Abstract
Background and aims
Green manure is commonly used to improve soil organic carbon (SOC) stock, which is mainly combined with soil minerals and stored in aggregates. The effects of three green manure varieties on mineral associated organic carbon (mSOC) and clay minerals in macroaggregates and microaggregates and SOC sequestration mechanism were explored in paddy soils in southern China.
Methods
A 36-year (1982–2018) field experiment was conducted on a rice-rice-green manure crop rotation system, including rice-rice-winter fallow (WF), rice-rice-Chinese milk vetch (MV), rice-rice-rape (RP), and rice-rice-ryegrass (RG). Fourier-transform infrared, X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy and high resolution transmission electron microscopy were used to analyze mSOC, revealing composition characteristics and interactions between SOC and minerals.
Results
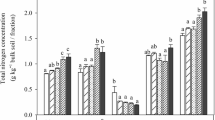
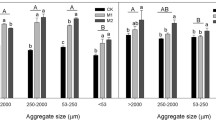
Green manure application increased SOC contents in the bulk soil by 8.4% (MV, p < 0.05), 1.2% (RP) and 4.8% (RG) compared to WF, and mainly altered SOC composition in mSOC of macroaggregates. Dominant functional groups in mSOC were polysaccharide C and alkene C. Phyllosilicate minerals of mSOC were mainly illite (51.0-61.9%) and kaolinite (29.2–37.3%). MV application caused significant changes in illite, with fractured lattice stripes within mSOC in macroaggregates and bent lattice stripes within mSOC in microaggregates. Futhermore, lattice fringe spacing under MV contracted from 1.0 to 0.7 nm within mSOC in microaggregates, suggesting that MV favored the transformation of illite into kaolinite. The SOC content of mSOC was positively correlated with the amount of illite but negatively with kaolinite.
Conclusions
Green manure returning (especially MV and RG) altered the SOC content of mSOC by converting 2:1 minerals into 1:1 minerals, and emerged as an effective strategy for SOC accumulation in paddy soils, which was further governed by aggregate size.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ablimit R, Li W, Zhang J et al (2022) Altering microbial community for improving soil properties and agricultural sustainability during a 10-year maize-green manure intercrop** in Northwest China. J Environ Manage 321:115859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115859
Andrade GRP, Cuadros J, Partiti CSM et al (2018) Sequential mineral transformation from kaolinite to Fe-illite in two Brazilian mangrove soils. Geoderma 309:84–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.08.042
Angst G, Mueller KE, Castellano MJ et al (2023) Unlocking complex soil systems as carbon sinks: multi-pool management as the key. Nat Commun 14:2967. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38700-5
Angst G, Mueller KE, Kögel-Knabner I et al (2017) Aggregation controls the stability of lignin and lipids in clay-sized particulate and mineral associated organic matter. Biogeochemistry 132:307–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-017-0304-2
Ankit, Singh A (2022) Chap. 2 - potassium (K+) transporters in plants: regulation and functional role in K+ uptake and homeostasis. In: Upadhyay SK (ed) Cation transporters in plants. Academic Press, pp 29–47
Ansari MA, Choudhury BU, Layek J et al (2022) Green manuring and crop residue management: Effect on soil organic carbon stock, aggregation, and system productivity in the foothills of Eastern Himalaya (India). Soil Tillage Res 218:105318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2022.105318
Barré P, Velde B, Abbadie L (2007) Dynamic role of illite-like clay minerals in temperate soils: facts and hypotheses. Biogeochemistry 82:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-006-9054-2
Chatterjee D, Nayak AK, Datta SC et al (2021) Transformation of crystalline and short-range order minerals in a long-term (47 years) rice-rice crop** system. CATENA 206:105488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105488
Chen Y, Hu N, Zhang Q et al (2019) Impacts of green manure amendment on detritus micro-food web in a double-rice crop** system. Appl Soil Ecol 138:32–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.02.013
Chen J, Qin W, Chen X et al (2020) Application of Chinese milk vetch affects rice yield and soil productivity in a subtropical double-rice crop** system. J Integr Agric 19:2116–2126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(19)62858-3
Chen M, Zhang S, Liu L et al (2023a) Organo-mineral complexes in soil colloids from an eight-year field experiment: Implications for carbon storage in saline-alkaline paddy soil. Pedosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedsph.2022.11.007
Chen M, Zhang S, Liu L, Ding X (2023b) Influence of organic fertilization on clay mineral transformation and soil phosphorous retention: evidence from an 8-year fertilization experiment. Soil Tillage Res 230:105702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2023.105702
Chen M, Zhang Y, Gao C et al (2023c) Mineral-microbial interactions in nine-year organic fertilization field experiment: a mechanism for carbon storage in saline-alkaline paddy soil. Plant Soil 489:465–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06032-4
Chenu C, Plante AF (2006) Clay-sized organo-mineral complexes in a cultivation chronosequence: revisiting the concept of the ‘primary organo-mineral complex’: clay-bound soil organic matter. Eur J Soil Sci 57:596–607. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2006.00834.x
Das R, Purakayastha TJ, Das D et al (2019) Long-term fertilization and manuring with different organics alter stability of carbon in colloidal organo-mineral fraction in soils of varying clay mineralogy. Sci Total Environ 684:682–693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.327
Elliott ET (1986) Aggregate structure and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in native and cultivated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 50:627–633. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1986.03615995005000030017x
Fernández-Ugalde O, Barré P, Hubert F et al (2013) Clay mineralogy differs qualitatively in aggregate-size classes: clay-mineral-based evidence for aggregate hierarchy in temperate soils. Eur J Soil Sci 64:410–422. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12046
Gao S, Cao W, Zhou G, Rees RM (2021) Bacterial communities in paddy soils changed by milk vetch as green manure: a study conducted across six provinces in south China. Pedosphere 31:521–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(21)60002-4
Geng H, Wang X, Shi S et al (2023) Fertilization makes strong associations between organic carbon composition and microbial properties in paddy soil. J Environ Manage 325:116605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116605
Guo J, Wang B, Wang G et al (2020) Effects of three cropland afforestation practices on the vertical distribution of soil organic carbon pools and nutrients in eastern China. Glob Ecol Conserv 22:e00913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e00913
Hacıosmanoğlu GG, Mejías C, Martín J et al (2022) Antibiotic adsorption by natural and modified clay minerals as designer adsorbents for wastewater treatment: a comprehensive review. J Environ Manage 317:115397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115397
Hemingway JD, Rothman DH, Grant KE et al (2019) Mineral protection regulates long-term global preservation of natural organic carbon. Nature 570:228–231. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1280-6
Hinsinger P, Elsass F, Jaillard B, Robert M (1993) Root-induced irreversible transformation of a trioctahedral mica in the rhizosphere of Rape. J Soil Sci 44:535–545. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1993.tb00475.x
Hinsinger P, Jaillard B, Dufey JE (1992) Rapid weathering of a trioctahedral mica by the roots of ryegrass. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56:977–982. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1992.03615995005600030049x
Hu A, Huang R, Liu G et al (2022) Effects of green manure combined with phosphate fertilizer on movement of soil organic carbon fractions in tropical sown pasture. Agronomy 12:1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051101
Huang Y, Huang L, Nie J et al (2022) Effects of substitution of chemical fertilizer by Chinese milk vetch on distribution and composition of aggregates-associated organic carbon fractions in paddy soils. Plant Soil 481:641–659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05668-y
Huang C, Meng S, Tan W et al (2021) Regional differences in mineral weathering characteristics of zonal soils under intensive agriculture. Appl Clay Sci 215:106336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2021.106336
Huang L, Tan W, Liu F et al (2007) Composition and transformation of 1.4 nm minerals in cutan and matrix of alfisols in central China. J Soils Sediments 7:240–246. https://doi.org/10.1065/jss2006.12.198
** VL, Wienhold BJ, Mikha MM, Schmer MR (2021) Crop** system partially offsets tillage-related degradation of soil organic carbon and aggregate properties in a 30-yr rainfed agroecosystem. Soil Tillage Res 209:104968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.104968
Kamran M, Huang L, Nie J et al (2021) Effect of reduced mineral fertilization (NPK) combined with green manure on aggregate stability and soil organic carbon fractions in a fluvo-aquic paddy soil. Soil Tillage Res 211:105005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.105005
Kleber M, Bourg IC, Coward EK et al (2021) Dynamic interactions at the mineral–organic matter interface. Nat Rev Earth Environ 2:402–421. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-021-00162-y
Kopittke PM, Dalal RC, Hoeschen C et al (2020) Soil organic matter is stabilized by organo-mineral associations through two key processes: the role of the carbon to nitrogen ratio. Geoderma 357:113974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.113974
Kubar KA, Huang L, Xue B et al (2021) Straw management stabilizes the chemical composition of soil organic carbon (SOC): the relationship with aggregate-associated c in a rice‐Rape crop** system. Land Degrad Dev 32:851–866. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3727
Lin C, Hseu Z-Y, Chen Z-S (2002) Clay mineralogy of spodosols with high clay contents in the subalpine forests of Taiwan. Clays Clay Miner 50:726–735. https://doi.org/10.1346/000986002762090254
Liu J, Guan Y, Shao Z, Wang H (2022) Mechanical effect of clay under the acid-base action: a case study on montmorillonite and illite. Front Earth Sci 10
Matocha CJ, Grove JH, Karathanasis TD, Vandiviere M (2016) Changes in soil mineralogy due to nitrogen fertilization in an agroecosystem. Geoderma 263:176–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.09.002
Mayer M, Krause H-M, Fliessbach A et al (2022) Fertilizer quality and labile soil organic matter fractions are vital for organic carbon sequestration in temperate arable soils within a long-term trial in Switzerland. Geoderma 426:116080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2022.116080
Meunier A (2007) Soil hydroxy-interlayered minerals: a re-interpretation of their crystallochemical properties. Clays Clay Miner 55:380–388. https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2007.0550406
Mustafa A, Minggang X, Ali Shah SA et al (2020) Soil aggregation and soil aggregate stability regulate organic carbon and nitrogen storage in a red soil of southern China. J Environ Manage 270:110894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110894
Ndzana GM, Huang L, Zhang Z et al (2019) The transformation of clay minerals in the particle size fractions of two soils from different latitude in China. CATENA 175:317–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.12.026
Ndzana GM, Zhang Y, Yao S et al (2022) The adsorption capacity of root exudate organic carbon onto clay mineral surface changes depending on clay mineral types and organic carbon composition. Rhizosphere 23:100545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2022.100545
Pu Y, Lang S, Wang A et al (2022) Distribution and functional groups of soil aggregate-associated organic carbon along a marsh degradation gradient on the Zoige Plateau, China. CATENA 209:105811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105811
Regelink IC, Stoof CR, Rousseva S et al (2015) Linkages between aggregate formation, porosity and soil chemical properties. Geoderma 247–248:24–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.01.022
Ren F, Zhang X, Liu J et al (2018) A synthetic analysis of livestock manure substitution effects on organic carbon changes in China’s arable topsoil. CATENA 171:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.06.036
Rhoades JD (1983) Cation exchange capacity. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of Soil Analysis. American Society of Agronomy, pp 149–157
Rumpel C, Eusterhues K, Kögel-Knabner I (2010) Non-cellulosic neutral sugar contribution to mineral associated organic matter in top-and subsoil horizons of two acid forest soils. Soil Biol Biochem 42:379–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.11.004
Saidy AR, Smernik RJ, Baldock JA et al (2013) The sorption of organic carbon onto differing clay minerals in the presence and absence of hydrous iron oxide. Geoderma 209–210:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.05.026
Scherrer P (1912) Bestimmung Der Inneren Struktur Und Der Größe Von Kolloidteilchen Mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Kolloidchemie Ein Lehrbuch. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 387–409
Shi XZ, Yu DS, Warner ED et al (2004) Soil database of 1:1,000,000 digital soil survey and reference system of the Chinese genetic soil classification system. Soil Horiz 45:129. https://doi.org/10.2136/sh2004.4.0129
Six J, Conant RT, Paul EA, Paustian K (2002) Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: implications for C-saturation of soils. Plant Soil 241:155–176
Six J, Elliott Et, Paustian K, Doran JW (1998) Aggregation and soil organic matter accumulation in cultivated and native grassland soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 62:1367–1377. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1998.03615995006200050032x
Song HJ, Lee JH, Canatoy RC et al (2021) Strong mitigation of greenhouse gas emission impact via aerobic short pre-digestion of green manure amended soils during rice crop**. Sci Total Environ 761:143193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143193
Song W, Shu A, Liu J et al (2022) Effects of long-term fertilization with different substitution ratios of organic fertilizer on paddy soil. Pedosphere 32:637–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(21)60047-4
Sposito G, Skipper NT, Sutton R et al (1999) Surface geochemistry of the clay minerals. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:3358–3364. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.7.3358
Vetterlein D, Kühn T, Kaiser K, Jahn R (2013) Illite transformation and potassium release upon changes in composition of the rhizophere soil solution. Plant Soil 371:267–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1680-6
Voisin A-S, Guéguen J, Huyghe C et al (2014) Legumes for feed, food, biomaterials and bioenergy in Europe: a review. Agron Sustain Dev 34:361–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-013-0189-y
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-193401000-00003
Wang R, Wu H, Sardans J et al (2020) Carbon storage and plant-soil linkages among soil aggregates as affected by nitrogen enrichment and mowing management in a meadow grassland. Plant Soil 457:407–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04749-0
Wen Y, Liu W, Deng W et al (2019) Impact of agricultural fertilization practices on organo-mineral associations in four long-term field experiments: implications for soil C sequestration. Sci Total Environ 651:591–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.233
Wen Y, You J, Zhu J, Hu H, Gao J, Huang J (2021a) Long-term green manure application improves soil K availability in red paddy soil of subtropical China. J Soils Sediments 21:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02768-z
Wen Y, Tang Y, Wen J, Wang Q, Bai L, Wang Y, Su S, Wu C, Lv J, Zeng X (2021b) Variation of intra-aggregate organic carbon affects aggregate formation and stability during organic manure fertilization in a fluvo-aquic soil. Soil Use Manage 37:151–163. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12676
Wilson MJ (2004) Weathering of the primary rock-forming minerals: processes, products and rates. Clay Min 39:233–266. https://doi.org/10.1180/0009855043930133
Wiseman CLS, Püttmann W (2006) Interactions between mineral phases in the preservation of soil organic matter. Geoderma 134:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.09.001
Witzgall K, Vidal A, Schubert DI et al (2021) Particulate organic matter as a functional soil component for persistent soil organic carbon. Nat Commun 12:4115. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24192-8
Wu X, Wei Y, Wang J et al (2017) Effects of soil physicochemical properties on aggregate stability along a weathering gradient. CATENA 156:205–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.04.017
Wu X, Wei Y, Wang J et al (2018) Effects of soil type and rainfall intensity on sheet erosion processes and sediment characteristics along the climatic gradient in central-south China. Sci Total Environ 621:54–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.202
Xu Y, Liu K, Yao S et al (2022) Formation efficiency of soil organic matter from plant litter is governed by clay mineral type more than plant litter quality. Geoderma 412:115727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2022.115727
Xue B, Huang L, Huang Y et al (2019) Effects of organic carbon and iron oxides on soil aggregate stability under different tillage systems in a rice–Rape crop** system. CATENA 177:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.01.035
Xue B, Huang L, Li X et al (2022) Effect of clay mineralogy and soil organic carbon in aggregates under straw incorporation. Agronomy 12:534. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020534
Yang Z, Xu M, Zheng S et al (2012) Effects of long-term winter planted green manure on physical properties of Reddish Paddy Soil under a double-rice crop** system. J Integr Agric 11:655–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(12)60053-7
Yang Z, Zheng S, Nie J et al (2014) Effects of long-term winter planted green manure on distribution and storage of organic carbon and nitrogen in water-stable aggregates of reddish paddy soil under a double-rice crop** system. J Integr Agric 13:1772–1781. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(13)60565-1
Yao Z, Zhang D, Liu N et al (2019) Dynamics and sequestration potential of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks of leguminous green manure-based crop** systems on the loess plateau of China. Soil Tillage Res 191:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.03.022
Yin K, Hong H, Churchman GJ et al (2013) Hydroxy-interlayered vermiculite genesis in Jiujiang late-pleistocene red earth sediments and significance to climate. Appl Clay Sci 74:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2012.09.017
Yonekura Y, Ohta S, Kiyono Y et al (2013) Soil organic matter dynamics in density and particle-size fractions following destruction of tropical rainforest and the subsequent establishment of Imperata grassland in Indonesian Borneo using stable carbon isotopes. Plant Soil 372:683–699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1763-4
Yuan G, Huan W, Song H et al (2021) Effects of straw incorporation and potassium fertilizer on crop yields, soil organic carbon, and active carbon in the rice–wheat system. Soil Tillage Res 209:104958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.104958
Yue Q, Sun J, Hillier J et al (2023) Rotation with green manure increased rice yield and soil carbon in paddies from Yangtze River valley, China. Pedosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedsph.2022.11.009
Zhang Z, Huang L, Liu F et al (2019) Transformation of clay minerals in nanoparticles of several zonal soils in China. J Soils Sediments 19:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2013-4
Zhang Y, de Vries W, Thomas BW, Hao X, Shi X (2017a) Impacts of long-term nitrogen fertilization on acid buffering rates and mechanisms of a slightly calcareous clay soil. Geoderma 305:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.05.021
Zhang Z, Huang L, Liu F, Wang M, Fu Q, Zhu J (2017b) The properties of clay minerals in soil particles from two ultisols, China. Clays Clay Miner 65:273–285. https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2017.064064
Zhang X, Zhang R, Gao J et al (2017c) Thirty-one years of rice-rice-green manure rotations shape the rhizosphere microbial community and enrich beneficial bacteria. Soil Biol Biochem 104:208–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.10.023
Zhang Z, Nie J, Liang H et al (2022) The effects of co-utilizing green manure and rice straw on soil aggregates and soil carbon stability in a paddy soil in South China. J Integr Agric S2095311922002507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jia.2022.09.025
Zhao Z, Gao S, Lu C et al (2021) Effects of different tillage and fertilization management practices on soil organic carbon and aggregates under the rice–wheat rotation system. Soil Tillage Res 212:105071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.105071
Zhou G, Gao S, Lu Y et al (2020) Co-incorporation of green manure and rice straw improves rice production, soil chemical, biochemical and microbiological properties in a typical paddy field in southern China. Soil Tillage Res 197:104499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104499
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all the staff of the National Agro-Ecosystem Observation and Research Station in Qiyang Country, Hunan Province of China.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41977020), the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA(CARS-22) and the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFD030090203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yanan Huang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing. Li Huang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Resources, Writing - review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition. Jusheng Gao: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Resources, Writing - review & editing, Supervision. Mingjian Geng: Resources, Writing - review & editing. Bin Xue: Writing - review & editing. Huimin Zhang: Resources, Writing - review & editing. **g Huang: Resources, Writing - review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Al Imran Malik.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Huang, L., Gao, J. et al. Effects of long-term green manure application on organic carbon fractions and clay minerals and their interactions in paddy soil aggregates. Plant Soil (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06383-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06383-y