Abstract
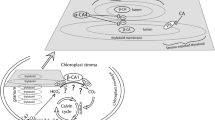
The review incorporates recent information on carbonic anhydrase (CA, EC: 4.2.1.1) pertaining to types, homology, regulation, purification, in vitro stability, and biological functions with special reference to higher plants. CA, a ubiquitous enzyme in prokaryotes and higher organisms represented by four distinct families, is involved in diverse biological processes, including pH regulation, CO2 transfer, ion exchange, respiration, and photosynthetic CO2 fixation. CA from higher plants traces its origin with prokaryotes and exhibits compartmentalization among their organs, tissues, and cellular organelles commensurate with specific functions. In leaves, CA represents 1−20 % of total soluble protein and abundance next only to ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBPCO) in chloroplast, facilitating CO2 supply to phosphoenol pyruvate carboxylase in C4 and CAM plants and RuBPCO in C3 plants. It confers special significance to CA as an efficient biochemical marker for carbon sequestration and environmental amelioration in the current global warming scenario linked with elevated CO2 concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, L., Brundell, J., Falkering, S.O., Nyman, P.O.: Carbonic anhydrase from Neisseria sicca strain 6021. I Bacterial growth and purification of the enzyme. — Biochim. biophys. Acta 284: 298–310, 1972.
Aizawa, K., Miyachi, S.: Carbonic anhydrase and CO2 concentrating mechanisms in microalgae and cyanobacteria. — FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 39: 215–233, 1986.
Alber, B.B., Ferry, J.G.: A carbonic anhydrase from the archaeon Methanosarcina thermophila. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 6909–6913, 1994.
Alber, B.E., Colangelo, C.M., Dong, J., Stalhandske, C.M., Baird, T.T., Tu, C., Fierk, C.A., Silverman, D.N., Scott, R.A., Ferry, J.G.: Kinetic and spectroscopic characterization of the gamma carbonic anhydrase from the methanoarchaeon Methanosarcina thermophila. — Biochemistry 38: 13119–13128, 1999.
Atkins, C.A.: Occurrence and some properties of carbonic anhydrate from legume root nodules. — Phytochemistry 13: 93–98, 1974.
Atkins, C.A., Patterson, B.D., Graham, D.: Plant carbonic anhydrases I. Distribution of types among species. — Plant Physiol. 50: 214–217, 1972a.
Atkins, C.A., Patterson, B.D., Graham, D.: Plant carbonic anhydrases II. Preparation and some properties of monocotyledon and dicotyledon enzyme types. — Plant Physiol. 50: 218–223, 1972b.
Badger, M.R., Price, G.D.: Carbonic anhydrase activity associated with the cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC7942. — Plant Physiol. 89: 51–60, 1989.
Badger, M.R., Price, G.D.: The role of carbonic anhydrase in photosynthesis. — Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol. 45: 369–392, 1994.
Bowen, G.W.: Carbonic anhydrase in marine algae. — Plant Physiol. 44: 726–732, 1969.
Bradfield, J.R.G.: Plant carbonic anhydrase. — Nature 159: 467–468, 1947.
Braus-Stromeyer, S.A., Schnappauf, G., Braus, G.H., Gossnet, A.S., Drake, H.L.: Carbonic anhydrase in Acetobacterium woodii and acetogenic bacteria. — J. Bacteriol. 179: 7197–7200, 1997.
Burnell, J.N.: Immunological study of carbonic anhydrase in C3 and C4 plants using antibodies to maize cytosolic and spinach chloroplastic carbonic anhydrase. — Plant Cell Physiol. 31: 423–427, 1990.
Burnell, J.N., Hatch, M.D.: Low bundle sheath carbonic anhydrase is apparently essential for effective C4 pathway operation. — Plant Physiol. 86: 1252–1256, 1988.
Burnell, J.N., Sizuki, I., Sugiyama, T.: Light induction and the effect of nitrogen status upon the activity of carbonic anhydrase in maize leaves. — Plant Physiol. 94: 384–387, 1990.
Cerfigni, T., Teofani, F., Bassanelli, C.: Effect of CO2 on carbonic anhydrase in Avena sativa and Zea mays. — Phytochemistry 10: 2991–2994, 1971.
Champagnol, F.: Compt. rend. Acad. Sci. Paris 289: 1273–1275, 1976. [Not read in original.]
Chang, C.W.: Carbonic anhydrase of the cotton plant. — Phytochemistry 14: 119–121, 1975a.
Chang, C.W.: Activation energy for thermal inactivation and Km of carbonic anhydrase from the cotton plant. — Plant Sci. Lett. 4: 109–113, 1975b.
Chang, C.W.: Carbonic dioxide and senescence in cotton plants. — Plant Physiol. 55: 515–519, 1975c.
Chen, T.M., Brown, R.H., Black, C.C.: CO2 compensation concentration, rate of photosynthesis, and carbonic anhydrase activity of plants. — Weed Sci. 18: 399–403, 1970.
Christianson, D.W., Cox, J.D.: Catalysis by metal activated hy-droxide in zinc and manganese metalloenzymes. — Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68: 33–57, 1999.
Colman, B.: Second International Symposium on inorganic carbon utilization by aquatic photosynthetic organisms. — Can. J. Bot. 69: 907–1027, 1991.
Cox, H., Me-Lendon, G.L., Lane, T.W., Prince, R.C., Pickering, I.J., George, G.N.: The active site structure of Thalassiosira weissflogii carbonic anhydrase I. — Biochemistry 39: 12128–12130, 2000.
Earnhardt, J. N., Qian, M., Tu, C., Lakkis, M.M., Bergenhem, N.C., Laipis, P.J., Tashian, R.E., Silverman, D.N.: The catalytic properties of marine carbonic anhydrase VII. — Biochemistry 37: 10837–10845, 1998.
Edwards, G.E., Mohamed, A.K.: Reduction in carbonic anhydrase activity in zinc deficient leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris L. — Crop Sci. 13: 351–354, 1973.
Eriksson, M., Karlsson, J., Ramazanov, Z., Gardestrom, P., Samuelsson, G.: Discovery of an algal mitochondrial carbonic anhydrase: molecular cloning and characterization of low CO2 induced polypeptide in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 12031–12034, 1996.
Eriksson, M., Villand, P., Gardestrom, P., Samuelsson, G.: Induction and regulation of expression of a low CO2 induced mitochondrial carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. — Plant Physiol. 116: 637–641, 1998.
Everson, R.G.: Carbonic anhydrase and CO2 fixation in isolated chloroplasts. — Phytochemistry 9: 25–32, 1970.
Everson, R.G., Slack, C.R.: Distribution of carbonic anhydrase in relation to the C4 pathway of photosynthesis. — Phytochemistry 7: 581–584, 1968.
Fawcett, T.W., Browse, J.A., Volokita, M., Bartlett, S.G.: Spinach carbonic anhydrase primary structure deduced from the sequence of a cDNA clone. — J. biol. Chem. 265: 5414–5417, 1990.
Fujiwara, S., Fukuzawa, H., Tachiki, A., Miyachi, S.: Structure and differential expression of two genes encoding carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 9779–9783, 1990.
Fukuzawa, H., Fujiwara, S., Yamamoto, Y., Dionisio-Sese, M.L., Miyachi, S.: cDNA cloning, sequence, and expression of carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Regulation by environmental CO2 concentration. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 4383–4387, 1990.
Fukuzawa, H., Suzuki, E., Komukai, Y., Miyachi, S.: A gene homologous to chloroplast carbonic anhydrase (icfA) is essential to photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation by Synechococcus PCC7942. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 4437–4441, 1992.
Funke, R.P., Kovar, J.L., Weeks, D.P.: Intracellular carbonic anhydrase is essential to photosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii at atmospheric level of CO2. — Plant Physiol. 114: 237–244, 1997.
Ghoshal, D., Goyal, A.: Carbon concentration mechanism(s) in unicellular green algae and cyanobacteria. — J. Plant Biochem. Biotech. 10: 83–90, 2001.
Gill, S.R., Fedorka-Cray, P.J., Tweten, R.K., Sleeper, B.P.: Purification and properties of the carbonic anhydrase of Rhodospirillum rubrum. — Arch. Microbiol. 138: 113–118, 1984.
Giuliano, G., Pichersky, E., Malik, V.S., Timko, M.P., Scolnik, P.A., Cashmore, A.R.: An evolutionary conserved protein binding sequence upstream of a plant light-regulated gene. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 7089–7093, 1988.
Goustiana, L.M., Fournadjievna, S.T., Pesheva, I.S., Kudrev, M.C.: Two forms of carbonic anhydrase in pea roots. — Compt. rend. Acad. bulg. Sci. 41: 103–105, 1998.
Goyal, A., Shiraiwa, Y., Tolbert, N.E.: External and internal carbonic anhydrases in Dunaliella species. — Mar. Biol. 113: 349–355, 1992.
Graham, D., Atkins, C.A., Reed, M.L., Patterson, B.D., Smillie, R.M.: Carbonic anhydrase, photosynthesis, and light-induced pH changes. — In: Hatch, M.D., Osmond, C.B., Slatyer, R.O. (ed.): Photosynthesis and Photorespiration. Pp. 267–274. John Wiley and Sons, New York — London — Sydney — Toronto 1971.
Graham, D., Reed, M.L.: Carbonic anhydrase and the regulation of photosynthesis. — Nature-new Biol. 231: 81–83, 1971.
Graham, D., Reed, M.L., Patterson, B.D., Hockley, D.G., Dwyer, M.R.: Chemical properties, distribution and physiology of plant and algal carbonic anhydrase. — Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 429: 222–237, 1984.
Green, L.S., Laudenbach, D.E., Grossman, A.R.: Nature of the light-induced H+ efflux and Na+ uptake in cyanobacteria. — Plant Physiol. 89: 1220–1225, 1989.
Green, P.J., Kay, S.A., Chua, N.H.: Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. — EMBO J. 6: 2543–2549, 1987.
Gutierrez, M., Huber, S.C., Ku, S.B., Kanai, R., Edwards, G.E.: Intracellular localization of carbon metabolism in mesophyll cells of C4 plants. — In: Avron, M. (ed.): Proceedings of the Third International Congress of Photosynthesis. Vol. II. Pp. 1219–1230. Elsevier, Amsterdam — Oxford — New York 1975.
Hatch, M.D., Burnell, J.N.: Carbonic anhydrase activity in leaves and its role in the first step of C4 photosynthesis. — Plant Physiol. 93: 825–828, 1990.
Hewett-Emmett, D., Tashian, R.E.: Functional diversity, conservation and convergence in the evolution of the alpha beta and gamma carbonic anhydrase gene families. — Mol. phylogenet. Evol. 5: 52–77, 1996.
Hiltonen, T., Bjorkbacka, H., Forsman, C. Clarke, A.K., Samuelsson, G.: Intracellular beta carbonic anhydrase of the unicellular green alga coccomyxa. — Plant Physiol. 117: 1341–1349, 1998.
Houghton, R.A.: The future role of tropical forests in affecting the carbon dioxide concentration of the atmosphere. — Ambio 19: 204–209, 1990.
Husic, H.D., Marcus, C.A.: Identification of intracellular carbonic anhydrase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a carbonic anhydrase directed photoaffinity label. — Plant Physiol. 105: 133–139, 1994.
Imamura, M., Tsuzuki, M., Hogetsu, D., Miyachi, S.: Role of carbonic anhydrase in algal photosynthesis. — In: Akoyunoglou, G. (ed.): Photosynthesis. Vol. IV. Pp. 471–482. Balaban International Science Services, Philadelphia 1981.
Jiang, W., Gupta, D.: Structure of the carbonic anhydrase vi (CA-6) genes evidence for two distinct groups with in the alpha-CA gene family. — Biochem. J. 344: 385–390, 1999.
Kachru, R.B., Anderson, L.E.: Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes. V. Pea-leaf carbonic anhydrases. — Planta 118: 235–240, 1974.
Kamo, T., Shimogawara, K., Fukuzawa, H., Muto, S., Miyachi, S.: Subunit constitution of carbonic anhydrate from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. — Eur. J. Biochem. 192: 557–562, 1990.
Karlsson, J., Clarke, A.K., Chen, Z.Y., Hugghins, S.Y., Park, Y.I., Husic, D., Moroney, J.V., Samuelsson, G.: A novel alpha type carbonic anhydrase associated with thylakoid membrane in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is required for growth at ambient CO2. — EMBO J. 17: 1208–1216, 1998.
Karlsson, J., Hiltonen, T., Husic, D., Ramazanov, Z., Samuelsson, G.: Intracellular carbonic anhydrase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. — Plant Physiol. 109: 533–539, 1995.
Khan, N.A.: Variation in carbonic anhydrase activity and its relationship with photosynthesis and dry mass of mustard. — Photosynthetica 30: 317–320, 1994.
Kim, H.J., Bracey, M.H., Barlett, S.G.: Nucleotide sequence of a gene encoding carbonic anhydrase in Arabidopsis thaliana. — Plant Physiol. 105: 449, 1994.
Kimber, M.S., Pai, E.F.: The active site architecture of Pisum sativum beta carbonic anhydrase is a mirror image of that of alpha carbonic anhydrases. — EMBO J. 19:1407–1418, 2000.
Kisiel, W., Graf, G. Purification and characterization of carbonic anhydrase from Pisum sativum. — Phytochemistry 11: 113–117, 1972.
Kisker, C., Schindelin, H., Alber, B.E., Ferry, J.G., Rees, D.C.: A left hand β helix revealed by the crystal structure of a carbonic anhydrase from the archaeon Methanosarcina thermophila. — EMBO J. 15: 2323–2330, 1996.
Kositsin, A.V., Khalidova, G.B.: [Electrophoretic properties of carbonic anhydrase from tomato chloroplasts.]. — Fiziol. Rast. 21: 1178–1181, 1974. [In Russ.; not read in original.]
Ku, S.B., Edwards, G.E.: Photosynthesis in mesophyll protoplasts and bundle sheath cells of various types of C4 plants. IV. Enzymes of respiratory metabolism and energy utilizing enzymes of photosynthetic pathways. — Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 77: 16–32, 1975.
Lane, T.W., Morel, F.M.: A biological function for cadmium in marine diatoms. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 4627–4631, 2000.
Lee, J.G., Morel, F.M.M.: Replacement of Zn by cadmium in marine phytoplankton. — Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 127: 305–309, 1995.
Lee, J.G., Morel, F.M.M.: In vivo substitution of Zn by cobalt (II) substituted carbonic anhydrase II of the exchange of oxygen-18 between CO2 and H2O. — Biochemistry 24: 5881–5887, 1996.
Liljas, A., Laurberg, M.: A wheel invented three times: The molecular structures of the three carbonic anhydrases. — EMBO Rep. 1: 16–17, 2000.
Majeau, N., Arnoldo, M.A., Coleman, J.R.: Modification of carbonic anhydrase activity by antisense and over-expression constructs in transgenic tobacco. — Plant mol. Biol. 25: 377–385, 1994.
Majeau, N., Coleman, J.R.: Isolation and characterization of a cDNA coding for pea chloroplastic carbonic anhydrase. — Plant Physiol. 95: 264–268, 1991.
Majeau, N., Coleman, J.R.: Nucleotide sequence of a complementary DNA encoding tobacco chloroplastic carbonic anhydrase. — Plant Physiol. 100: 1077–1078, 1992.
Majeau, N., Coleman, J.R.: Correlation of carbonic anhydrase and ribulose-1,5 bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase expression in pea. — Plant Physiol. 104: 1393–1399, 1994.
Meldrum, N.N., Roughton, F.J.W.: Carbonic anhydrase: its properties. — J. Physiol. 80: 113–142, 1933.
Millikan, C.R.: Relative effects of zinc and copper deficiencies on lucerne and subterranean clover. — Aust. J. biol. Sci. 6: 164–177, 1953.
Mitsahashi, S., Mizushima, T., Yamashita, E., Yamamoto, M., Kumasaka, T., Moriyama, H., Miyachi, S., Tsukihra, T.: X-ray structure of beta carbonic anhydrase from the red alga Porphyridium purpureum reveals a novel catalytic site for CO2 hydration. — J. biol. Chem. 275: 5521–5526, 2000.
Morel, F.M.M., Reinfelder, J.R., Roberts, S.B., Chamberlain, C.P., Lee, J.G., Yee, D.: Zinc and carbon co-limitation of marine phytoplankton. — Nature 369: 740–742, 1994.
Moroney, J.V., Bartlett, S.G., Samuelsson, G.: Carbonic anhydrases in plants and algae. — Plant Cell Environ. 24: 141–153, 2001.
Moroney, J.V., Kitayama, M., Togasaki, R.K., Tolbert, N.E.: Evidence for inorganic carbon transport by intact chloroplasts of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. — Plant Physiol. 83: 460–463, 1987.
Moroney, J.V., Somanchi, A.: How do algae concentrate CO2 increase the efficiency of photosynthetic carbon fixation? — Plant Physiol. 119: 9–16, 1999.
Mount, S.M.: A catalogue of splice junction sequences. — Nucleic Acids Res. 10: 459–472, 1982.
Nimer, N.A., Iglesias-Rodriguez, M.D., Merrett, M.J.: Bicarbonate utilization by marine phytoplankton species. — J. Phycol. 33: 625–631, 1997.
Nishimura, M., Graham, D., Akazawa, T.: Isolation of intact chloroplasts and other cell organelles from spinach leaf protoplasts. — Plant Physiol. 58: 309–314, 1976.
Okabe, K., Yang, S.-Y., Tsuzuki, M., Miyachi, S.: Carbonic anhydrase: its content in spinach leaves and its taxonomic diversity studied with anti-spinach leaf carbonic anhydrase anti-body. — Plant Sci. Lett. 33: 145–153, 1984.
Okazaki, M., Yoshida, T., Feruya, K.: The effects of light on carbonic anhydrases in the etiolated leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris and in intact chloroplasts from spinach. — Bull. Tokyo Gakugei Univ., Ser. IV 28: 199–206, 1976.
Pesheva, I., Kodama, M., Dionisio-Sese, M.L., Miyachi, S.: Changes in photosynthetic characteristics induced by transferring air-grown cells of Chlorococcum littorale to high-CO2 conditions. — Plant Cell Physiol. 35: 379–387, 1994.
Pocker, Y., Ng, J.S.Y.: Plant carbonic anhydrase: Properties and carbon dioxide hydration kinetics. — Biochemistry 12: 5127–5134, 1973.
Pocker, Y., Sarkanen, S.: Carbonic anhydrase structure, catalytic versatility and inhibition. — Adv. Enzymol. 47: 149–274, 1978.
Poincelot, R.P.: Intracellular distribution of carbonic anhydrase in spinach leaves. — Biochim. biophys. Acta 258: 637–642, 1972.
Polson, D.E.: A Physiologic-Genetic Study of the Differential Response of Navy Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) to Zinc. — Ph. D. Thesis. Michigan State University, No. 68-11,082, 1968.
Price, G.D., Caemmerer, S. von, Evans, J.R., Yu, J.-W., Lloyd, J., Oja, V., Kell, P., Harrison, K., Gallagher, A., Badger, M.R.: Specific reduction of chloroplast carbonic anhydrase activity by antisense RNA in transgenic tobacco plants has a minor effect on photosynthetic CO2 assimilation. — Planta 193: 331–340, 1994.
Price, N.M., Morel, F.M.M.: Cadmium and cobalt substitution for zinc in a marine diatom. — Nature 344: 658–660, 1990.
Raines, C.A., Horsnell, P.R., Holder, C., Lloyed, J.C.: Arabidopsis thaliana carbonic anhydrase: cDNA sequence and effect of CO2 on mRNA levels. — Plant mol. Biol. 20: 1143–1148, 1992.
Randall, P.J., Bauma, D.: Zinc deficiency, carbonic anhydrase and photosynthesis in leaves of spinach. — Plant Physiol. 52: 229–232, 1973.
Rathnam, C.K.M., Das, V.S.R.: Aspartate-type C-4 photosynthetic carbon metabolism in leaves of Eleusine coracana GAERTN. — Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 74: 377–393, 1975.
Reed, M.L.: Intracellular location of carbonic dehydratase (carbonic anhydrase) in leaf tissue. — Plant Physiol. 63: 216–217, 1979.
Reed, M.L., Graham, D.: Carbonic anhydrase in plants: distribution, properties and possible physiological roles. — Progr. Phytochem. 7: 47–49, 1981.
Roberts, S.B., Lane, T.W., Morel, F.M.M.: Carbonic anhydrase in the marine diatom Thalassiosira weissflogii. — J. Phycol. 33: 845–850, 1997.
Rossi, C.A., Cherst, A., Cortivo, M.: Studies on carbonic anhydrase from spinach leaves: Isolation and properties. — In: Forster, R.E., Edsall, J.T., Otis, A.B., Haughton, F.J.W. (ed.): CO2: Chemical, Biochemical and Physiological Aspects. Pp. 131–138. NASA, Washington 1969.
Sasaki, H., Hirose, T., Watanabe, Y., Ohsugi, R.: Carbonic anhydrase activity and CO2 transfer resistance in Zn-deficient rice leaves. — Plant Physiol. 118: 929–934, 1998.
Smith, K.S., Ferry, J.G.: Prokaryotic carbonic anhydrases. — FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 24: 335–366, 2000.
Smith, K.S.. Jakubzick, C., Whittam, T.S., Ferry, J.G.: Carbonic anhydrase: is an ancient enzyme widespread in prokaryotes. — Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 15184–15189, 1999.
Stemler, A.J.: The case for chloroplast thylakoid carbonic anhydrase. — Physiol. Plant. 99: 348–353, 1997.
Strop, P., Smith, K.S., Iverson, T.M., Ferry, J.G., Rees, D.C.: Crystal structure of the “cab” type beta class carbonic anhydrase from the archaeon Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. — J. biol. Chem. 276: 10299–10305, 2001.
Sultemeyer, D., Klughammer, B., Badger, M., Price, G.D.: Fast induction of high affinity HCO3 transport in cyanobacteria. — Plant Physiol. 116: 183–192, 1998.
Tashian, R.F.: The carbonic anhydrase: Widening perspectives on their evolution, expression and function. — Bioassays 10: 186–192, 1989.
Tobin, A.J.: Carbonic anhydrase from parsley leaves. — J. biol. Chem. 245: 2656–2666, 1970.
Tripp, B.C., Smith, K., Ferry, J.G.: Carbonic anhydrase: New insights for an ancient enzyme. — J. biol. Chem. 276: 48615–48618, 2001.
Tsuzuki, M., Miyachi, S.: The function of carbonic anhydrase in aquatic photosynthesis. — Aquat. Bot. 34: 85–104, 1989.
Tsuzuki, M., Miyachi, S., Edwards, G.E.: Localization of carbonic anhydrase in mesophyll cells of terrestrial C3 plants in relation to CO2 assimilation. — Plant Cell Physiol. 26: 881–891, 1985.
Tsuzuki, M., Muto, S., Miyachi, S.: Role of carbonic anhydrase in photosynthesis of higher plants: a possible limiting step in CO2 transport. — In: Akoyunoglu, G. (ed.): Photosynthesis. Vol. IV. Pp. 483–492. Balaban International Science Services, Philadelphia 1981.
Tu, C.K., Silverman, D.N.: Catalysis by cobalt (II) substituted carbonic anhydrase II of the exchange of oxygen-18 between CO2 and H2O. — Biochemistry 24: 5881–5887, 1985.
Veith, F.P., Blankeship, L.C.: Carbonic anhydrase in bacteria. — Nature 197: 76–77, 1963.
Walk, R.-A., Metzner, H.: Reinigung und Charakterisierung von Chloroplasten-Carbonat-Dehydratase (Isoenzym I) aus Blättern von Lactuca sativa. — Hoppe-Seyler's Z. physiol. Chem. 356: 1733–1741, 1975.
Waygood, E.R.: Carbonic anhydrase (Plant and animal). — In: Colowick, S.P., Kaplan, N.O. (ed.): Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 2. Pp. 836–846. Academic Press, New York 1955.
Waygood, E.R., Clendenning, K.A.: Carbonic anhydrase in green plants. — Can. J. Res. 28: 673–689, 1950.
Werdan, K.H., Heldt, W., Gelley, G.: Accumulation of bicarbonate in intact chloroplasts following a pH gradient. — Biochim. biophys. Acta 288: 430–441, 1972.
Wood, J.G., Sibly, P.M.: Carbonic anhydrase activity in plants in relation to zinc content. — Aust. J. sci. Res. B 5: 244–255, 1952.
Woodwell, G.M.: The carbon dioxide question. — Sci. American 283(1): 34–43, 1978.
Yagawa, Y., Shiraiwa, Y., Miyachi, S.: Carbonic anhydrase from the blue green alga (cyanobacterium) Anabaena variabilis. — Plant Cell Physiol. 25: 775–783, 1984.
Yee, D., Morel, F.M.M.: In vivo substitution of zinc by cobalt in carbonic anhydrase of a marine diatom. — Limnol. Oceanogr. 41: 575–577, 1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiwari, A., Kumar, P., Singh, S. et al. Carbonic anhydrase in relation to higher plants. Photosynthetica 43, 1–11 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-005-1011-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-005-1011-0