Abstract
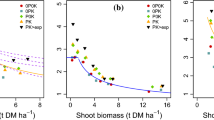
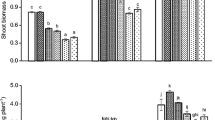
There are several indications that legumes are capable of accessing sparingly soluble phosphorus (P) in the soil through root-induced processes. We hypothesize that this plant-induced mobilization of P can be demonstrated if the plant accessible P assessed by isotopic dilution (‘L-value’) exceeds the corresponding values assessed in soil extracts (‘E-values’). A greenhouse experiment was set up to assess if L/E ratios are affected by P supply and by crop type. The L- and E-values were determined in three P-deficient soils of the Nigerian Northern Guinea savanna (NGS), applied with various rates of TSP, for two cowpea varieties (Vigna unguiculata L., cv Dan-Ila and cv IT-82D-716) and maize (Zea mays L., cv oba super I) as a reference. Plants grown in control soils were severely P-deficient. Plant growth and shoot P uptake significantly increased with increasing P application in all three soils and for all crops, but relative yield and shoot-P responses to P application were similar between maize and cowpea. Both L- and E-values increased with increasing P application. Average L/E ratios for maize were 1.4±0.3 and were unaffected by the P application. For cowpea in contrast, L/E ratios were 3.1±0.2 (significantly larger than one) in one of the three control soils and significantly decreased to 1.3±0.1 at largest P supply. Elevated L/E ratios in cowpea were not associated with an increase in P uptake compared to the other two control soils in which no increase in L/E ratio was observed. It is concluded that cowpea is able to access non-labile P under P-deficient conditions. However, this process cannot overcome P deficiency in these soils, probably because P uptake is limited by the small P concentration in the soil solution (1–2 μg P L−1) and this limitation is not overcome by an increase in the accessible soil P quantity (L-value).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N Ae J Arihara K Okada T Yoshihara T Otani C Johansen (1993 ) The role of piscidic acid secreted by pigeonpea roots grown in an Alfisol with low P-fertility P J Randall (Eds) Genetic Aspects of Plant Mineral Nutrition Kluwer Academic Publishers Dordrecht 279–288
M Amato (1983) ArticleTitleDetermination of 12C and 14C in plant and soil Soil Biol. Biochem. 15 611–612 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XoslGnug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(83)90059-7
F Amer S Mahdi A Alradi (1969) ArticleTitleLimitations in isotopic measurements of labile phosphate in soils J. Soil Sci. 20 91–100 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3cXnsl2rtg%3D%3D
S M Braum P A Helmke (1995) ArticleTitleWhite lupin utilizes soil phosphorus that is unavailable to soybean Plant Soil 176 95–100 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXot1Olurs%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00017679
P C Brookes (1982) ArticleTitleCorrection for seed-phosphorus effects in L-value determinations J. Sci. Food Agric. 33 329–335 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XksFClurY%3D
S Bühler A Oberson S Sinaj D K Friesen E Frossard (2003) ArticleTitleIsotope methods for assessing plant available phosphorus in acid tropical soils Eur. J. Soil Sci. 54 605–616 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2389.2003.00542.x
R Chhabra J Pleysier A Cremers (1975 ) Proceedings of the International Clay Conference Applied Publishing Ltd Wilmette, IL 443–449
R C Dalal E G Hallsworth (1977) ArticleTitleMeasurement of isotopically exchangeable soil phosphorus and interrelationships among parameters of quantity, intensity, and capacity factors Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 41 81–86 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2sXhvVyiu7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1977.03615995004100010025x
InstitutionalAuthorNameFAO (1991 ) World Soil Resources: An Explanatory Note on the FAO World Soil Resources Map at 1:25 000 000 Scale Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Rome 58
FAO–UNESCO 1990 Soil Map of the World: Revised Legend. World Soil Resources Report 60. FAO, Rome
J C Fardeau (1993) ArticleTitleLe phosphore assimilable des sols: Sa représentation par un modèle functionnel à plusieurs compartiments Agronomie 13 317–331
E J C M Frossard Fardeau Brossard J L Morel (1994) ArticleTitleSoil isotopically exchangeable phosphorus: A comparison between E and L values Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 58 846–851 Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800030031x
T S Gahoonia N E Nielsen (1992) ArticleTitleThe effect of root induced pH changes on the depletion of inorganic and organic phosphorus in the rhizosphere Plant Soil 143 185–191 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XltlSnsb0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00007872
R E Hamon M J McLaughlin (2002) ArticleTitleInterferences in the determination of isotopically exchangeable P in soils and a method to minimise them Aust. J. Soil Res. 40 1383–1397 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXlvFeisQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1071/SR02045
P J Hocking G Keerthisinghe F W Smith P J Randall (1997 ) Comparison of the ability of different crop species to access poorly available soil phosphorus T Ando (Eds) Plant nutrition – for Sustainable Food Production and Environment Kluwer Academic Publishers Dordrecht 305–308
E Hoffland G R Findenegg J A Nelemans (1989) ArticleTitleSolubilization of rock phosphate by rape. II. Local exudation of organic acids as a response to P-starvation Plant Soil 113 161–165 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1M**tFWmt7s%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02280176
I C R Holford G E G Mattingly (1976) ArticleTitlePhosphate adsorption and availability plant of phosphate Plant Soil 44 377–389 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE28XktVCnsb0%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00015889
W J Horst M Kamh J M Jibrin V O Chude (2001) ArticleTitleAgronomic measures for increasing P availability to crops Plant Soil 237 211–223 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XovVWltw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1013353610570
InstitutionalAuthorNameInternational Institute of Tropical Agriculture (1982 ) Automated and Semi-Automated Methods for Soil and Plant Analysis. Manual series no. 7 IITA Ibadan 33
D L Jones (1998) ArticleTitleOrganic acids in the rhizosphere – a critical review Plant Soil 205 25–44 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhtlGjs78%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004356007312
M Kamh W J Horst F Amer H Mostafa P Maier (1999) ArticleTitleMobilization of soil and fertilizer phosphate by cover crops Plant Soil 211 19–27 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXnt1Krt7c%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004543716488
G Keerthisinghe P J Hocking P R Ryan E Delhaize (1998) ArticleTitleEffect of phosphorus supply on the formation and function of proteoid roots of white lupin (Lupinus albus L.) Plant Cell Environ. 21 467–478 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlt1elsrg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-3040.1998.00300.x
G Krasilnikoff T Gahoonia N E Nielsen (2003) ArticleTitleVariation in phosphorus uptake efficiency by genotypes of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) due to differences in root and root hair length and induced rhizosphere processes Plant Soil 251 83–91 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3s**tlKgtLY%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1022934213879
S Larsen (1952) ArticleTitleThe use of 32P in studies on the uptake of phosphorus by plants Plant Soil 4 1–10 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG3sXjvFSr Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01343505
E Maertens A Thijs E Smolders F Degryse P T Cong R Merckx (2004) ArticleTitleAn anion resin membrane technique to overcome detection limits of isotopically exchanged P in P-sorbing soils Eur. J. Soil Sci. 55 63–69 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2c**sFCgtb8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2389.2004.00588.x
P W Moody T Dickson J C Dwyer B L Compton (1990) ArticleTitlePredicting yield responsiveness and phosphorus fertilizer requirements of soybeans from soil tests Aust. J. Soil Res. 28 399–246
P W Moody G F Haydon T Dickson (1983) ArticleTitleMineral nutrition of soybeans grown in the South Burnett region of south-eastern Queensland. 2. Prediction of grain yield response to phosphorus with soil tests Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 23 38–42 Occurrence Handle10.1071/EA9830038
C Morel C Plenchette (1994) ArticleTitleIs the isotopically exchangeable phosphate of a loamy soil the plant-available P? Plant Soil 158 287–297 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2c**s12js7s%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00009502
J Murphy H P Riley (1962) ArticleTitleA modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters Anal. Chim. Acta 27 31–36 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF38XksVyntr8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
G Neumann V Römheld (1999) ArticleTitleRoot excretion of carboxylic acids and protons in phosphorus-deficient plants Plant Soil 211 121–130 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXnt1Kqsr4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004380832118
I Novozamsky V J G Houba R Eck ParticleVan W Vark ParticleVan (1983) ArticleTitleA novel digestion technique for multi-element plant analysis Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 14 239–248 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXhvFKqt70%3D Occurrence Handle10.1080/00103628309367359
R S Russell J B Rickson S N Adams (1954) ArticleTitleIsotope equilibria between phosphates in soil and their significance in the assessment of fertility by tracer methods J. Soil Sci. 5 85–105 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG2MXhtleqtQ%3D%3D
N Sanginga O Lyasse B B Singh (2000) ArticleTitlePhosphorus use efficiency and nitrogen balance of cowpea breeding lines in a low P soil of the derived savanna zone in West Africa Plant Soil 220 119–128 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXks1Kltr4%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004785720047
InstitutionalAuthorNameSAS Institute Inc (1999 ) SAS User’s Guide: Statistics SAS Institute, Inc Cary, NC
U Schwertmann (1964) ArticleTitleDifferenzierung der eisen-oxide des bodens durch photochemische extraktion mit saurer ammonium oxalat-lösung Z Pflanz Bodenkunde 105 194–202 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF2MXotlCj
P L Searle (1984) ArticleTitleThe Berthelot or indophenol reaction and its use in the analytical chemistry of nitrogen. A review Analyst 109 549–568 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXlsVartbk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1039/an9840900549
B Vanlauwe J Diels N Sanginga R J Carsky J Deckers R Merckx (2000) ArticleTitleUtilization of rock phosphate by crops on a representative toposequence in the Northern Guinea savanna zone of Nigeria: Response by maize to previous herbaceous legume crop** and rock phosphate treatments Soil Biol. Biochem. 32 2079–2090 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXpvFWj Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00150-4
P P Veldhoven ParticleVan G P Mannaerts (1987) ArticleTitleInorganic and organic phosphate measurements in the nanomolar range Anal. Biochem. 161 45–48 Occurrence Handle3578786 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0003-2697(87)90649-X
A M Wolf D E Baker H B Pionke (1986) ArticleTitleThe measurement of labile phosphorus by the isotopic dilution and anion resin methods Soil Sci. 141 60–69 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XhtVynsLk%3D
F S Zhang J Ma Y P Cao (1997) ArticleTitlePhosphorus deficiency enhances root exudation of low-molecular weight organic acids and utilization of sparingly soluble inorganic phosphates by radish (Raphanus sativus L.) and rape (Brassica napus L.) plants Plant Soil 196 261–264 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXotVOgu7o%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004214410785
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pypers, P., Van Loon, L., Diels, J. et al. Plant-available P for Maize and Cowpea in P-deficient Soils from the Nigerian Northern Guinea Savanna – Comparison of E- and L-values. Plant Soil 283, 251–264 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-0016-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-0016-1