Abstract
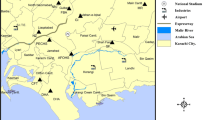
The chemical composition of precipitation in the city of Mersin on the Mediterranean coast of Turkey has been studied. Spatial and temporal variability of rainwater constituents have been determined from samples collected at two central and two suburban stations for the December 2003–May 2005 period. A total of 246 samples covering all precipitation events were analyzed to determine pH, conductivity, as well as major anion (Cl−, \({\text{NO}}_3^ - \), \({\text{SO}}_4^{2 - } \)); major cation (H+, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, \({\text{NH}}_4^ + \)) and formaldehyde (HCHO) concentrations. The pH varied within a range of 4.8–8.5, with only 8 out of 246 samples being acidic (pH < 5.6), and the remaining highly alkaline samples being neutralized by either \({\text{NH}}_4^ + \) in rainwater, or by CaCO3 resulting from wet deposition of atmospheric dust. The volume weighted mean ΣAnion/ΣCation ratio was 0.49. The equivalent concentration of major ionic species followed the order: \({\text{Ca}}^{2 + } > {\text{HCO}}_3^ - > {\text{SO}}_4^{2 - } > {\text{Cl}}^ - > {\text{NH}}_4^ + > {\text{Na}}^ + > {\text{Mg}}^{2 + } > {\text{NO}}_3^ - > {\text{K}}^ + > {\text{H}}^ + \). Formaldehyde concentrations varied in the range of 0.01–17.9 μM, and was found to be dependent on precipitation volume. Relatively higher \({\text{NH}}_4^ + \), \({\text{SO}}_4^{2 - } \), \({\text{NO}}_3^ - \) and HCHO concentrations, mainly of anthropogenic origin, measured near the city center suggest increased pollution from local anthropogenic sources, e.g., residential heating, industrial and/or traffic emissions. In general, the results of this study suggest local precipitation chemistry is more strongly influenced by natural (mineral dust and marine) sources compared to anthropogenic ones.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkoyunlu, B. O., Tayanç, M., & Karaca, M. (2001). Analysis of bulk and sub-event wet deposition in Gebze. Paper presented at the 2nd International Symposium on Air Quality Management at Urban, Regional and Global Scales, pp. 509–516, Istanbul, Turkey, September.
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2005). Study of chemical composition in wet atmospheric precipitation in Eshidiya area, Jordan. Atmospheric Environment, 39, 6175–6183.
Al-Momani, I. F., Ataman, O. Y., Anwari, M. A., Tuncel, S., Köse, C., & Tuncel, G. (1995b). Chemical composition of precipitation near an industrial area at İzmir, Turkey. Atmospheric Environment, 29, 1131–1143.
Al-Momani, I. F., Momani, K. A., & Jaradat, Q. M. (2000). Chemical composition of wet precipitation in Irbid, Jordan. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 35, 47–57.
Al-Momani, I. F., Tuncel, S., Eler, Ü., Örtel, E., Şirin, G., & Tuncel, G. (1995a). Major ion composition of wet and dry deposition in the Eastern Mediterranean Basin. Science of the Total Environment, 164, 75–85.
Avila, A., Alarcon, M., & Queralt, I. (1998). The chemical composition of dust transported in red rains-its contribution to the biogeochemical cycle of a holm oak forest in Catalonia (Spain). Atmospheric Environment, 32(2), 179–191.
Baeyens, W., Dehairs, F., & Dedeurwaerder, H. (1990). Wet and dry deposition fluxes above the North Sea. Atmospheric Environment, 24A(7)), 1693–1703.
Baez, A. P., Belmont, R. D., & Padilla, H. G. (1997). Chemical composition of precipitation at two sampling sites in Mexico: A 7-year study. Atmospheric Environment, 31(6), 915–925.
Benning, L., & Wahner, A. (1998). Measurements of atmospheric formaldehyde (HCHO) and acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) during POPCORN 1994 using 2,4-DNPH coated silica cartridges. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 31, 105–117.
Berlyand, M. E., Volberg, N. Sh., Lavrinenko, R. F., & Rusina, E. N. (1982). Problems of correlation of global and local monitoring of air pollution. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment (Hist. Arc.), 2, 393–402.
Beysens, D., Ohayon, C., Muselli, M., & Clus, O. (2006). Chemical and biological characteristics of dew and rain water in an urban coastal area (Bordeaux, France). Atmospheric Environment, 40, 3710–3723.
Cleveland, W. S., Graedel, T. E., & Kleiner, B. (1977). Urban formaldehyde: observed correlation with source emissions and photochemistry. Atmospheric Environment, 11, 357–360.
Çevre Durum Raporu, ÇDR. (2006). 2005 Yılı Mersin İl Çevre Durum Raporu, T. C. Mersin Valiliği, İl Çevre ve Orman Müdürlüğü, pp. 263.
Deandrade, J. B., Pinheiro, H. L. C., & Andrade, M. V. (1995). The formaldehyde and acetaldehyde content of atmospheric aerosol. Journal of Brazilian Chemical Society, 6, 287–290.
Dikaiakos, J. G., Tsitouris, C. G., Siskos, P. A., Melissos, D. A., & Nastos, P. (1990). Precipitation composition in Athens, Greece. Atmospheric Environment, 24B(1)), 171–176.
Economou, C., & Mihalopoulos, N. (2002). Formaldehyde in the rainwater in the eastern Mediterranean: Occurence, deposition and contribution to organic carbon budget. Atmospheric Environment, 36, 1337–1347.
Galloway, J. N., Likens, G. E., & Hawley, M. E. (1984). Acid precipitation: Natural versus anthropogenic components. Science, 226, 829–831.
GESAMP (Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Pollution). (1985). Atmospheric transport of contaminants into the Mediterranean Region. Reports and Studies, no.26, pp.53.
Granat, L. (1972). On the relation between the chemical composition in atmospheric precipitation. Tellus, 6, 550–560.
Grosjean, D., & Wright, B. (1983). Carbonyls in urban fog, ice fog, cloudwater and rainwater. Atmospheric Environment, 17, 2093–2096.
Gülsoy, G., Tayanç, M., & Ertürk, F. (1999). Chemical analyses of the major ions in the precipitation of İstanbul, Turkey. Environment Pollution, 105, 273–280.
Hontoria, C., Saa, A., Almorox, J., Cuadra, L., Sanchez, A., & Gasco, J. M. (2003). The chemical composition of precipitation in Madrid. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 146, 35–54.
Hu, G. P., Balasubramanian, R., & Wu, C. D. (2003). Chemical characterization of rainwater at Singapore. Chemosphere, 51, 747–755.
Jaradat, Q. M., Momani, K. A., Jiries, A. G., El-Alali, A., Batarseh, M. I., Sabri, T. G., & Al-Momani, I. F. (1999). Chemical composition of urban wet deposition in Amman, Jordan. Water Air Soil Pollution, 112, 55–65.
Kapur, S., Saydam, C., Akça, E., Çavuşgil, V. S., Karaman, C., Atalay, I., & Özsoy, T. (2000). Carbonate pools in soils of the Mediterranean: A case study from Anatolia. In R. Lal, J. M. Kimble, H. Eswaran, & B. A. Stewart (Eds.) Global climate change and pedogenic carbonates (pp. 187–212). Florida: Lewis.
Kaya, G., & Tuncel, G. (1997). Trace element and major ion composition of wet and dry deposition in Ankara, Turkey. Atmospheric Environment, 31, 3985–3998.
Khare, P., Satsangi, G. S., Kumar, N., Kumari, K. M., & Srivastava, S. S. (1997). HCHO, HCOOH and CH3COOH in air and rain water at a rural tropical site in North Central India. Atmospheric Environment, 31, 3867–3875.
Kieber, R. J., Rhines, M. F., Willey, J. D., & Avery, G. B. (1999). Rainwater formaldehyde: concentration, deposition and photochemical formation. Atmospheric Environment, 33, 3659–3667.
Klemm, O., Ziomas, I. C., Balis, D., Suppan, P., Slerm, J., Romero, R., & Vyras, L. G. (1998). A summer air pollution study in Athens, Greece. Atmospheric Environment, 32, 2071–2087.
Kubilay, N., Nickovic, S., Moulin, C., & Dulac, F. (2000). An illustration of the transport and deposition of mineral dust onto the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmospheric Environment, 34(8), 1293–1303.
Kubilay, N., & Saydam, A. C. (1995). Trace elements in the atmospheric particulates over the Eastern Mediterranean; concentrations, sources and temporal variability. Atmospheric Environment, 29, 2289–2300.
Lacaux, J. P., Delmas, R., Kouadio, G., Cros, B., & Andreae, M. O. (1992). Precipitation chemistry in the Moyombe forest of equatorial Africa. Journal of Geophysical Research, 97, 6195–6206.
Liggio, J., & McLaren, R. (2003). An optimized method for the determination of volatile and semi-volatile aldehydes and ketons in ambient particulate matter. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 83, 819–835.
Loye-Pilot, M. D., Martin, J. M., & Morelli, J. (1986). Influence of Saharan dust on the rain acidity and atmospheric input to the Mediterranean. Nature, 321, 427–428.
Milliman, J. D., Jeftic, L., & Setsini, G. (1992). The Mediterranean Sea and climate change. In L. Jeftic et al. (Eds.), Climatic Change and Mediterranean (pp. 1–14). UNEP.
Nash, T. (1953). The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochemical Journal, 55, 416–421.
Örnektekin, S., & Çakmaklı, S. (2003). Chemical composition and acidity of rain at the Gulf of İskenderun, North-East Mediterranean. Water Air and Soil Pollution Focus, 3, 151–166.
Özsoy, E. (1981). On the atmospheric factors affecting the Levantine Sea. European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts, technical report no. 25, pp.29.
Özsoy, T., & Saydam, A. C. (2000). Acidic and alkaline precipitation in the Cilician Basin, north-eastern Mediterranean Sea. Science of the Total Environment, 253, 93–109.
Özsoy, B., & Saydam, A. C. (2001). Iron speciation in precipitation in the north-eastern Mediterranean and its relationship with Sahara dust. Journal of Atmopheric Chemistry, 40(1), 41–76.
Pena, R. M., Garcia, S., Herrero, C., Losada, M., Vazquez, A., & Lucas, T. (2002). Organic acids and aldehydes in rainwater in a northwest region of Spain. Atmospheric Environment, 36, 5277–5288.
Possanzini, M., Palo, V., Petricca, M., Fratarcangeli, R., & Brocco, D. (1996). Measurements of lower carbonyls in Rome ambient air. Atmospheric Environment, 30, 3757–3764.
Riley, J. P., & Skirrow, G. (1975). Chemical oceanography, Vol. 2 (p. 6002nd ed.). London: Academic.
Sakugawa, H., Kaplan, R., & Shepard, L. I. (1993). Measurements of H2O2, aldehydes and organic acids in Los Angeles rainwater: their sources and deposition rates. Atmospheric Environment, 27B, 203–219.
Samara, C., & Tsitouridou, R. (2000). Fine and coarse ionic aerosol components in relation to wet and dry deposition. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 120, 71–88.
Samara, C., Tsitouris, C. G., & Balafoutis, C. (1992). Chemical composition of rain in Thessaloniki, Greece, in relation to meteorological conditions. Atmospheric Environment, 26B(3), 359–367.
Seyfioğlu, R., Odabaşı, M., & Çetin, E. (2005). Formaldehyde deposition in İzmir, Turkey. Paper presented at the 1st International Conference on the Air Pollution and Combustion, Middle East Technical University, pp. 72, Ankara, Turkey, June.
Tuncel, G., & Ungör, S. (1996). Rain water chemistry in Ankara, Turkey. Atmospheric Environment, 30(15), 2721–2727.
Tuncer, B., Bayar, B., Yeşilyurt, C., & Tuncel, G. (2001). Ionic composition of precipitation at the Central Anatolia (Turkey). Atmospheric Environment, 35, 5989–6002.
Wall, S. M., John, W., & Ondo, J. L. (1988). Measurement aerosol size distribution for nitrate and major ionic species. Atmospheric Environment, 22, 1649–1656.
Weller, R., & Schrems, O. (2000). Meridional distribution of hydroperoxides and formaldehyde in the marine boundary layer of the Atlantic (48°N–35°S) measured during Albatros campaign. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105, 14401–14412.
Yetiş, C., Kelling, G., Gökçen, S. L., & Baroz, F. (1995). A revised stratigraphic framework for later Cenozoic sequences in the Northeastern Mediterranean Region. Geol. Rund., 84, 794–812.
Zafiriou, O. C., Alford, J., Herrena, M., Peltzer, E. T., & Gagosian, R. B. (1980). Formaldehyde in remote marine air and rain: flux measurements and estimates. Geophysical Research Letters, 5, 341–344.
Acknowledgement
A substantial part of this study was funded by the Turkish Scientific and Technical Research Council, Tübitak, through the project 102Y144. This work was also supported by Mersin University grant no. BAP-FEFKB2004-3. We thank Dr. Abdullah Öksüz, Dr. Kemal Sangün and the technical personnel of the Central Research Laboratory of Mustafa Kemal University; Mehmet Bayrakçıoğlu, Hidayet Duman, Atilla Çekiç and Seher Mısırlıoğlu, for their help and valuable support concerning the HPLC and ICP-AES analyses. We are grateful to Prof. Emin Özsoy (IMS-METU) for a critical reading of the manuscript and his valuable contribution for providing access to the ECMWF trajectory data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özsoy, T., Türker, P. & Örnektekin, S. Precipitation Chemistry as an Indicator of Urban Air Quality in Mersin, North-Eastern Mediterranean Region. Water Air Soil Pollut 189, 69–83 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9557-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9557-z