Abstract
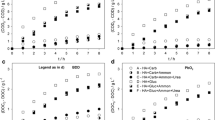
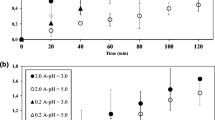
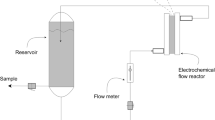
In this work, the electrochemical treatment of an effluent from the pharmaceutical industry with boron-doped diamond electrodes was investigated. The electrolyses were carried out in a discontinuous operation mode under galvanostatic conditions, using a bench-scale plant equipped with a single-compartment electrochemical flow cell. The effect of operating conditions, such as current density (from 25.7 to 179.4 mA cm2) and flow rate (from 104.8 to 564.7 cm3 min−1), at residence times between 0 and 570 min, was studied. Design of experiments was used for optimizing the process. The global contribution of operative parameters and evolution of the residence time in TOC removal was studied, and a time of 77 min was obtained in order to evaluate the highest influence of the operative parameters. For this time, ANOVA test reported significance for four of the five involved variables. The current density was found to have a considerable positive effect on TOC removal, whereas the flow rate was found to have a moderate negative effect on target variable.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed Basha, C., Chithra, E., & Sripriyalakshmi, N. K. (2009). Electro-degradation and biological oxidation of non-biodegradable organic contaminants. Chemical Engineering Journal, 149, 25–34.
Bensalah, N., Quiroz Alfaro, M. A., & Martínez-Huitle, C. A. (2009). Electrochemical treatment of synthetic wastewaters containing Alphazurine A dye. Chemical Engineering Journal, 149, 348–352.
Bhatia, S., Othman, Z., & Ahmad, A. L. (2007). Pretreatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME) using Moringa oleifera seeds as natural coagulant. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 145(1–3), 120–126.
Brillas, E., Calpe, J. C., & Casado, J. (2000). Mineralization of 2,4-D by advanced electrochemical oxidation processes. Water Research, 34, 2253–2262.
Carballa, M., Omil, F., Lema, J. M., Llompart, M., Garcia-Jares, C., Rodriguez, I., Gomez, M., & Ternes, A. (2004). Behavior of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and hormones in a sewage treatment plant. Water Research, 38, 2918–2926.
Chen, G. (2004). Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Separation and Purification Technology, 38(1), 11–41.
Chen, X., Gao, F., & Chen, G. (2005). Comparison of Ti/BDD and Ti/SnO2–Sb2O5 electrodes for pollutant oxidation. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 35(2), 185–191.
Deligiorgis, A., Xekoukoulotakis, N. P., Diamadopoulos, E., & Mantzavinos, D. (2008). Electrochemical oxidation of table olive processing wastewater over boron-doped diamond electrodes: Treatment optimization by factorial design. Water Research, 42, 1229–1237.
Domènech, X., Ribera, M., & Peral, J. (2011). Assessment of pharmaceuticals fate in a model environment. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 218, 413–422.
González, T., Domínguez, J. R., Palo, P., Sánchez-Martín, J., & Cuerda-Correa, E. (2011). Development and optimization of the BDD-electrochemical oxidation of the antibiotic trimethoprim in aqueous solution. Desalination, 280(1–3), 197–202.
Güven, G., Perendeci, A., & Tanyolaç, A. (2009). Chemical treatment of simulated beet sugar factory wastewater. Chemical Engineering Journal, 151, 149–159.
Lazic, Z. R. (2004). Design of experiments in chemical engineering. A practical guide. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
Marselli, B., García-Gomez, J., Michaud, P. A., Rodrigo, M. A., & Comninellis, Ch. (2003). Electrogeneration of hydroxyl radicals on boron-doped diamond electrodes. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2003(150), D79–D83.
Martínez-Huitle, C. A., & Ferro, S. (2006). Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for the wastewater treatment: Direct and indirect processes. Chemical Society Reviews, 35, 1324–1340.
Milani, A. S., Wang, H., Frey, D. D., & Abeyaratne, R. C. (2009). Evaluating three DOE methodologies: Optimization of a composite laminate under fabrication error. Quality Engineering, 21, 96–110.
Montgomery, D. C. (2001). Design and analysis of experiments (5th ed.). New York: Wiley.
Panizza, M., & Cerisola, G. (2005). Application of diamond electrodes to electrochemical processes. Electrochimica Acta, 51, 191–199.
Pérez-Estrada, L. A., Malato, S., Gernjak, W., Agüera, A., Thurman, E. M., Ferrer, I., & Fernández-Alba, A. R. (2005). Photo-Fenton degradation of diclofenac: Identification of main intermediates and degradation pathway. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 8300–8306.
Petrović, M., Hernando, D., Díaz-Cruz, S., & Barceló, D. (2005). Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of pharmaceutical residues in environmental samples: A review. Journal of Chromatography A, 1067, 1–14.
Ragugnetti, M., Adams, M., Guimarães, A., Sponchiado, G., Carvalho-Vasconcellos, E., & Rivas-Oliveira, C. (2011). Ibuprofen genotoxicity in aquatic environment: An experimental model using Oreochromis niloticus. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 218, 361–364.
Rajkumar, D., & Palanivelu, K. (2004). Electrochemical treatment of industrial wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 113(1–3), 123–129.
Scharf, S., Gans, O., Sattelberger, R. (2002). Arzneimittelwirkstoffe inm Zu- und Ablauf von Kläranlagen. Umweltbundesamt Wien. Report UBA-BE-201.
Sharma, V. K., & Mishra, S. K. (2006). Ferrate(VI) oxidation of Ibuprofen: A kinetic study. Environmental Chemical Letters, 3, 182–185.
StatPoint Technologies Inc. (2009). StatGraphics centurion XVI user manual. Virginia, USA.
Tarr, M. (Ed.). (2003). Chemical degradation methods for wastes and pollutants. Environmental and industrial applications. New York: Marcel-Dekker.
Zwiener, C., & Frimmel, F. H. (2000). Oxidative treatment of pharmaceuticals in water. Water Research, 34, 1881–1885.
Acknowledgments
This investigation has been supported by the Comisión Interministerial de Ciencia y Tecnología CTQ 2010-14823/PPQ project as well as the Junta de Extremadura under PRI-07A031 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
DOC 29 kb
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domínguez, J.R., González, T., Palo, P. et al. Electrochemical Degradation of a Real Pharmaceutical Effluent. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 2685–2694 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1059-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1059-3