Abstract
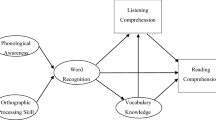
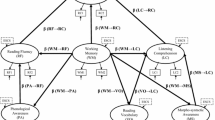
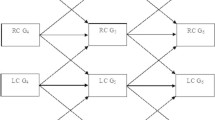
In this paper, first language (L1) and second language (L2) oral language and word reading skills were used as predictors to devise a model of reading comprehension in young Cantonese-speaking English language learners (ELLs) in the United States. L1 and L2 language and literacy measures were collected from a total of 101 Cantonese-speaking ELLs during the early spring of second grade. Results show that English vocabulary and English word decoding, as measured with real and nonsense words, played significant roles in English reading comprehension. In particular, results highlight the crucial role of English vocabulary in the development of L2 English literacy skills. English listening comprehension did not predict English reading comprehension. Theoretical and practical implications are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedi, J., Lord, C., Hostetter, C., & Baker, E. (2000). Impact of accommodation strategies on English language learners’ test performance. Educational Measurements: Issues and Practice, 19(3), 16–26.
Agresti, A. (2007). An introduction to categorical data analysis (2nd ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Anglin, J. (1993). Vocabulary development: A morphological analysis. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 58(10).
August, D., Carlo, M., Dressler, C., & Snow, C. (2005). The critical role of vocabulary development for English language learners. Learning Disabilities Research and Practice, 20, 50–57.
Beck, I. L., McKeown, M. G., & Kucan, L. (2002). Bringing words to life: Robust vocabulary instruction. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Beck, I. L., Perfetti, C. A., & McKeown, M. G. (1982). Effects of long-term vocabulary instruction on lexical access and reading comprehension. Journal of Educational Psychology, 74, 506–521.
Bialystok, E., McBride-Chang, C., & Luk, G. (2005). Bilingualism, language proficiency, and learning to read in two writing systems. Journal of Educational Psychology, 97(4), 580–590.
Biemiller, A. (2003). Oral comprehension sets the ceiling on reading comprehension. American Educator, 27(1), 23–44.
Biemiller, A., & Boote, C. (2006). An effective method for building meaning vocabulary in primary grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98(1), 44–57.
Branum-Martin, L., Mehta, P. D., Fletcher, J. M., Carlson, C. D., Ortiz, A., Carlo, M., et al. (2006). Bilingual phonological awareness: Multilevel construct validation among Spanish-speaking kindergarteners in transitional bilingual education classrooms. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98, 170–181.
Burke, S. M., Pflaum, S. W., & Knafle, J. D. (1982). The influence of Black English on diagnosis of reading in learning disabled and normal readers. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 15, 19–22.
Carlisle, J. F., Beeman, M., Davis, L. H., & Spharim, G. (1999). Relationships of metalinguistic capabilities and reading achievement for children who are becoming bilingual. Applied Psycholinguistics, 20, 459–478.
Carver, R. P. (1994). Percentage of unknown vocabulary words in text as a function of the relative difficulty of the text: Implications for instruction. Journal of Reading Behavior, 26(4), 413–437.
Catts, H. W., Hogan, T. P., & Adolf, S. M. (2005). Developmental changes in reading and reading disabilities. In H. W. Catts & A. G. Kamhi (Eds.), The connections between language and reading disabilities (pp. 25–40). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Chaney, C. (1992). Language development, metalinguistic skills, and print awareness in 3-year-old children. Applied Psycholinguistics, 13, 485–514.
Chen, X., Anderson, R. C., Li, W., Hao, M., Wu, X., & Shu, H. (2004). Phonological awareness of bilingual and monolingual Chinese children. Journal of Educational Psychology, 96(1), 142–151.
Chen, X., Hao, M., Geva, E., Zhu, J., & Shu, H. (2009). The role of compound awareness in Chinese children’s vocabulary acquisition and character reading. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 22, 615–631.
Cheng, C. M. (1992). Lexical access in Chinese: Evidence from automatic activation of phonological information. In H. C. Chen & O. J. L. Tzeng (Eds.), Language processing in Chinese. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Cheung, H., Chan, M., & Chong, K. (2007). Use of orthographic knowledge in reading by Chinese-English bi-scriptal children. Language Learning, 57(3), 469–505.
Chien, C., Kao, L., & Wei, L. (2008). The role of phonological awareness development in young Chinese EFL learners. Language Awareness, 17(4), 271–288.
Chow, B. W., McBride-Chang, C., & Burgess, S. (2005). Phonological processing skills and early reading abilities in Hong Kong Chinese kindergarteners learning to read English as a second language. Journal of Educational Psychology, 97(1), 81–87.
Cobo-Lewis, A. B., Pearson, B. Z., Eilers, R. E., & Umbel, V. C. (2002). Effects of bilingualism and bilingual education on oral and written Spanish skills: A multifactor study of standardized test outcomes. In D. K. Oller & R. E. Eilers (Eds.), Language and literacy in bilingual children (pp. 98–117). Clevedon: Multilingual Matters Ltd.
Cummins, J. (1984). Bilingualism in special education. San Diego, CA: College Hill Press.
Cummins, J. (1991). Interdependence of first and second language proficiency in bilingual children. In E. Bialystok (Ed.), Language processing in bilingual children (pp. 70–89). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Dunn, L. M., & Dunn, L. M. (1997). Peabody picture vocabulary test (3rd ed.). Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Service.
Durgunoglu, A. Y. (2002). Cross-linguistic transfer in literacy development and implications for language learners. Annals of Dyslexia, 52, 189–204.
Durgunoglu, A. Y., Nagy, W. E., & Hancin-Bhatt, B. J. (1993). Crosslanguage transfer of phonological awareness. Journal of Educational Psychology, 85, 453–465.
Freebody, P., & Anderson, R. C. (1983). Effects of vocabulary difficulty, text cohesion, and schema availability on reading comprehension. Reading Research Quarterly, 18, 277–323.
García, G. E. (1991). Factors influencing the English reading test performance of Spanish-speaking Hispanic children. Reading Research Quarterly, 26(4), 371–392.
Geva, E., & Siegel, L. S. (2000). Orthographic and cognitive factors in the concurrent development of basic reading skills in two languages. Reading & Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 12, 1–30.
Gottardo, A., Chiappe, P., Yan, B., Siegel, L., & Gu, Y. (2006). Relationships between first and second language phonological processing skills and reading in Chinese-English speakers living in English-Speaking contexts. Educational Psychology, 26(3), 367–393.
Gottardo, A., & Mueller, J. (2009). Are first- and second-language factors related in predicting second-language reading comprehension? A Study of Spanish-speaking children acquiring English as a second language from first to second grade. Journal of Educational Psychology, 101(2), 330–344.
Gottardo, A., Yan, B., Siegel, L. S., & Wade-Woolley, L. (2001). Factors related to English reading performance in children with Chinese as a first language: More evidence of cross-language transfer of phonological processing. Journal of Educational Psychology, 93(3), 530–542.
Gough, P. B., & Tunmer, W. E. (1986). Decoding, reading, and reading disability. RASE. Remedial & Special Education, 7, 6–10.
Hakuta, K. (1986). The mirror of language. New York: Basic Books.
Hart, B., & Risley, T. (1995). Meaningful differences in the everyday experiences of young American children. Baltimore, MD: Brookes.
Hemphill, L., & Tivnan, T. (2008). The importance of early vocabulary for literacy achievement in high-poverty schools. Journal of Education for Students Placed at Risk, 13, 426–451.
Ho, C. S., & Bryant, P. (1997). Development of phonological awareness of Chinese children in Hong Kong. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 26(1), 109–126.
Hoover, W. A., & Gough, P. B. (1990). The simple view of reading. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 2, 127–160.
Juel, C. (1991). Beginning reading. In M. L. Kamil, P. B. Mosenthal, P. D. Pearson, & R. Barr (Eds.), Handbook of reading research (Vol. 2, pp. 759–788). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Juel, C., Griffith, P. L., & Gough, P. B. (1986). Acquisition of literacy: A longitudinal study of children in first and second grade. Journal of Educational Psychology, 78(4), 243–255.
Keenan, J. M., Betjemann, R. S., & Olson, R. K. (2008). Reading comprehension tests vary in the skills they assess: Differential dependence on decoding and oral comprehension. Scientific Studies of Reading, 12(3), 281–300.
Keung, Y., & Ho, C. H. (2009). Transfer of reading-related cognitive skills in learning to read Chinese (L1) and English (L2) among Chinese elementary school children. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 34, 103–112.
Kline, R. B. (2010). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Leong, C. K. (1986). What does accessing a morphemic scripts tell us about reading and reading disorders in an alphabetic scripts? Annals of Dyslexia, 36, 82–102.
Leong, C. K., Tse, S. K., Loh, K. Y., & Hau, K. T. (2008). Text comprehension in Chinese children: Relative contribution of verbal working memory, pseudoword reading, rapid automatized naming, and onset-rime phonological segmentation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 100(1), 135–149.
Lu, L., & Liu, H. S. (1998). The peabody picture vocabulary test-revised in Chinese. Taipei: Psychological Publishing.
Mancilla-Martinez, J., & Lesaux, N. (2010). Predictors of reading comprehension for struggling readers: The case of Spanish-speaking language minority learners. Journal of Educational Psychology, 102(3), 701–711.
Mancilla-Martinez, J., & Lesaux, N. (2011). The gap between Spanish-speakers’ word reading and word knowledge: A longitudinal study. Child Development, 82(5), 1544–1560.
Manis, F. R., Lindsey, K. A., & Bailey, C. E. (2004). Development of reading in grades K-2 in Spanish-speaking English-language learners. Learning Disabilities Research & Practice, 19, 214–224.
Marinova-Todd, S. H., Zhao, J., & Bernhardt, M. (2010). Phonological awareness skills in the two languages of Mandarin-English bilingual children. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics, 24, 387–400.
McBride-Chang, C., Bialystok, E., Chong, K. K. Y., & Li, Y. (2004). Levels of phonological awareness in three cultures. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 89, 93–111.
McCardle, P., Mele-McCarthy, J., & Leos, K. (2005). English language learners and learning disabilities: Research agenda and implications for practice. Learning Disabilities Research and Practice, 20(2), 68–78.
Muter, V., Hulme, C., Snowling, M. J., & Stevenson, J. (2004). Phonemes, rimes, vocabulary, and grammatical skills as foundations of reading development: Evidence from a longitudinal study. Developmental Psychology, 40(5), 665–681.
Nakamoto, J., Lindsey, K. A., & Manis, F. R. (2008). A cross-linguistic investigation of English language learners’ reading comprehension in English and Spanish. Scientific Studies of Reading, 12(4), 351–371.
National Reading Panel. (2000). Teaching children to read: An evidence based assessment of the scientific research literature on reading and its implications for reading instruction. Washington, DC: National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
Oller, D. K., & Eilers, R. E. (2002). Language and literacy in bilingual children. North York, ON: Multilingual Matters Ltd.
Oller, D. K., & Pearson, B. Z. (2002). Assessing the effects of bilingualism: A background. In D. K. Oller & R. E. Eilers (Eds.), Language and literacy in bilingual children (pp. 3–21). Clevedon: Multilingual Matters.
Perfetti, C. A. (1998). Two basic questions about reading and learning to read. In P. Reitsma & L. Verhoeven (Eds.), Problems and interventions in literacy development (pp. 15–48). Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Proctor, C. P., Carlo, M., August, D., & Snow, C. (2005). Native Spanish speaking children reading in English: Toward a model of comprehension. Journal of Educational Psychology, 97, 246–256.
Proctor, C. P., Carlo, M., August, D., & Snow, C. (2006). The intriguing role of Spanish language vocabulary knowledge in predicting English reading comprehension. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98, 159–169.
RAND Reading Study Group. (2002). Reading for understanding: Toward an R&D program in reading comprehension (Tech. Report for the Office of Educational Research and Improvement). Santa Monica, CA: Rand Corporation.
Roberts, G., Good, R., & Corcoran, S. (2005). Story retell: A fluency-based indicator of reading comprehension. School Psychology Quarterly, 20, 304–317.
Roehrig, A. D., Petscher, Y., Nettles, S. M., Hudson, R. F., & Torgeson, J. K. (2008). Accuracy of the DIBELS oral reading fluency measure for predicting third grade reading comprehension outcomes. Journal of School Psychology, 46, 343–366.
Royer, J. M., & Carlo, M. S. (1991). Transfer of comprehension skills from native to second language. Journal of Reading, 34, 450–455.
Scarborough, H. S. (1989). Prediction of reading dysfunction from familial and individual differences. Journal of Educational Psychology, 81, 101–108.
Shu, H., & Anderson, R. C. (1997). Role of radical awareness in the character and word acquisition of Chinese children. Reading Research Quarterly, 32, 78–89.
Snow, C. E., Burns, M. S., & Griffin, P. (1998). Preventing reading difficulties in young children. Washington, DC: National Academy Press.
Tannenbaum, K. R., Torgesen, J. K., & Wagner, R. K. (2006). Relationships between word knowledge and reading comprehension in third grade children. Scientific Studies of Reading, 10, 381–398.
Tong, X., & McBride-Chang, C. (2010). Chinese-English biscriptal reading: Cognitive component skills across orthographies. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 23, 293–310.
Tunmer, W. E., & Hoover, A. (1992). Cognitive and linguistic factors in learning to read. In R. Treiman, C. Ehri, & P. B. Gough (Eds.), Reading acquisition (pp. 175–214). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Uchikoshi, Y., & Maniates, H. (2010). How does bilingual instruction enhance English achievement?: A mixed-methods study of Cantonese-speaking and Spanish-speaking bilingual classrooms. Bilingual Research Journal, 33(3), 1–22.
Uchikoshi, Y. (in press). Development of vocabulary in Spanish-speaking and Cantonese-speaking English Language Learners. Applied Psycholinguistics.
Umbel, V. M., Pearson, B. Z., Fernandez, M. C., & Oller, D. K. (1992). Measuring bilingual children’s receptive vocabularies. Child Development, 63, 1012–1020.
Wagner, R. K., Torgesen, J. K., & Rashotte, C. A. (1999). Comprehensive test of phonological processing. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed.
Wang, M., Cheng, C. X., & Chen, S. W. (2006). Contribution of morphological awareness to Chinese-English biliteracy acquisition. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98, 542–553.
Wang, M., Yang, C., & Cheng, C. (2009). The contributions of phonology, orthography, and morphology in Chinese-English biliteracy acquisition. Applied Psycholinguistics, 30, 291–314.
Wong-Fillmore, L. W. (1991). When learning a second language means losing the first. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 6(3), 323–347.
Woodcock, R. W. (1991). Woodcock language proficiency battery—Revised. Circle Pines, MN: American Guidance Services.
Yeung, P., Ho, C. S., Chik, P. P., Lo, L., Luan, H., Chan, D. W., et al. (2011). Reading and spelling Chinese among beginning readers: What skills make a difference? Scientific Studies of Reading, 15(4), 285–313.
Ziegler, J. C., & Goswami, U. (2005). Reading acquisition, developmental dyslexia, and skilled reading across languages: A psycholinguistic grain size theory. Psychological Bulletin, 131, 3–29.
Acknowledgments
The research reported in this paper was supported by the Foundation for Child Development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchikoshi, Y. Predictors of English reading comprehension: Cantonese-speaking English language learners in the U.S.. Read Writ 26, 913–939 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-012-9398-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-012-9398-z