Abstract
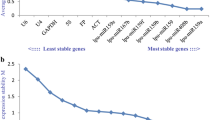
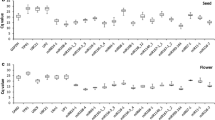
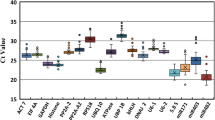
Quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR is a powerful tool for precise gene expression quantification. Using suitable reference genes is crucial for a proper normalization and interpretation of results, particularly in dynamic transcriptional networks with the involvement of several miRNAs and their targets, such as somatic embryogenesis (SE). Here, we aimed to identify genes to be used as internal controls for quantitative detection of miRNAs and mRNAs during the SE process in Solanum betaceum. The expression of EF1α, GAPDH, ACT, UBQ10, Fe-SOD, U6, snoR14, miR159a, miR162 and miR166a was tested in nine time-points of the SE process, particularly during induction, embryo development and conversion. Analyses of transcriptional stability were performed using RefFinder tool that integrates geNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper and Delta-Ct algorithms. Among these candidates, Fe-SOD, ACT and U6 emerged consistently as the most suitable to normalize gene expression, whereas miR166a was the most appropriate for normalization in calli samples. In order to validate these results, expression of miR396 and GRF1 was quantified and normalized with the most and the least stable genes and also with the most stable miRNA. Fe-SOD + ACT revealed to be the optimal combination for precise quantification of miRNA-mediated regulation of gene expression during SE in tamarillo.
Key message
Fe-SOD + ACT is the most suitable combination of reference genes for RT-qPCR normalization and accurate quantification of miRNAs and their targets during tamarillo somatic embryogenesis induction, embryo development and conversion stages.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Andersen C, Jensen J, Orntoft T (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Can Res 64:5245–5250
Canhoto JM, Lopes ML, Cruz GS (2005) Protocol of somatic embryogenesis in tamarillo (Cyphomandra betacea (Cav.) Sendtn.). In: Jain SM, Gupta PK (eds) Protocol for somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 379–389
Corredoira E, Merkle S, Martínez M, Toribio M, Canhoto J, Correia S, Ballester A, Vieitez A (2019) Non-zygotic embryogenesis in hardwood species. Crit Rev Plant Sci 38:29–97
Correia SI, Canhoto JM (2012) Biotechnology of tamarillo (Cyphomandra betacea): from in vitro cloning to genetic transformation. Sci Hortic 148:161–168
Correia S, Canhoto JM (2018) Somatic embryogenesis of tamarillo (Solanum betaceum Cav.). In: Jain S, Gupta P (eds) Step wise protocols for somatic embryogenesis of important woody plants. Springer, Cham, pp 171–179
Correia S, Lopes M, Canhoto J (2009) Somatic embryogenesis in tamarillo (Cyphomandra betacea): recent advances. Acta Hortic 839:157–164
Correia S, Cunha A, Salgueiro L, Canhoto J (2012) Somatic embryogenesis in tamarillo (Cyphomandra betacea): approaches to increase efficiency of embryo formation and plant development. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 109:143–152
Correia S, Alhinho A, Casimiro B, Miguel C, Oliveira M, Veríssimo P, Canhoto J (2019) NEP-TC a rRNA methyltransferase involved on somatic embryogenesis of tamarillo (Solanum betaceum Cav.). Front Plant Sci 10:438. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00438
Derveaux S, Vandesompele J, Hellemans J (2010) How to do successful gene expression analysis using real-time PCR. Methods 50:227–230
Freitas N, Barreto H, Fernandes-Brum C, Moreira R, Chalfun-Junior A, Paiva L (2017) Validation of reference genes for qPCR analysis of Coffea arabica L. somatic embryogenesis-related tissues. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 128:663–678
Garcia-Gonzales R, Quiroz K, Carrasco B, Caligari P (2010) Plant tissue culture: current status, opportunities and challenges. Cienc Investig Agrar 37:5–30
Gonçalves S, Cairney J, Maroco J, Oliveira M, Miguel C (2005) Evaluation of control transcripts in real-time RT-PCR expression analysis during maritime pine embryogenesis. Planta 222:556–563
Gutierrez L, Mauriat M, Guénin S, Pelloux J, Lefebvre J, Louvet R, Rusterucci C, Moritz T, Guerineau F, Bellini C, van Wuytswinkel O (2008a) The lack of a systematic validation of reference genes: a serious pitfall undervalued in reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 6:609–618
Gutierrez L, Mauriat M, Pelloux J, Bellini C, Wuytswinkel O (2008b) Towards a systematic validation of references in real-time RT-PCR. Plant Cell 20:1734–1735
Hellemans J, Mortier G, Paepe A, Speleman F, Vandesompele J (2007) qBase relative quantification framework and software for management and automated analysis of real-time quantitative PCR data. Genome Biol 8:R19. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2007-8-2-r19
Horstman A, Bemer M, Boutilier K (2017) A transcriptional view on somatic embryogenesis. Regeneration 4:201–216
Huggett J, Dheda K, Bustin S, Zumla A (2005) Real-time RT-PCR normalisation; strategies and considerations. Genes Immun 6:279–284
Ikeuchi M, Ogawa Y, Iwase A, Sugimoto K (2016) Plant regeneration: cellular origins and molecular mechanisms. Development 143:1442–1451
Iliev I, Gajdošová A, Libiaková G, Jain S (2010) Plant micropropagation. In: Davey M, Anthony P (eds) Plant cell culture: essential methods. Wiley, London, pp 1–24
Joseph J, Poolakkalody N, Shah J (2018) Plant reference genes for development and stress response studies. J Biosci 43:173–187
Kou S, Wu X, Liu Z, Liu Y, Xu Q, Guo W (2012) Selection and validation of suitable reference genes for miRNA expression normalization by quantitative RT-PCR in citrus somatic embryogenic and adult tissues. Plant Cell Rep 31:2151–2163
Li T, Chen J, Qiu S, Zhang Y, Wang P, Yang L, Lu Y, Shi J (2012) Deep sequencing and microarray hybridization identify conserved and species-specific microRNAs during somatic embryogenesis in hybrid yellow poplar. PLoS ONE 7:e43451. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043451
Lin Y, Lai Z (2010) Reference gene selection for qPCR analysis during somatic embryogenesis in longan tree. Plant Sci 178:359–365
Livak K, Schmittgen T (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lopes M, Ferreira M, Carloto J, Cruz G, Canhoto J (2000) Somatic embryogenesis induction in tamarillo (Cyphomandra betacea). In: Jain S, Gupta P, Newton R (eds) Somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 433–455
Loyola-Vargas V, Ochoa-Alejo N (2016) Somatic embryogenesis. an overview. In: Loyola-Vargas V, Ochoa-Alejo N (eds) Somatic embryogenesis: fundamental aspects and applications. Springer, Cham, pp 1–10
Luo M, Gao Z, Li H, Li Q, Zhang C, Xu W, Song S, Ma C, Wang S (2018) Selection of reference genes for miRNA qRT-PCR under abiotic stress in grapevine. Sci Rep 8:4444. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22743-6
Méndez-Hernández H, Ledezma-Rodríguez M, Avilez-Montalvo R, Juárez-Gómez Y, Skeete A, Avilez-Montalvo J, De-la-Peña C, Loyola-Vargas V (2019) Signaling overview of plant somatic embryogenesis. Front Plant Sci 10:77. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00077
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nicot N, Hausman J, Hoffmann L, Evers D (2005) Housekee** gene selection for real-time RT-PCR normalization in potato during biotic and abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 56:2907–2914
Pfaffl M, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians T (2004) Determination of stable housekee** genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol Lett 26:509–515
Prohens J, Nuez F (2001) The tamarillo (Cyphomandra betacea): a review of a promising small fruit crop. Small Fruits Review 1:43–68
Siddiqui Z, Abbasa Z, Ansari M, Khan M (2018) The role of miRNA in somatic embryogenesis. Genomics 111:1026–1033
Silver N, Best S, Jiang J, Thein S (2006) Selection of housekee** genes for gene expression studies in human reticulocytes using real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 7:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-7-33
Spiegelaere W, Dern-Wieloch J, Weigel R, Schumacher V, Schorle H, Nettersheim D, Bergmann M, Brehm R, Kliesch S, Vandekerckhove L, Fink C (2015) Reference gene validation for RTqPCR, a note on different available software packages. PLoS ONE 10:e0122515. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122515
Szczygieł-Sommer A, Gaj MD (2019) The miR396-GRF regulatory module controls the embryogenic response in Arabidopsis via an auxin-related pathway. Int J Mol Sci 20:5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205221
Tu L, Zhang X, Liu D, ** S, Cao J, Zhu L, Deng F, Tan J, Zhang C (2007) Suitable internal control genes for qRT-PCR normalization in cotton fiber development and somatic embryogenesis. Chin Sci Bull 52:2379–2385
Vandesompele J, de Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, van Roy N, de Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Vanguilder H, Vrana K, Freeman W (2008) Twenty-five years of quantitative PCR for gene expression analysis. Biotechniques 44:619–626
Vries SC, Weijers D (2017) Plant embryogenesis. Curr Biol 27:853–909
Wójcik A, Wójcikowska B, Gaj M (2020) Current perspectives on the auxin-mediated genetic network that controls the induction of somatic embryogenesis in plants. Int J Mol Sci 21:1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041333
**e F, **ao P, Chen D, Xu L, Zhang B (2012) miRDeepFinder: a miRNA analysis tool for deep sequencing of plant small RNAs. Plant Mol Biol 80:75–84
Yang X, Wang L, Yuan D, Lindsey K, Zhang X (2013) Small RNA and degradome sequencing reveal complex miRNA regulation during cotton somatic embryogenesis. J Exp Bot 64:1521–1536
Zhang J, Gai M, Xue B, Jia N, Wang C, Wang J, Sun H (2017a) The use of miRNAs as reference genes for miRNA expression normalization during Lilium somatic embryogenesis by real-time reverse transcription PCR analysis. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 129:105–118
Zhang J, Xue B, Gai M, Song S, Jia N, Sun H (2017b) Small RNA and transcriptome sequencing reveal a potential miRNA-mediated interaction network that functions during somatic embryogenesis in Lilium pumilum DC. Fisch. Front Plant Sci 8:566. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00566
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (Portugal) [doctoral research grant number SFRH/BD/136925/2018 awarded to Daniela Cordeiro; P2020|COMPETE grant number PTDC/BAA-AGR/32265/2017, BP4BP – Tamarillo breeding: better plants for better products]; and the Centre for Functional Ecology of the University of Coimbra.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing—original draft. MR: Investigation, Writing—Reviewing and Editing. FB: Resources, Writing- Reviewing and Editing. JC: Supervision, Writing—Reviewing and Editing, Funding acquisition. SC: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—Reviewing and Editing, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Goetz Hensel.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cordeiro, D., Rito, M., Borges, F. et al. Selection and validation of reference genes for qPCR analysis of miRNAs and their targets during somatic embryogenesis in tamarillo (Solanum betaceum Cav.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 143, 109–120 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01901-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01901-7