Abstract
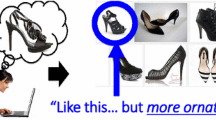
We introduce an approach to image retrieval and auto-tagging that leverages the implicit information about object importance conveyed by the list of keyword tags a person supplies for an image. We propose an unsupervised learning procedure based on Kernel Canonical Correlation Analysis that discovers the relationship between how humans tag images (e.g., the order in which words are mentioned) and the relative importance of objects and their layout in the scene. Using this discovered connection, we show how to boost accuracy for novel queries, such that the search results better preserve the aspects a human may find most worth mentioning. We evaluate our approach on three datasets using either keyword tags or natural language descriptions, and quantify results with both ground truth parameters as well as direct tests with human subjects. Our results show clear improvements over approaches that either rely on image features alone, or that use words and image features but ignore the implied importance cues. Overall, our work provides a novel way to incorporate high-level human perception of scenes into visual representations for enhanced image search.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
von Ahn, L., & Dabbish, L. (2004). Labeling images with a computer game. In CHI.
Akaho, S. (2001). A kernel method for canonical correlation analysis. In International meeting of Psychometric Society.
Baeza-Yates, R., & Ribeiro-Neto, B. (1999). Modern information retrieval. Reading: Addison Wesley.
Barnard, K., Duygulu, P., de Freitas, N., Forsyth, D., Blei, D., & Jordan, M. (2003). Matching words and pictures. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3, 1107–1135.
Bekkerman, R., & Jeon, J. (2007). Multi-modal clustering for multimedia collections. In CVPR.
Berg, T., Berg, A., Edwards, J., & Forsyth, D. (2004). Who’s in the picture. In NIPS.
Blaschko, M. B., & Lampert, C. H. (2008). Correlational spectral clustering. In CVPR.
Bruce, N., & Tsotsos, J. (2005). Saliency based on information maximization. In NIPS.
Datta, R., Joshi, D., Li, J., & Wang, J. (2008). Image retrieval: ideas, influences, and trends of the New Age. ACM Computing Surveys, 40(2), 1–60.
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L. J., Li, K., & Fei-Fei, L. (2009). Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In CVPR.
Duygulu, P., Barnard, K., de Freitas, N., & Forsyth, D. (2002). Object recognition as machine translation: learning a lexicon for a fixed image vocabulary. In ECCV.
Einhauser, W., Spain, M., & Perona, P. (2008). Objects predict fixations better than early saliency. Journal of Vision, 8(14), 1–26.
Elazary, L., & Itti, L. (2008). Interesting objects are visually salient. Journal of Vision, 8(3), 1–15.
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C. K. I., Winn, J., & Zisserman, A. (2007). The PASCAL visual object classes challenge 2007 (VOC2007) Results. http://www.pascal-network.org/challenges/VOC/voc2007/workshop/index.html.
Farhadi, A., Hejrati, M., Sadeghi, A., Young, P., Rashtchian, C., Hockenmaier, J., & Forsyth, D. (2010). Every picture tells a story: generating sentences for images. In ECCV.
Fergus, R., Fei-Fei, L., Perona, P., & Zisserman, A. (2005). Learning object categories from Google’s image search. In ICCV.
Fleiss, J. L. (1971). Measuring nominal scale agreement among many raters. Psychological Bulletin, 76(5), 378–382.
Fyfe, C., & Lai, P. (2001). Kernel and nonlinear canonical correlation analysis. International Journal of Neural Systems, 10, 365–374.
Gupta, A., & Davis, L. (2008). Beyond nouns: exploiting prepositions and comparative adjectives for learning visual classifiers. In ECCV.
Hardoon, D., & Shawe-Taylor, J. (2003). KCCA for different level precision in content-based image retrieval. In Third international workshop on content-based multimedia indexing.
Hardoon, D. R., Szedmak, S., & Shawe-Taylor, J. (2004). Canonical correlation analysis: an overview with application to learning methods. Neural Computation, 16(12).
Hotelling, H. (1936). Relations between two sets of variants. Biometrika, 28, 321–377.
Hwang, S. J., & Grauman, K. (2010a). Accounting for the relative importance of objects in image retrieval. In British machine vision conference.
Hwang, S. J., & Grauman, K. (2010b). Reading between the lines: object localization using implicit cues from image tags. In CVPR.
Jarvelin, K., & Kekalainen, J. (2002). Cumulated gain-based evaluation of IR techniques. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 20(4), 422–446.
Kadir, T., & Brady, M. (2001). Saliency, scale and image description. International Journal of Computer Vision, 45(2), 83–105.
Kulis, B., & Grauman, K. (2009). Kernelized locality-sensitive hashing for scalable image search. In ICCV.
Lavrenko, V., Manmatha, R., & Jeon, J. (2003). A model for learning the semantics of pictures. In NIPS.
Li, L., Wang, G., & Fei-Fei, L. (2007). Optimol: automatic online picture collection via incremental model learning. In CVPR.
Li, L. J., Socher, R., & Fei-Fei, L. (2009). Towards total scene understanding: classification, annotation and segmentation in an automatic framework. In CVPR.
Li, Y., & Shawe-Taylor, J. (2006). Using KCCA for Japanese-English cross-language information retrieval and document classification. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 27(2).
Loeff, N., & Farhadi, A. (2008). Scene discovery by matrix factorization. In ECCV.
Lowe, D. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. IJCV, 60(2).
Makadia, A., Pavlovic, V., & Kumar, S. (2008). A new baseline for image annotation. In ECCV.
Monay, F., & Gatica-Perez, D. (2003). On image auto-annotation with latent space models. In ACM multimedia.
Qi, G. J., Hua, X. S., & Zhang, H. J. (2009). Learning semantic distance from community-tagged media collection. In ACM multimedia.
Quack, T., Leibe, B., & Gool, L. V. (2008). World-scale mining of objects and events from community photo collections. In CIVR.
Quattoni, A., Collins, M., & Darrell, T. (2007). Learning visual representations using images with captions. In CVPR.
Russell, B., Torralba, A., Murphy, K., & Freeman, W. (2005). Labelme: a database and web-based tool for image annotation (Tech. rep). MIT.
Schroff, F., Criminisi, A., & Zisserman, A. (2007). Harvesting image databases from the web. In ICCV.
Smeulders, A., Worring, M., Santini, S., Gupta, A., & Jain, R. (2000). Content-based image retrieval at the end of the early years. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 22(12), 1349–1380.
Spain, M., & Perona, P. (2008). Some objects are more equal than others: measuring and predicting importance. In ECCV.
Tatler, B., Baddeley, R., & Gilchrist, I. (2005). Visual correlates of fixation selection: effects of scale and time. Vision Research, 45, 643–659.
Torralba, A. (2003). Contextual priming for object detection. International Journal of Computer Vision, 53(2), 169–191.
Vijayanarasimhan, S., & Grauman, K. (2008). Keywords to visual categories: multiple-instance learning for weakly supervised object categorization. In CVPR.
Wolfe, J., & Horowitz, T. (2004). What attributes guide the deployment of visual attention and how do they do it? Neuroscience, 5, 495–501.
Yakhnenko, O., & Honavar, V. (2009). Multiple label prediction for image annotation with multiple kernel correlation models. In Workshop on visual context learning, in conjunction with CVPR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, S.J., Grauman, K. Learning the Relative Importance of Objects from Tagged Images for Retrieval and Cross-Modal Search. Int J Comput Vis 100, 134–153 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-011-0494-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-011-0494-3