics. Clinical Cancer Research, 26, 2151–2162.
Fan, T. W., Lane, A. N., Higashi, R. M., Farag, M. A., Gao, H., Bousamra, M., & Miller, D. M. (2009). Altered regulation of metabolic pathways in human lung cancer discerned by (13)C stable isotope-resolved metabolomics (SIRM). Molecular Cancer, 8, 41.
Girouard, J., Belgorosky, D., Hamelin-Morrissette, J., Boulanger, V., D’Orio, E., Ramla, D., Perron, R., Charpentier, L., van Themsche, C., Eijan, A. M., Berube, G., & Reyes-Moreno, C. (2020). Molecular therapy with derivatives of amino benzoic acid inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in murine models of bladder cancer through inhibition of TNFalpha/NFKappaB and iNOS/NO pathways. Biochemical Pharmacology, 176, 113778.
Goldstraw, P., Crowley, J., Chansky, K., Giroux, D. J., Groome, P. A., Rami-Porta, R., Postmus, P. E., Rusch, V., Sobin, L., International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer International Staging, C. & Participating, I. (2007). The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for the revision of the TNM stage grou**s in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification of malignant tumours. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 2, 706–714.
Gueta, I., Perach Ovadia, Y., Markovits, N., Schacham, Y. N., Epsztein, A., & Loebstein, R. (2020). Is pyroglutamic acid a prognostic factor among patients with suspected infection? A Prospective Cohort Study. Scientific Reports, 10, 10128.
Hori, S., Nishiumi, S., Kobayashi, K., Shinohara, M., Hatakeyama, Y., Kotani, Y., Hatano, N., Maniwa, Y., Nishio, W., Bamba, T., Fukusaki, E., Azuma, T., Takenawa, T., Nishimura, Y., & Yoshida, M. (2011). A metabolomic approach to lung cancer. Lung Cancer, 74, 284–292.
Howlader, N., Noone, A., Krapcho, M., Miller, D., Brest, A., Yu, M., Ruhl, J., Tatalovich, Z., Mariotto, A., Lewis, D. R., Chen, H. S., Feuer, E. J., & Cronin, K. A. (2021). Based on November 2020 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2021. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2018. National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD.
Huang, J., Weinstein, S. J., Moore, S. C., Derkach, A., Hua, X., Mondul, A. M., Sampson, J. N., & Albanes, D. (2019). Pre-diagnostic serum metabolomic profiling of prostate cancer survival. Journals of Gerontology. Series a, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 74, 853–859.
Ji, X., Qian, J., Rahman, S. M. J., Siska, P. J., Zou, Y., Harris, B. K., Hoeksema, M. D., Trenary, I. A., Heidi, C., Eisenberg, R., Rathmell, J. C., Young, J. D., & Massion, P. P. (2018). xCT (SLC7A11)-mediated metabolic reprogramming promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression. Oncogene, 37, 5007–5019.
**, X., Yun, S. J., Jeong, P., Kim, I. Y., Kim, W. J., & Park, S. (2014). Diagnosis of bladder cancer and prediction of survival by urinary metabolomics. Oncotarget, 5, 1635–1645.
Jung, S. Y., Song, H. S., Park, S. Y., Chung, S. H., & Kim, Y. J. (2011). Pyruvate promotes tumor angiogenesis through HIF-1-dependent PAI-1 expression. International Journal of Oncology, 38, 571–576.
Kami, K., Fujimori, T., Sato, H., Sato, M., Yamamoto, H., Ohashi, Y., Sugiyama, N., Ishihama, Y., Onozuka, H., Ochiai, A., Esumi, H., Soga, T., & Tomita, M. (2013). Metabolomic profiling of lung and prostate tumor tissues by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Metabolomics, 9, 444–453.
Klavins, K., Drexler, H., Hann, S., & Koellensperger, G. (2014). Quantitative metabolite profiling utilizing parallel column analysis for simultaneous reversed-phase and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography separations combined with tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 86, 4145–4150.
Loo, J. M., Scherl, A., Nguyen, A., Man, F. Y., Weinberg, E., Zeng, Z., Saltz, L., Paty, P. B., & Tavazoie, S. F. (2015). Extracellular metabolic energetics can promote cancer progression. Cell, 160, 393–406.
Maas, M. N., Hintzen, J. C., Porzberg, M. R., & Mecinović, J. (2020). Trimethyllysine: From carnitine biosynthesis to epigenetics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21, 9451.
McShane, L. M., Altman, D. G., Sauerbrei, W., Taube, S. E., Gion, M., Clark, G. M., Statistics Subcommittee of the NCI-EORTC Working Group on Cancer Diagnostics. (2005). REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Nature Clinical Practice. Urology, 2, 416–422.
Medina, V. A., & Rivera, E. S. (2010). Histamine receptors and cancer pharmacology. British Journal of Pharmacology, 161, 755–767.
Miller, H. A., Yin, X., Smith, S. A., Hu, X., Zhang, X., Yan, J., Miller, D. M., van Berkel, V. H., & Frieboes, H. B. (2021). Evaluation of disease staging and chemotherapeutic response in non-small cell lung cancer from patient tumor-derived metabolomic data. Lung Cancer, 156, 20–30.
Peng, F., Liu, Y., He, C., Kong, Y., Ouyang, Q., **e, X., Liu, T., Liu, Z., & Peng, J. (2018). Prediction of platinum-based chemotherapy efficacy in lung cancer based on LC-MS metabolomics approach. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 154, 95–101.
Puchades-Carrasco, L., Jantus-Lewintre, E., Perez-Rambla, C., Garcia-Garcia, F., Lucas, R., Calabuig, S., Blasco, A., Dopazo, J., Camps, C., & Pineda-Lucena, A. (2016). Serum metabolomic profiling facilitates the non-invasive identification of metabolic biomarkers associated with the onset and progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget, 7, 12904–12916.
Sellers, K., Fox, M. P., Bousamra, M., Slone, S. P., Higashi, R. M., Miller, D. M., Wang, Y., Yan, J., Yuneva, M. O., Deshpande, R., Lane, A. N., & Fan, T. W. (2015). Pyruvate carboxylase is critical for non-small-cell lung cancer proliferation. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 125, 687–698.
Serpa, J. (2020). Cysteine as a carbon source, a hot spot in cancer cells survival. Frontiers in Oncology, 10, 947.
Shen, J., Ye, Y., Chang, D. W., Huang, M., Heymach, J. V., Roth, J. A., Wu, X., & Zhao, H. (2017). Circulating metabolite profiles to predict overall survival in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving first-line chemotherapy. Lung Cancer, 114, 70–78.
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Fuchs, H. E., & Jemal, A. (2021). Cancer statistics, 2021. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 71, 7–33.
Stout, J. T., & Caskey, C. T. (1985). HPRT: Gene structure, expression, and mutation. Annual Review of Genetics, 19, 127–148.
Suzuki, T., & Takahashi, E. (1975). Metabolism of xanthine and hypoxanthine in the tea plant (Thea sinensis L.). The Biochemical Journal, 146, 79–85.
Tanner, J. J., Fendt, S. M., & Becker, D. F. (2018). The proline cycle as a potential cancer therapy target. Biochemistry, 57, 3433–3444.
Tian, Y., Wang, Z., Liu, X., Duan, J., Feng, G., Yin, Y., Gu, J., Chen, Z., Gao, S., Bai, H., Wan, R., Jiang, J., Liu, J., Zhang, C., Wang, D., Han, J., Zhang, X., Cai, L., He, J., & Wang, J. (2018). Prediction of chemotherapeutic efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer by serum metabolomic profiling. Clinical Cancer Research, 24, 2100–2109.
Tip**, M. E., & Bishop, C. M. (1999). Probabilistic principal component analysis. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 61, 611–622.
Townsend, M. H., Anderson, M. D., Weagel, E. G., Velazquez, E. J., Weber, K. S., Robison, R. A., & O’Neill, K. L. (2017). Non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines A549 and NCI-H460 express hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyltransferase on the plasma membrane. Oncotargets and Therapy, 10, 1921–1932.
van den Berg, R. A., Hoefsloot, H. C., Westerhuis, J. A., Smilde, A. K., & van der Werf, M. J. (2006). Centering, scaling, and transformations: Improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genomics, 7, 142.
Wald, L. L., Nelson, S. J., Day, M. R., Noworolski, S. E., Henry, R. G., Huhn, S. L., Chang, S., Prados, M. D., Sneed, P. K., Larson, D. A., Wara, W. M., McDermott, M., Dillon, W. P., Gutin, P. H., & Vigneron, D. B. (1997). Serial proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging of glioblastoma multiforme after brachytherapy. Journal of Neurosurgery, 87, 525–534.
Wikoff, W. R., Grapov, D., Fahrmann, J. F., Defelice, B., Rom, W. N., Pass, H. I., Kim, K., Nguyen, U., Taylor, S. L., Gandara, D. R., Kelly, K., Fiehn, O., & Miyamoto, S. (2015). Metabolomic markers of altered nucleotide metabolism in early stage adenocarcinoma. Cancer Prevention Research (philadelphia, Pa.), 8, 410–418.
Wilson, J. M., Tarr, G. E., & Kelley, W. N. (1983). Human hypoxanthine (guanine) phosphoribosyltransferase: An amino acid substitution in a mutant form of the enzyme isolated from a patient with gout. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 80, 870–873.
**e, H., Hou, Y., Cheng, J., Openkova, M. S., **a, B., Wang, W., Li, A., Yang, K., Li, J., Xu, H., Yang, C., Ma, L., Li, Z., Fan, X., Li, K., & Lou, G. (2017). Metabolic profiling and novel plasma biomarkers for predicting survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncotarget, 8, 32134–32146.
Yu, H., **a, H., Tang, Q., Xu, H., Wei, G., Chen, Y., Dai, X., Gong, Q., & Bi, F. (2017). Acetylcholine acts through M3 muscarinic receptor to activate the EGFR signaling and promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation. Scientific Reports, 7, 40802.
Yue, P., Lopez-Tapia, F., Paladino, D., Li, Y., Chen, C. H., Namanja, A. T., Hilliard, T., Chen, Y., Tius, M. A., & Turkson, J. (2016). Hydroxamic acid and benzoic acid-based STAT3 inhibitors suppress human glioma and breast cancer phenotypes in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Research, 76, 652–663.
Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Li, X., Wu, J., Zhao, L., Li, W., & Liu, J. (2021). Dynamics-based discovery of novel, potent benzoic acid derivatives as orally bioavailable selective estrogen receptor degraders for ERalpha+ breast cancer. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 64, 7575–7595.
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge Melissa Hall, Andrei Smolenkov, and Danyelle Clark for James Graham Brown Cancer Center Biorepository support; Andrea Spencer, Lauren Whelan, Dr. John Hamm, and Dr. Stephen Wyatt for collection of samples at Norton Hospital.
Funding
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute Grant R15CA203605 (Frieboes).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Research involving human and animals participants
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by Internal Review Board protocols at University of Louisville Hospital (IRB 05.0523) and Norton Hospital (IRB 18.0264).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, H.A., Rai, S.N., Yin, X. et al. Lung cancer metabolomic data from tumor core biopsies enables risk-score calculation for progression-free and overall survival. Metabolomics 18, 31 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-022-01891-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-022-01891-x