Abstract
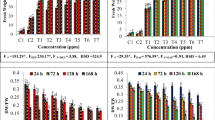
Fluoride, a common phytotoxic air, water and soil pollutant is commonly released to the environment by a number of industrial processes. Agricultural soils high in fluoride are common due to long term accumulation of fluoride from multi-sources and extensive application of phosphate fertilizers. The effect of sodium fluoride (0, 50,100,150 mM) on growth, pigments content, changes in biochemical parameters, along with fluoride and other ions accumulation was investigated in Salicornia brachiata grown in solution cultures under controlled conditions. With fluoride treatment growth as fresh or dry mass accumulation increased marginally. However, higher concentrations decreased the biomass and shoot tip became blunt; margin of the shoot changed its colour to reddish brown and developed necrotic spots. Photosynthetic pigments (chlorophylls and carotenoids) content decreased, while, anthocyanin content increased significantly with fluoride treatment. Peroxidase (POX), superoxide dismutase (SOD), ATPase and acid phosphate activities were negatively regulated. In addition F−, Na+, Mn2+ and Fe2+ ions concentration increased while, K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ contents decreased with fluoride treatment. To our knowledge this is the first report on fluoride tolerance in a marshy halophytes using as high as 150 mM concentration and the results suggest that S. brachiata is a moderately fluoride tolerant annual halophyte and may be useful to vegetate the fluoride contaminated marshy lands.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnesen, A. K. M., & Krogstad, T. (1998). Sorption and desorption of fluoride in soil polluted from the aluminum smelter at Ardal in western Norway. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 103, 357–373.
Arnon, D. I. (1949). Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplast. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiology, 24, 1–15.
Beauchamp, C., & Fridovich, I. (1971). Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay to acrylamide gels. Analytical Biochemistry, 44, 276–287.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Chang, S. C., & Kaufman, P. B. (2000). Effects of staurosporine, okadaic acid and sodium fluoride on protein phosphorylation in gravi-responding oat shoot pulvini. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 38, 315–323.
Cherian, S., & Reddy, M. P. (2000). Salt tolerance in the halophyte Suaeda nudiflora moq: Effect of NaCl on growth, ion accumulation and oxidative enzymes. Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 5, 32–37.
Cherian, S., & Reddy, M. P. (2003). Evaluation of NaCl tolerance in callus cultures of Suaeda nudiflora, moq. Biologia Plantarum, 46, 193–198.
Cronin, S. J., Neall, V. E., Leconintre, J. A., Hedley, M. J., & Loganathan, P. (2003). Environmental hazards of fluoride in volcanic ash: A case study from Ruapehu volcanic, New Zealand. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 121, 271–291.
Elkahoui, S., Hernandez, J. A., Abdelly, C., Ghrir, R., & Limam, F. (2005). Effects of salt on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities of Catharanthus roseus suspension cells. Plant Science, 168, 607–613.
EPA (1978). Diagnosing vegetation injury caused by air pollution. US Environmental Protection Agency, Ohio, EPA-450/3-78-005, 5.1–5.24.
Facanha, A. R., & Meis, L. D. (1995). Inhibition of maize root H+-ATPase by fluoride and fluoroaluminate complexes. Plant Physiology, 108, 241–245.
Flowers, T. J., Troke, P. F., & Yeo, A. R. (1977). The mechanism of salt tolerance in halophytes. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 28, 89–121.
Fornasiero, R. B. (2001). Phytotoxic effects of fluorides. Plant Science, 161, 979–985.
Fornasiero, R. B. (2003). Fluorides effects on Hypericum perforatum plants: First field observations. Plant Science, 165, 507–513.
Gerbeau, P., Amodeo, G., Henzler, T., Santoni, V., Ripoche, P., & Maurel, C. (2002). The water permeability of Arabidopsis plasma membrane is regulated by divalent cations and pH. Plant Journal, 30, 71–81.
Ghosh, P. K., Reddy, M. P., Pandya, J. B., Patolia, J. S., Waghela, S. M., Gandhi, M. R., et al. (2005). Preparation of nutritious salt of plant origin. US patent No: 6, 929, 809 16 August, 2005.
Giannopolitis, C. N., & Reis, S. K. (1977). Superoxide dismutase: Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiology, 59, 309–314.
Glenn, E. P., & O’Leary, J. W. (1984). Relationship between salt accumulation and water content of dicotyledonous halophytes. Plant Cell and Environment, 7, 253–261.
Glenn, E. P., O’Leary, J. W., Watson, M. C., Thompson, T. L., & Kuehl, R. O. (1991). Salicornia bigelovii Torr.: An oilseed halophyte for seawater irrigation. Science, 251, 1065–1067.
Gould, K. S., Markam, K. R., Smith, R. H., & Goris, J. J. (2000). Functional role of anthocyanin in the leaves of Quintina serrata, A. Cunn. Journal of Experimental Botany, 51, 1107–1115.
Hodges, D. M., & Nozzolillo, C. (1996). Anthocyanin and anthocyanoplast content of cruciferous seedlings subjected to mineral nutrient deficiencies. Journal of Plant Physiology, 147, 749–754.
Ikan, R. (1969). Natural products. A laboratory guide. New York: Academic.
Kamaluddin, M., & Zwiazek, J. J. (2003). Fluoride inhibits root water transport and affects leaf expansion and gas exchange in aspen (Populus tremuloides) seedlings. Physiologia Plantarum, 117, 368–375.
Kasamo, K. (1979). Characterization of membrane bound Mg2+ activated ATPase isolated from the lower epidermis of tobacco leaves. Plant and Cell Physiology, 201, 281–292.
Kaur, J., & Duffus, C. (1989). The effect of sodium fluoride on cereal seed germination and seedling growth. Plant Cell and Environment, 12, 155–161.
Kim, C. K., & Weber, D. J. (1980). Isolation and characterization of adenosine triphosphatase from Salicornia pacifica var. utahensis. Plant and Cell Physiology, 21, 755–763.
Klumpp, G., Furlan, C. M., Domingos, M., & Klumpp (2000). Response of stress indicators and growth parameters of Tibouchina pulchra Cogn. exposed to air and soil pollution near industrial complex of Cubatao, Brazil. Science of the total Environment, 246, 79–91.
Klumpp, A., Klumpp, G., Domingos, M., & Silva, M. D. (1996). Fluoride impact on native tree species of the Atlantic Forest near Cubatao, Brazil. Air Soil and Water Pollution, 87, 57–71.
Loganathan, P., Hedley, M. J., Wallace, G. C., & Roberts, A. H. C. (2001). Fluoride accumulation in pasture forages and soils following long-term applications of phosphorus fertilizers. Environmental Pollution, 115, 275–282.
Luttge, U., & Smith, A. C. (1984). Structural, biophysical, and biochemical aspects of the role of leaves in plant adaptation to salinity and water stress. In R. C. Staples & G. H. Toenniessen (Eds.), Salinity tolerance in plants: Strategies for crop improvement (pp. 125–150). New York: Wiley.
Mackowiak, C. L., Grossl, P. R., & Bugbee, B. G. (2003). Biogeochemistry of fluoride in a plant-solution system. Journal of Environmental Quality, 32, 2230–2237.
Maggio, A., Reddy, M. P., & Joly, R. J. (2000). Leaf gas exchange and solute accumulation in the halophyte Salvadora persica grown at moderate salinity. Environment and Experimental Botany, 44, 31–38.
Miller, G. W. (1993). The effect of fluoride on higher plants with special emphasis on early physiological and biochemical disorders. Fluoride, 26, 3–22.
Miller, G. W., Shupe, J. L., & Vedina, O. T. (1999). Accumulation of fluoride in plants exposed to geothermal and industrial water. Fluoride, 32, 74–83.
Miller, G. W., Yu, M. H., & Pushnik, J. C. (1983). Basic metabolic and physiological effects of fluorides on vegetation. In N. C. Leone, H. B. Peterson, & J. L. Shupe (Eds.), Fluorides (pp. 83–104). Salt Lake City, UT: Paragon.
Ming-Ho, Y. (1997). Effects of sodium fluoride on soluble sugars and invertase in germinating mung bean (Vigna radiata) seeds. Environmental Science, 5(2), 121–125.
Murphy, A. J., & Hoover, J. C. (1992). Inhibition of the Na+, K+-ATPase by fluoride. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 16995–17000.
Posthumus, A. C. (1983). Higher plants as indicators and accumulators of gaseous air pollution. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 3, 263–272.
Rakowski, K. J., Zwiazek, J. J., & Sumner, M. J. (1995). Hydrogen fluoride effects on plasma membrane composition, ATPase activity and cell structure in needles of eastern white pine (Pinus strobus) seedlings. Trees, 9, 190–194.
Reddy, M. P., & Iyengar, E. R. R. (1999). Crop responses to salt stress: Seawater applications and prospects. In M. M. Pessarkali (Ed.), Handbook of crop responses to salt stress ((pp. 1041–1066) 2nd ed.). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Scholl, G. (1987). Grundlagen des verfahrens der standardisierten graskultur zur messung der wirkdosis von luftverunreinigungen. VDI-Berichte, 609, 287–299.
Scott, L. C. (1999). Environmental significance of anthocyanins in plant stress responses. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 70, 1–9.
Shannon, L. N., Kay, E., & Lew, J. Y. (1966). Peroxidase isoenzymes from horse reddish roots. 1. Isolation and physiological properties. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 241, 2166–2172.
Short, D. C., & Colmer, T. D. (1999). Salt tolerance in the halophyte Halosarcia pergranulata sub sp. Pergranulata. Annals of Botany, 83, 207–213.
Stevens, D. P., McLaughlin, M. J., & Alston, A. M. (1998). Phytotoxicity of the fluoride ion and its uptake from solution culture by Avena sativa and Lycopersicon esculentum. Plant and Soil, 200, 119–129.
Streb, P., & Feierabend, J. (1996). Oxidative stress responses accompanying photoinactivation of catalase in NaCl treated rye leaves. Botany Acta, 109, 125–132.
Struglics, A., Redlund, K. M., Onstantinov, Y. M., Allen, J. F., & Moller, I. M. (2000). Protein phosphorylation/deopshosphorylation in the inner membrane of potato mitochondria. FEBS Letters, 475, 213–217.
Tomar, S., & Aery, N. C. (2000). Effect of sodium fluoride on seed germination, early seedling growth and biochemical constituents of wheat. Journal of Environmental Biology, 21, 333–336.
Weinstein, L. H. (1977). Fluoride and plant life. Journal of Occupational Medicine, 19, 49–78.
Weinstein, L. H., & Herman, A. R. (1982). Physiological responses of plants to fluorine. In M. H. Unsworth & D. Pormord (Eds.), Effects of gaseous pollutants in agriculture and horticulture (pp. 139–167). London: Butterworths.
Yamaya, T., & Matsumato, H. (1981). Properties of alkaline phosphatase in cucumber roots induced by calcium starvation. Plant and Cell Physiology, 22, 1355–1365.
Zwiazek, J., & Shay, J. M. (1988). Sodium fluoride induced metabolic changes in jack pine seedlings. II. Effect on growth, acid phosphatase, cytokines and pools of soluble proteins, amino acids and organic acids. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 18, 1311–1317.
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge Director Dr. P. K. Ghosh for encouragement and facilities, Dr. J.S. Patolia, Discipline Coordinator for constant support and Dr. K. M. Popat for help in fluoride quantification.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, M.P., Kaur, M. Sodium Fluoride Induced Growth and Metabolic Changes in Salicornia brachiata Roxb. Water Air Soil Pollut 188, 171–179 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9533-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-007-9533-7