Abstract
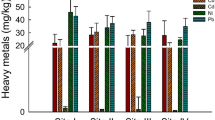
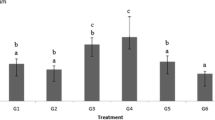
Soil is one of the compartments most affected by the accumulation of pollutants from anthropic sources. The present study allowed the identification of the sensitivity of the Allium cepa test system to evaluate solubilized soils from two points in the area contaminated by heavy metals, as well as a point of reference. They are all located in the municipality of Triunfo, state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The parameters used for evaluation were germination index, mitotic index, chromosomal aberrations (CA), and index of mutagenicity index (IMUT) presented by A. cepa. Significant responses of CA were observed in the two samples of contaminated soil, but IMUT was significant only for soil 3. The toxicity and cytotoxicity indexes did not show significant responses. The results indicate that the A. cepa plant test system was sensitive to investigate the genotoxicity of the soil samples and can be used as an alert in studies on soil contamination. It was partially concordant with the mutagenic responses already detected for the Salmonella/microsome assay in previous studies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABNT - Associação brasileira de normas técnicas. (2004). NBR 10006: Procedimento para obtenção de extrato solubilizado de resíduos sólidos. Rio de Janeiro/Brazil: ABNT.
Baird, C. (2002). Química Ambiental (2nd ed.). Porto Alegre: Bookman.
Bhattacharya, W. B. A. H., Stollenwerk, C. K. G., Mclaughlin, D. M. J., Bundschuh, E. J., & Panaullah, F. G. (2007). Arsenic in the environment: biology and chemistry. Science of the Total Environment, 379, 109–120.
Cabrera, G. L., & Rodriguez, D. M. G. (1999). Genotoxicity of soil from farmland irrigated with wastewater using three plant bioassays. Mutation Research, 426, 211–214.
Chandra, S., Chauhan, L. K. S., Murthy, R. C., Saxena, P. N., Pande, P. N., & Gupta, S. K. (2005). Comparative biomonitoring of leachates from hazardous solid waste of two industries using Allium test. Science of Total Environ, 346, 56–59.
Claxton, L. D., Matthews, P., & Warren, S. (2004). The genotoxicity of ambient outdoor air, a review: Salmonella mutagenicity. Mutation Research, 567, 347–399.
Fatima, R. A., & Ahmad, M. (2006). Genotoxicity of industrial wastewaters obtained from two different pollution sources in northern India: a comparison of three bioassays. Mutation Research, 609, 81–91.
Fenech, M. (2000). The in vitro micronucleus technique. Mutation Research, 455, 81–95.
Fenech, M., Crott, J., Turner, J., & Brown, S. (1999). Necrosis, apoptosis, cytostasis and DNA damage in human lymphocytes measured assay: description of the method and results for hydrogen peroxide. Mutagenesis, 14(6), 605–612.
FEPAM/CNPq, Vargas, V. M. F. (coord.). (2010). Estratégias ecotoxicológicas para caracterizar áreas contaminadas como medida de risco à saúde populacional. Porto Alegre: FEPAM. Relatório do Projeto FEPAM/CNPq 555187/2006-3.
Fernandes, T. C. C., Mazzeo, D. E. C., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2007). Mechanism of micronuclei formation in polyploidizated cells of Allium cepa exposed to trifluralin herbicide. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 88, 252–259.
Fiskejö, G. (1985). The Allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring. Hereditas, 102, 99–112.
Fiskesjö, G. (1988). The Allium test—an alternative in environmental studies: the relative toxicity of metal ions. Mutation Research, 197, 243–260.
Grant, W. F. (1982). Chromosome aberration assays in Allium. A report of the US Environmental Agency Gene-Tox program. Mutation Research, 99, 273–291.
Grant, W. F. (1994). The present status of higher plant bioassays for detection of environmental mutagens. Mutation Research, 310, 175–185.
Health and environmental guidelines for selected timber treatment chemicals. (1997). Wellington. Available at: http://www.mfe.govt.nz/publications/hazardous.
International Agency for Research on Cancer/EPA’s Genetic Activity Profile Database - IARC (2009). Available at: http://monographs.iarc.fr.
Jedynak, L., Kowalska, J., Harasimowicz, J., & Golimowski, J. (2009). Speciation analysis of arsenic in terrestrial plants from arsenic contaminated area. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 945–952.
Leme, D. M., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2008). Chromosome aberration and micronucleus frequencies in Allium cepa cells exposed to petroleum polluted water—a case study. Mutation Research, 650, 80–86.
Leme, D. M., & Marin-Morales, M. A. (2009). Allium cepa test in environmental monitoring: a review on its application. Mutation Research, 682, 71–81.
Majer, B. J. (2002). Effects of heavy metal contamination of soils on micronucleus induction in Tradescantia and on microbial enzyme activities: a comparative investigation. Mutation Research, 515, 111–124.
Math, Xu, Z., Xu, C., McConnell, H., Rabago, E. V., Arreola, G. A., et al. (1995). The improved Allium/Vicia root tip micronucleus assay for clastogenicity of environmental pollutants. Mutation Research, 334, 185–195.
Meyer, D. D., Silva, F. M. R. J., Souza, J. W. M., Pohren, R. S., Rocha, J. A. V. & Vargas, V. M. F (2013). Using the Salmonella/microsome assay to delineate the background of mutagenicity from inorganic compounds in soil samples. In press.
Monarca, S., Feretti, D., Zerbini, I., Alberti, A., Zani, C., Resola, S., et al. (2002). Soil contamination detected using bacterial and plant mutagenicity tests and chemical analyses. Environmental Research, 88, 64–69.
Natarajan, A. T. (2002). Chromosome aberration: past, present and future. Mutation Research, 504, 3–16.
Nielsen, M. H., & Rank, J. (1994). Screening of toxicity and genotoxicity in wastewater by the use of the Allium test. Hereditas, 121, 249–254.
Peralta-Videa, A. J. R., Lopez, A. M. L., Narayan, A. M., Saupe, A. G., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. (2009). The biochemistry of environmental heavy metal uptake by plants: implications for the food chain. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 41, 1665–1677.
Philp, R. B. (2001). Ecosystems and human health: Toxicology and environmental hazards. Boca Raton: CRC Lewis Publishers.
Pohren, R. S., Rocha, J. A. V., Leal, K. A., & Vargas, V. M. F. (2012). Soil mutagenicity as a strategy to evaluate environmental and health risks in a contaminated area. Environment International, 44, 40–52.
Rank, J., & Nielsen, M. H. (1998). Genotoxicity testing of wastewater sludge using the Allium cepa anaphase-telophase chromosome aberration assay. Mutation Research, 418, 113–119.
Silva-Junior F.M.R. (2008). Atividade mutagênica em solos sob influência de rejeitos de carvão. Dissertação de Mestrado em Ecologia. Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre.
Silva-junior, F. M. R., & Vargas, V. M. F. (2008). Avaliação de áreas sob a influência de uma termelétrica a carvão através de ensaio de genotoxicidade. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Ecotoxicology, 2, 1–3.
Silva-Júnior, F. M. R., & Vargas, V. M. F. (2008). Using the Salmonella assay to delineate the dispersion routes of mutagenic compounds from coal wastes in contaminated soil. Mutation Research, Environmental Mutagenesis, 673, 116–123.
Smaka-Kincl, V., Stegnar, P., Lovka, M., & Toman, M. J. (1996). The evaluation of waste, surface and ground water quality using the Allium test procedure. Mutation Research, 368, 171–179.
Tagliari, K. C., Vargas, V. M. F., Zimiani, K. C., & Cecchini, R. C. (2004). Oxidative stress damage in the liver of fish and rats receiving an intraperitoneal injection of hexavalent chromium as evaluated by chemiluminescence. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 17, 149–150.
Vargas, V. M. F. (2003). Mutagenic activity as a parameter to assess ambient air quality for protection of the environmental and human health. Reviews in Mutation Research, 544(2,3), 313–319.
Vargas, V. M. F., Motta, V. E. P., & Henriques, J. A. P. (1993). Mutagenic activity detected by the Ames test in river water under the influence of petrochemical industries. Mutation Research, 319, 31–45.
Vargas, V. M. F., Guidobono, R. R., & Henriques, J. A. P. (1995). Use of two short term test to evaluate genotoxicity of river water treated with different concentration extraction procedure. Mutation Research, 343, 31–52.
Vargas, V. M. F., Horn, R. C., Guidobono, R. R., Mittelstaedt, A. B., & Azevedo, I. M. G. (1998). Mutagenic activity of airborne particulate matter from urban areas of Porto Alegre, Brazil. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 21, 1–7.
Vargas V. M. F., Pohren, R. S., Silva-Junior F. M. R, Moreira, J. W., Vaz, C. R., Rocha J. et al. (2012). Mutagenic potential and profile of PAHs in soils contaminated by wood preservatives: effects on the environment and on human health. In W. C. Flag & H. E. Meneses (Eds.), Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Chemistry, Occurrence and Health Issues. Nova Science Publishers: USA.
Villela, I. V., Lau, A., & Silveira, J. (2003). In A. Alcance (Ed.), Bioensaios para o Monitoramento de Genotoxicidade Ambiental. Porto Alegre: Genética Toxicológica.
Volesky, B. (2001). Detoxification of metal-bearing effluents: biosorption for the next century. Hydrometallurgy, 59, 203–216.
Watanabe, T., & Hirayama, T. (2001). Genotoxicity of soil. Journal of Health Science, 47(5), 433–448.
White, P. A., & Claxton, L. D. (2004). Mutagens in contaminated soil: a review. Mutation Research, 567, 227–345.
Yu, M.-H. (2001). Environmental toxicology: Impacts of environmental toxicants on living systems. Boca Raton: CRC Lewis Publishers.
Zagatto, P. A, Bertoletti, E. (org.) (2008). Ecotoxicologia Aquática – princípios e aplicações. São Carlos, São Paulo, BR: RiMa Editora.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Souza Pohren, R., da Costa, T.C. & Vargas, V.M.F. Investigation of Sensitivity of the Allium cepa Test as an Alert System to Evaluate the Genotoxic Potential of Soil Contaminated by Heavy Metals. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1460 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1460-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1460-1