Abstract
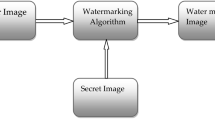
We present a tamper detection algorithm based on cat map and discrete wavelet decomposition. The algorithm is fragile to any tampering modification, but it is robust to harmless common image processing operations like JPEG compression, resizing, noising and filtering. The detection algorithm generates a witness image showing the tampered regions based on the blind analysis made on the tampered image. The embedding algorithm uses the approximation coefficient of a \(m \times m\) block image as the watermark to be inserted in the details coefficients of another block. The blocks pairs are associated using a cat map permutation of \(m \times m\) blocks. Moreover, we have been able to recover most of the original watermarked image based on a threshold depicted from the witness image. Simulations results demonstrate the efficiency of the tamper detection and recovery algorithm. We use many metrics to quantify the imperceptibility level like the PSNR, wPSNR, UIQ and SSIM. Also sensitivity and false alarm levels of the detection algorithm are measured and reported.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miscellaneous gray level image \(256 \times 256\). Computer Vision Group, University of Granada. http://decsai.ugr.es/cvg/dbimagenes/g256.php
Arnold, V., Avez, A.: Ergodic Problems of Classical Mechanics, 564. Benjamin, New York (1968)
Bao, J., Yang, Q.: Period of the discrete Arnold cat map and general cat map. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 1365–1375 (2012)
Chang, C., Hu, Y., Lu, T.: A watermarking-based image ownership and tampering authentication scheme. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 27, 439–446 (2006)
Daubechies, I.: Ten lectures on wavelets. In: CBMS-NSF Conference Series in Applied Mathematics SIAM Ed (1992)
Dyson, F., Falk, H.: Period of a discrete cat map**. Am. Math. Mon. 99(7), 603–614 (1992)
Hsu, C.S., Tu, S.F.: Probability-based tampering detection scheme for digital images. Opt. Commun. 283, 1737–1743 (2010)
Lin, P., Hsieh, C., Huang, P.: A hierarchical digital watermarking method for image tamper detection and recovery. Pattern Recognit. 38, 2519–2529 (2005)
Mallat, S.: A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 11(7), 674–693 (1989)
Meyer, Y.: Ondelettes et opérateurs, vol. I–III. Hermann, Paris (1990)
Pereira, S., Voloshynovskiy, S., Madueno, M., Marchand-Maillet, S., Pun, T.: Second generation benchmarking and application oriented evaluation. In: Information Hiding Workshop III Pittsburgh, PA, USA, (April 2001). http://cvml.unige.ch/ResearchProjects/Watermarking/Checkmark/
Peterson, G.: Arnold’s cat map. http://online.redwoods.cc.ca.us/instruct/darnold/laproj/Fall97/Gabe/catmap.pdf (1997)
Redi, J.A., Taktak, W., Dugelay, J.L.: Digital image forensics: a booklet for beginners. Multimed. Tools Appl. 51, 133–162 (2011)
Voloshynovskiy, S., Pereira, S., Iquise, V., Pun, T.: Attack modelling: towards a second generation watermarking benchmark. Signal Process. 81, 1177–1214 (2001)
Voloshynovsky, S., Herrigel, A., Baumgaertner, N., Pun, T.: A stochastic approach to content adaptive digital image watermarking. In: IH ’99 Proceedings of the Third International Workshop on Information Hiding, pp. 211–236. Dresden, Germany (1999)
Wu, L., Cao, X., Zhang, W., Wang, Y.: Detecting image forgeries using metrology. Mach. Vis. Appl. 23, 363–373 (2012)
Li, X.H., Zhao, Y.Q., Liao, M., Shih, F.Q., Shi, Y.Q.: Passive detection of copy-paste forgery between jpeg images. J. Cent. South Univ. 19, 2831–2851 (2012)
Yerushalmy, I., Hel-Or, H.: Digital image forgery detection based on lens and sensor aberration. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 92, 71–91 (2011)
Yu-**, Z., Sheng-hong, L., Shi-lin, W.: Detecting shifted double jpeg compression tampering utilizing both intra-block and inter-block correlations. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 18(1), 7–16 (2013)
Wang, Z.: A.C.B.: a universal image quality index. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 9(3), 81–84 (2002)
Wang, Z., Bovik, A.C., Sheik, H.R., Simoncelli, E.P.: Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(4), 600–612 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benrhouma, O., Hermassi, H. & Belghith, S. Tamper detection and self-recovery scheme by DWT watermarking. Nonlinear Dyn 79, 1817–1833 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1777-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1777-3