Abstract
Understanding evaporation from porous media in the presence of soluble salts plays a key role in describing many environmental processes. Several studies done in this field led to a wide acceptance that the prediction of soil salinization driven by evaporation from the unsaturated zone and mainly encountered in arid and semiarid regions is a challenging task because of the temporal and spatial variabilities of soil rocks combined with different interactions between the porous medium and the atmosphere. In this work, we present a reactive transport model developed with the aim of describing the processes of evaporation, salt accumulation and precipitation. We took the model presented in our previous paper (Jambhekar et al. in Transp Porous Media 114:341–369, 2016) as the basis and developed it with the required geochemical model to account for evaporative salt co-precipitation. The salts considered in this work are halite (NaCl) and gypsum (CaSO\(_{4}\cdot 2\mathrm{H}_{2}\)O). We focus particularly on the influence of spatial heterogeneities in the porous medium on the dynamics of the physical processes. In the numerical simulations performed in this work, we distinguished different heterogeneity configurations. The results show that the drying from heterogeneous porous media initially affects the coarser pores, where the salt crystals first appear.







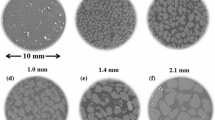
[taken from Nachshon et al. (2011b)]














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelo, C.A.J., Posma, D.: Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd edn. Balkema, Leiden (2005)
Balan, B., Mohaghegh, S., Ameri, S.: State-of-the-art in permeability determination from well log data: part 1—a comparative study, model development. In: SPE, p. 30978 (1995)
Battistelli, A., Calore, C., Pruess, K.: Analysis of salt effects on the depletion of fractured reservoir blocks, pp. 1613–1618. In World Geothermal Congress, Florence, Proceedings (1995)
Batzle, M.L., Wang, Z.: Seismic properties of pore fluids. Geophysics 57, 1396–1408 (1992)
Bechtold, M., Haber-Pohlmeier, S., Vanderborght, J., Pohlmeier, A., Ferré, T.P.A., Vereecken, H.: Near-surface solute redistribution during evaporation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 38, L17404 (2011). doi:10.1029/2011GL048147
Bernabé, Y., Mok, U., Evans, B.: Permeability-porosity relationships in rocks subjected to various evolution processes. Pure Appl. Geophys. 160(5), 937–960 (2003)
Bonn, N.S., Desarnaud, J., Bertrand, F., Chateau, X., Bonn, D.: Damage in porous media due to salt crystallization. Phys. Rev. E 81, 066110 (2010)
Bouchelaghem, F.: A numerical and analytical study on calcite dissolution and gypsum precipitation. Appl. Math. Model. 34, 467–480 (2010)
Bouhlila, R.: Ecoulement, transport et réactions géochimiques couplés dans les milieux poreux. Thèse de doctorat détat en sciences de lUniversité Tunis II (ENIT), Cas des sels et des saumures (1999)
Brooks, R.H., Corey, A.T.: Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media. Hydrology Papers. Colorado State University, Fort Collins (1964)
Class, H., Helmig, R., Bastian, P.: Numerical simulation of non-isothermal multiphase multicomponent processes in porous media: 1. An efficient solution technique. Adv. Water Resour. 25(5), 533–550 (2002)
Colon, F., et al.: Experimental investigation of the effect of dissolution on sandstone permeability, porosity and reactive surface area. Geomech. Cosmochim. Acta 68, 805–817 (2004)
Derluyn, H., Moonen, P., Carmeliet, J.: Deformation and damage due to drying-induced salt crystallization in porous limestone. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 63, 242–255 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.jmps.2013.09.005
Desarnaud, J., Derluyn, H., Molari, L., de Miranda, S., Cnudde, V., Shahidzadeh, N.: Drying of salt contaminated porous media: effect of primary and secondary nucleation. J. Appl. Phys. 118, 114901 (2015). doi:10.1063/1.4930292
Eloukabi, H., Sghaier, N.: Ben Nasrallah, S., Prat, M.: Experimental study of the effect of sodium chloride on drying of porous media: the crusty-patchy efflorescence transition. Int. J. Heat Transf. 56, 80–93 (2013)
Espinosa-Marzal, R.M., Scherer, G.W.: Impact of in-pore salt crystallization on transport properties. Environ. Earth Sci. 69, 2657–2669 (2013)
Flemisch, B., Darcis, M., Erbertseder, K., Faigle, B., Lauser, A., Mosthaf, K., Müthing, S., Nuske, P., Tatomir, A., Wolff, M., Helmig, R.: DuMuX: DUNE for multi-phase, component, scale, physics., flow and transport in porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 34(9), 1102–1112 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.advwatres.2011.03.007
Fujimaki, H., Shimano, T., Inoue, M., Nakane, K.: Effect of a salt crust on evaporation from a bare saline soil. Vadose Zone J. 5(4), 1246–1256 (2006)
Hachicha, M.: Les sols sals et leur mise en valeur en Tunisie. Revue Scheresse 18(1), 45–50 (2007)
Helmig, R.: Multiphase Flow and Transport Processes in the Subsurfaces: A Contribution to the Modeling of Hydrosystems. Springer, Berlin (1997)
Helmig, R., Huber, R.: Comparison of Galerkin-type discretization techniques for two-phase flow in heterogeneous porous media. Adv. Water Resour. 21, 697–711 (1998)
Helmig, R., Weiss, A., Wohlmuth, B.: Dynamic effects in heterogeneous porous media. Comput. Geosci. 11, 261–274 (2007)
Hidri, F.: Evaporation from a porous medium containing a dissolved salt. Influence of heterogeneities at Darcy’s scale on the distribution of ions at the evaporative surface. Ph.D. Thesis (2013)
Jambhekar, V.A.: Numerical modeling and analysis of evaporative salinization in a coupled free-flow porous-media system. Ph.D. Thesis (2016)
Jambhekar, V.A., Helmig, R., Schröder, N., Shokri, N.: Free-flow-porous-media coupling for evaporation-driven transport and precipitation of salt. Transp. Porous Media (2015). doi:10.1007/s11242-015-0516-7
Jambhekar, V.A., Mejri, E., Schröder, N., Helmig, R., Shokri, N.: Kinetic approach to model reactive transport and mixed salt precipitation in a coupled free-flow-porous-media system. Transp. Porous Media 114, 341–369 (2016)
Koniorczyk, M.: Salt precipitation and crystallization in non-isothermal, partially saturated porous materials considering ions interaction model. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55, 665–679 (2012)
Lai, K.H., Chen, J.S., Liu, C.W., Yang, S.Y.: Effect of permeability-porosity functions on simulated morphological evolution of a chemical dissolution front. Hydrol. Process. (2012). doi:10.1002/hyp.9492
Laabidi, E., Bouhlila, R.: Impact of mixing induced calcite precipitation on the flow and transport. Carbonates Evaporites (2016). doi:10.1007/s13146-016-0305-6
Le, D., Hoang, H., Mahadevan, J.: Impact of capillary-driven liquid films on salt crystallization. Transp. Porous Media 80, 229–252 (2009)
Lehmann, P., Assouline, S., Or, D.: Characteristic lenghts affecting evaporative drying of porous media. Phys. Rev. E 77, 056309 (2008)
Lehmann, P., Or, D.: Evaporation and capillary coupling across vertical textural contrasts in porous media. Phys. Rev. E 80, 046318 (2009)
Madé, B., Clément, A., Britz, B.: Modelling mineral/solution interactions: the thermodynamic and kinetic code KINDISP. Comput. Geosci. 20(9), 1347–1363 (1994)
Mosthaf, K., Baber, K., Flemisch, B., Helmig, R., Leijnse, A., Rybak, I., Wohlmuth, B.: A coupling concept for two-phase compositional porous-medium and single-phase compositional free flow. Water Resour. Res. 47, W10522 (2011). doi:10.1029/2011WR010685
Nachshon, U., Shahraeeni, E., Or, D., Dragila, M., Weisbrod, N.: Infrared thermography of evaporative fluxes and dynamics of salt deposition on heterogeneous porous surfaces. Water Resour. Res. 47, W12519 (2011a). doi:10.1029/2011WR010776
Nachshon, U., Weisbrod, N., Dragila, M.I., Grader, A.: Combined evaporation and salt precipitation in homogeneous and heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour. Res. 47, W03513 (2011b). doi:10.1029/2010WR009677
Nassar, I.N., Horton, R.: Salinity and compaction effects on soil water evaporation and water and solute distribution. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 63, 752 (1999)
Nicolai, A., Grunewald, J., Zhang, J.S.: Salztransport und Phasenumwandlung-Modellierung und numerische Lsung im Simulationsprogramm Delphin 5. Bauphysik 29(3), 231–239 (2007). doi:10.1002/bapi.200710032
Pape, H., Clauser, C., Iffland, J.: Permeability prediction based on fractal pore-space geometry. Geophysics 64, 1447–1460 (1997)
Peyson, Y., Bazin, B., Magnier, C., Kohler, E., Youssef, S.: Permeability alteration due to salt precipitation driven by drying in the context of \(CO_2\) injection. Energy Procedia 4, 4387–4394 (2011)
Pina Jasson, E., Donado, L.D., Bustos, M.C.: Multi-component reactive transport modelling in a 1D column. In: XIX International Conference on Water Resources CMWR (2012)
Sghaier, N., Prat, M.: Effect of efflorescence formation on drying kinetics of porous media. Transp. Porous Media 80, 441–454 (2009). doi:10.1007/S11242-009-9373-6
Shimojima, F., Yoshioka, R., Tamagawa, I.: Salinization owing to evaporation from bare soil surfaces and its influences on the evaporation. J. Hydrol. 176, 109–136 (1996)
Shokri, N., Lehman, P., Or, D.: Liquid-phase continuity and solute concentration dynamics during evaporation from porous media: pore scale processes near vaporization surface. Phys. Rev. E 81(4, Part2), 046308 (2010)
Tsypkin, G., Woods, A.W.: Precipitate formation in a porous rock through evaporation of saline water. J. Fluid Mech. 537, 35–53 (2005)
Van Dam, J.C., Feddes, R.A.: Numerical simulations of infiltration, evaporation and shallow groundwater levels with the Richards equation. J. Hydrol. 233, 72–85 (2000)
Veran-Tissoires, S., Marcoux, M., Prat, M.: Salt crystallization at the surface of a heterogeneous porous medium. Letters 98, 34005 (2012)
Veran-Tissoires, S., Prat, M.: Evaporation of a sodium chloride solution from a saturated porous medium with efflorescence formation. J. Fluid Mech. 749, 701–749 (2014)
Xu, T., Ontoy, Y., Molling, P., Spycher, N., Parini, M., Pruess, K.: Reactive transport modeling of injection well scaling and acidizing at Tiwi. Philippines. Geothermics 33(4), 447–491 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.geothermics
Zeidouni, M., Darvish, M.P., Keith, D.: Analytical solution to evaluate salt precipitation during \(CO_2\) injection in saline aquifers. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 3(5), 600–611 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) for funding the research work subject of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mejri, E., Bouhlila, R. & Helmig, R. Heterogeneity Effects on Evaporation-Induced Halite and Gypsum Co-precipitation in Porous Media. Transp Porous Med 118, 39–64 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-017-0846-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-017-0846-8