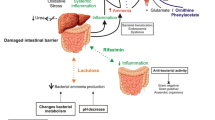
Abstract
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neuropsychiatric syndrome of both acute and chronic liver disease. As a metabolic disorder, HE is considered to be reversible and therefore is expected to resolve following the replacement of the diseased liver with a healthy liver. However, persisting neurological complications are observed in up to 47% of transplanted patients. Several retrospective studies have shown that patients with a history of HE, particularly overt-HE, had persistent neurological complications even after liver transplantation (LT). These enduring neurological conditions significantly affect patient's quality of life and continue to add to the economic burden of chronic liver disease on health care systems. This review discusses the journey of the brain through the progression of liver disease, entering the invasive surgical procedure of LT and the conditions associated with the post-transplant period. In particular, it will discuss the vulnerability of the HE brain to peri-operative factors and post-LT conditions which may explain non-resolved neurological impairment following LT. In addition, the review will provide evidence; (i) supporting overt-HE impacts on neurological complications post-LT; (ii) that overt-HE leads to permanent neuronal injury and (iii) the pathophysiological role of ammonia toxicity on astrocyte and neuronal injury/damage. Together, these findings will provide new insights on the underlying mechanisms leading to neurological complications post-LT.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AT2A:
-
Alzheimer type II astrocytes
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- BDL:
-
Bile-duct ligation
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- CCl4 :
-
Carbon tetrachloride
- cGMP:
-
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- CLD:
-
Chronic liver disease
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalogram
- GS:
-
Glutamine synthetase
- HE:
-
Hepatic encephalopathy
- LT:
-
Liver transplantation
- LTP:
-
Long-term potentiation
- mHE:
-
Minimal HE
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-D-aspartate
- PCA:
-
Portocaval anastomosis
- TAA:
-
Thioacetamide
References
Montagnese S, Bajaj JS (2019) Impact of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis on quality-of-life issues. Drugs 79:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-018-1019-y
Bajaj JS, Saeian K, Hafeezullah M et al (2008) Patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy have poor insight into their driving skills. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:1135–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2008.05.025
Vilstrup H, Amodio P, Bajaj J et al (2014) Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 practice guideline by the American association for the study of liver diseases and the European association for the study of the liver. Hepatology 60:715–735. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27210
Jepsen P, Ott P, Andersen PK et al (2010) Clinical course of alcoholic liver cirrhosis: a Danish population-based cohort study. Hepatology 51:1675–1682. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23500
Bajaj JS, O’Leary JG, Tandon P et al (2017) Hepatic encephalopathy is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis independent of other extrahepatic organ failures. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:565–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2016.09.157
Amodio P, Del Piccolo F, Pettenò E et al (2001) Prevalence and prognostic value of quantified electroencephalogram (EEG) alterations in cirrhotic patients. J Hepatol 35:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(01)00129-5
Romero-Gómez M, Boza F, García-Valdecasas MS et al (2001) Subclinical hepatic encephalopathy predicts the development of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol 96:2718–2723. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.04130.x
Rose CF, Amodio P, Bajaj JS et al (2020) Hepatic encephalopathy: novel insights into classification, pathophysiology and therapy. J Hepatol 73:1526–1547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.013
Seraj SM, Campbell EJ, Argyropoulos SK et al (2017) Hospital readmissions in decompensated cirrhotics: factors pointing toward a prevention strategy. World J Gastroenterol 23:6868–6876. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i37.6868
Sood KT, Wong RJ (2019) Hepatic encephalopathy is a strong predictor of early hospital readmission among cirrhosis patients. J Clin Exp Hepatol 9:484–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2019.01.005
Hirode G, Vittinghoff E, Wong RJ (2019) Increasing burden of hepatic encephalopathy among hospitalized adults: an analysis of the 2010–2014 national inpatient sample. Dig Dis Sci 64:1448–1457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-05576-9
Aldridge DR, Tranah EJ, Shawcross DL (2015) Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy: role of ammonia and systemic inflammation. J Clin Exp Hepatol 5:S7–S20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2014.06.004
Bosoi CR, Rose CF (2009) Identifying the direct effects of ammonia on the brain. Metab Brain Dis 24:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-008-9112-7
Ochoa-Sanchez R, Rose CF (2018) Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease. J Clin Exp Hepatol 8:262–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2018.08.001
Roberts MS, Angus DC, Bryce CL et al (2004) Survival after liver transplantation in the United States: a disease-specific analysis of the UNOS database. Liver Transpl 10:886–897. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.20137
Zivković SA (2013) Neurologic complications after liver transplantation. World J Hepatol 5:409–416. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v5.i8.409
Weiss N, Thabut D (2019) Neurological complications occurring after liver transplantation: role of risk factors, hepatic encephalopathy, and acute (on chronic) brain injury. Liver Transpl 25:469–487. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.25420
Stracciari A, Guarino M (2001) Neuropsychiatric complications of liver transplantation. Metab Brain Dis 16:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1011698526025
Agildere AM, Başaran C, Cakir B et al (2006) Evaluation of neurologic complications by brain MRI in kidney and liver transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 38:611–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2005.12.113
Raffa GM, Agnello F, Occhipinti G et al (2019) Neurological complications after cardiac surgery: a retrospective case-control study of risk factors and outcome. J Cardiothorac Surg 14:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13019-019-0844-8
Estol CJ, Pessin MS, Martinez AJ (1991) Cerebrovascular complications after orthotopic liver transplantation: a clinicopathologic study. Neurology 41:815–819. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.41.6.815
Lescot T, Karvellas CJ, Chaudhury P et al (2013) Postoperative delirium in the intensive care unit predicts worse outcomes in liver transplant recipients. Can J Gastroenterol 27:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/289185
Lin X-H, Teng S, Wang L et al (2017) Fatigue and its associated factors in liver transplant recipients in Bei**g: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 7(2):e011840. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011840
Pflugrad H, Tryc AB, Goldbecker A et al (2019) Cerebral metabolite alterations in patients with posttransplant encephalopathy after liver transplantation. PLoS ONE 14(8):e0221626. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0221626
Rodrigue JR, Nelson DR, Reed AI et al (2010) Fatigue and sleep quality before and after liver transplantation. Prog Transplant 20:221–233. https://doi.org/10.7182/prtr.20.3.x82q1832184j4733
Teperman LW (2013) Impact of pretransplant hepatic encephalopathy on liver posttransplantation outcomes. Int J Hepatol 2013:952828. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/952828
Blanco R, De Girolami U, Jenkins RL, Khettry U (1995) Neuropathology of liver transplantation. Clin Neuropathol 14:109–117
Campagna F, Montagnese S, Schiff S et al (2014) Cognitive impairment and electroencephalographic alterations before and after liver transplantation: what is reversible? Liver Transpl 20:977–986. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.23909
Zhang X-D, Cheng Y, Poon CS et al (2015) Long-and short-range functional connectivity density alteration in non-alcoholic cirrhotic patients one month after liver transplantation: a resting-state fMRI study. Brain Res 1620:177–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2015.04.046
Senzolo M, Pizzolato G, Ferronato C et al (2009) Long-term evaluation of cognitive function and cerebral metabolism in liver transplanted patients. Transplant Proc 41:1295–1296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.03.087
Bhutiani N, Jones CM, Cannon RM et al (2018) Assessing relative cost of complications following orthotopic liver transplant. Clin Transplant 32:e13209. https://doi.org/10.1111/ctr.13209
Derle E, Kibaroğlu S, Öcal R et al (2015) Neurologic complications after liver transplant: experience at a single center. Exp Clin Transplant 13(Suppl 1):327–330. https://doi.org/10.6002/ect.mesot2014.p177
Moini M, Schilsky ML, Tichy EM (2015) Review on immunosuppression in liver transplantation. World J Hepatol 7:1355–1368. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i10.1355
Pillai AA, Levitsky J (2009) Overview of immunosuppression in liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 15:4225–4233. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.4225
Beydoun MA, Dore GA, Canas J-A et al (2018) Systemic inflammation is associated with longitudinal changes in cognitive performance among urban adults. Front Aging Neurosci 10:313. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00313
Brezzo G, Simpson J, Ameen-Ali KE et al (2020) Acute effects of systemic inflammation upon the neuro-glial-vascular unit and cerebrovascular function. Brain Behav Immun - Health 5:100074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100074
Kamdar KY, Rooney CM, Heslop HE (2011) Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease following liver transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 16:274–280. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOT.0b013e3283465715
Huffman JC, Popkin MK, Stern TA (2003) Psychiatric considerations in the patient receiving organ transplantation: a clinical case conference. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 25:484–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0163-8343(03)00090-2
Rabinstein AA, Keegan MT (2013) Neurologic complications of anesthesia: a practical approach. Neurol Clin Pract 3:295–304. https://doi.org/10.1212/CPJ.0b013e3182a1b9bd
Kumar SS, Mashour GA, Picton P (2018) Neurologic considerations and complications related to liver transplantation. Anesthesiology 128:1008–1014. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000002148
Wu L, Zhao H, Weng H, Ma D (2019) Lasting effects of general anesthetics on the brain in the young and elderly: “mixed picture” of neurotoxicity, neuroprotection and cognitive impairment. J Anesth 33:321–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-019-02623-7
Sotil EU, Gottstein J, Ayala E et al (2009) Impact of preoperative overt hepatic encephalopathy on neurocognitive function after liver transplantation. Liver Transplant 15:184–192. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.21593
Garcia-Martinez R, Rovira A, Alonso J et al (2011) Hepatic encephalopathy is associated with posttransplant cognitive function and brain volume. Liver Transpl 17:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.22197
Nardelli S, Allampati S, Riggio O et al (2017) Hepatic encephalopathy is associated with persistent learning impairments despite adequate medical treatment: a multicenter, international study. Dig Dis Sci 62:794–800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-016-4425-6
Pujol A, Graus F, Rimola A et al (1994) Predictive factors of in-hospital CNS complications following liver transplantation. Neurology 44:1226–1230. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.44.7.1226
Dhar R, Young GB, Marotta P (2008) Perioperative neurological complications after liver transplantation are best predicted by pre-transplant hepatic encephalopathy. Neurocrit Care 8:253–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-007-9020-4
Mechtcheriakov S, Graziadei IW, Mattedi M et al (2004) Incomplete improvement of visuo-motor deficits in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 10:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.20009
Ahluwalia V, Wade JB, Moeller FG et al (2015) The etiology of cirrhosis is a strong determinant of brain reserve: a multimodal magnetic resonance imaging study. Liver Transpl 21:1123–1132. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.24163
Patel AV, Wade JB, Thacker LR et al (2015) Cognitive reserve is a determinant of health-related quality of life in patients with cirrhosis, independent of covert hepatic encephalopathy and model for end-stage liver disease score. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:987–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2014.09.049
Fan Y, Liu X (2018) Alterations in expression and function of ABC family transporters at blood-brain barrier under liver failure and their clinical significances. Pharmaceutics 10(3):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030102
Wijdicks EF (2001) Neurotoxicity of immunosuppressive drugs. Liver Transpl 7:937–942. https://doi.org/10.1053/jlts.2001.27475
Scott TR, Kronsten VT, Hughes RD, Shawcross DL (2013) Pathophysiology of cerebral oedema in acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 19:9240–9255. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9240
Detry O, Arkadopoulos N, Ting P et al (1999) Intracranial pressure during liver transplantation for fulminant hepatic failure. Transplantation 67:767–770. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007890-199903150-00024
Fu KA, DiNorcia J, Sher L et al (2014) Predictive factors of neurological complications and one-month mortality after liver transplantation. Front Neurol 5:275. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2014.00275
Hori T, Ogura Y, Onishi Y et al (2016) Systemic hemodynamics in advanced cirrhosis: concerns during perioperative period of liver transplantation. World J Hepatol 8:1047–1060. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i25.1047
Olde Damink SWM, Dejong CHC, Jalan R (2009) Review article: hyperammonaemic and catabolic consequences of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 29:801–810. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2009.03938.x
Clément MA, Bosoi CR, Oliveira MM et al (2020) Bile-duct ligation renders the brain susceptible to hypotension-induced neuronal degeneration: implications of ammonia. J Neurochem 157:561–573. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15290
Magistretti PJ, Allaman I (2015) A cellular perspective on brain energy metabolism and functional imaging. Neuron 86:883–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.035
Buis CI, Wiesner RH, Krom RAF et al (2002) Acute confusional state following liver transplantation for alcoholic liver disease. Neurology 59:601–605. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.59.4.601
Lewis MB, Howdle PD (2003) Neurologic complications of liver transplantation in adults. Neurology 61:1174–1178. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000089487.42870.c6
Wijarnpreecha K, Chesdachai S, Jaruvongvanich V, Ungprasert P (2018) Hepatitis C virus infection and risk of Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 30:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0000000000000991
Mathew S, Faheem M, Ibrahim SM et al (2016) Hepatitis C virus and neurological damage. World J Hepatol 8:545–556. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i12.545
Weinstein G, Zelber-Sagi S, Preis SR et al (2018) Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with lower brain volume in healthy middle-aged adults in the Framingham Study. JAMA Neurol 75:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.3229
Escartin C, Galea E, Lakatos A et al (2021) Reactive astrocyte nomenclature, definitions, and future directions. Nat Neurosci 24:312–325. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-020-00783-4
Agarwal AN, Mais DD (2019) Sensitivity and specificity of Alzheimer type II astrocytes in hepatic encephalopathy. Arch Pathol Lab Med. https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2018-0455-OA
Bajaj JS, Schubert CM, Heuman DM et al (2010) Persistence of cognitive impairment after resolution of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 138:2332–2340. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.02.015
Chen H-J, Jiao Y, Zhu X-Q et al (2013) Brain dysfunction primarily related to previous overt hepatic encephalopathy compared with minimal hepatic encephalopathy: resting-state functional MR imaging demonstration. Radiology 266:261–270. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12120026
Ishihara T, Ito M, Niimi Y et al (2013) Clinical and radiological impact of liver transplantation for brain in cirrhosis patients without hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:2341–2347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2013.08.015
Lin W-C, Hsu T-W, Chen C-L et al (2014) Reestablishing brain networks in patients without overt hepatic encephalopathy after liver transplantation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34:1877–1886. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2014.143
Prasad S, Dhiman RK, Duseja A et al (2007) Lactulose improves cognitive functions and health-related quality of life in patients with cirrhosis who have minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 45:549–559. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21533
Chavarria L, Cordoba J (2015) Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy in hepatic encephalopathy. J Clin Exp Hepatol 5:S69–S74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2013.10.001
Zeneroli ML, Cioni G, Vezzelli C et al (1987) Prevalence of brain atrophy in liver cirrhosis patients with chronic persistent encephalopathy. Evaluation by computed tomography. J Hepatol 4:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80536-6
García Martínez R, Rovira A, Alonso J et al (2010) A long-term study of changes in the volume of brain ventricles and white matter lesions after successful liver transplantation. Transplantation 89:589–594. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3181ca7bb3
Butterworth RF (2007) Neuronal cell death in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 22:309–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-007-9072-3
Vasan S, Kumar A (2021) Wernicke encephalopathy. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island, FL
Kril JJ, Butterworth RF (1997) Diencephalic and cerebellar pathology in alcoholic and nonalcoholic patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology 26:837–841. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.510260405
Montoliu C, Gonzalez-Escamilla G, Atienza M et al (2012) Focal cortical damage parallels cognitive impairment in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Neuroimage 61:1165–1175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.041
Klejman A, Wegrzynowicz M, Szatmari EM et al (2005) Mechanisms of ammonia-induced cell death in rat cortical neurons: roles of NMDA receptors and glutathione. Neurochem Int 47:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2005.04.006
Takanashi J, Barkovich AJ, Cheng SF et al (2003) Brain MR imaging in neonatal hyperammonemic encephalopathy resulting from proximal urea cycle disorders. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1184–1187
Dolman CL, Clasen RA, Dorovini-Zis K (1988) Severe cerebral damage in ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Clin Neuropathol 7:10–15
Braissant O, McLin VA, Cudalbu C (2013) Ammonia toxicity to the brain. J Inherit Metab Dis 36:595–612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-012-9546-2
Mohammadian F, Firouzjaei MA, Haghani M et al (2019) Inhibition of inflammation is not enough for recovery of cognitive impairment in hepatic encephalopathy: effects of minocycline and ibuprofen. Brain Res Bull 149:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.04.015
Jeong JH, Kim DK, Lee N-S et al (2018) Neuroprotective effect of nortriptyline in overt hepatic encephalopathy through attenuation of mitochondrial dysfunction. ASN Neuro 10:1759091418810583. https://doi.org/10.1177/1759091418810583
Khanna A, Trigun SK (2016) Resveratrol normalizes hyperammonemia induced pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic conditions in rat brain. Int J Complement Altern Med 4(2):00115. https://doi.org/10.15406/ijcam.2016.04.00115
García-Lezana T, Oria M, Romero-Giménez J et al (2017) Cerebellar neurodegeneration in a new rat model of episodic hepatic encephalopathy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 37:927–937. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X16649196
Yang N, Liu H, Jiang Y et al (2015) Lactulose enhances neuroplasticity to improve cognitive function in early hepatic encephalopathy. Neural Regen Res 10:1457–1462. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.165516
Kosenko E, Kaminsky Y, Solomadin I et al (2007) Acute ammonia neurotoxicity in vivo involves increase in cytoplasmic protein P53 without alterations in other markers of apoptosis. J Neurosci Res 85:2491–2499. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21385
Rao KVR, Panickar KS, Jayakumar AR, Norenberg MD (2005) Astrocytes protect neurons from ammonia toxicity. Neurochem Res 30:1311–1318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-8803-2
Wang F, Chen S, Jiang Y et al (2018) Effects of ammonia on apoptosis and oxidative stress in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Mutagenesis 33:291–299. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/gey023
Cai Z, Zhu X, Zhang G et al (2019) Ammonia induces calpain-dependent cleavage of CRMP-2 during neurite degeneration in primary cultured neurons. Aging 11:4354–4366. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102053
Cai L, Chan JSY, Yan JH, Peng K (2014) Brain plasticity and motor practice in cognitive aging. Front Aging Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00031
Forrest MP, Parnell E, Penzes P (2018) Dendritic structural plasticity and neuropsychiatric disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 19:215–234. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2018.16
Yuan T-F, Li W-G, Zhang C et al (2020) Targeting neuroplasticity in patients with neurodegenerative diseases using brain stimulation techniques. Transl Neurodegener 9:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-020-00224-z
Chen J-R, Wang B-N, Tseng G-F et al (2014) Morphological changes of cortical pyramidal neurons in hepatic encephalopathy. BMC Neurosci 15:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-15-15
Chepkova AN, Sergeeva OA, Görg B et al (2017) Impaired novelty acquisition and synaptic plasticity in congenital hyperammonemia caused by hepatic glutamine synthetase deficiency. Sci Rep 7:40190. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40190
Anand KS, Dhikav V (2012) Hippocampus in health and disease: an overview. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 15:239–246. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-2327.104323
Muñoz MD, Monfort P, Gaztelu JM, Felipo V (2000) Hyperammonemia impairs NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation in the CA1 of rat hippocampus in vitro. Neurochem Res 25:437–441. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1007547622844
Izumi Y, Svrakic N, O’Dell K, Zorumski CF (2013) Ammonia inhibits long-term potentiation via neurosteroid synthesis in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neuroscience 233:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.035
Chen S-D, Wu C-L, Hwang W-C, Yang D-I (2017) More insight into BDNF against neurodegeneration: anti-apoptosis, anti-oxidation, and suppression of autophagy. Int J Mol Sci 18(3):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030545
Lau D, Bengtson CP, Buchthal B, Bading H (2015) BDNF reduces toxic extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signaling via synaptic NMDA receptors and nuclear-calcium-induced transcription of inhba/Activin A. Cell Rep 12:1353–1366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.038
Tanqueiro SR, Ramalho RM, Rodrigues TM et al (2018) Inhibition of NMDA receptors prevents the loss of BDNF function induced by Amyloid β. Front Pharmacol 9:237. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00237
Wilasco MIA, Uribe-Cruz C, Santetti D et al (2016) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in children and adolescents with cirrhosis due to biliary atresia. Ann Nutr Metab 69:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1159/000447364
Dhanda S, Gupta S, Halder A et al (2018) Systemic inflammation without gliosis mediates cognitive deficits through impaired BDNF expression in bile duct ligation model of hepatic encephalopathy. Brain Behav Immun 70:214–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2018.03.002
Galland F, Negri E, Da Ré C et al (2017) Hyperammonemia compromises glutamate metabolism and reduces BDNF in the rat hippocampus. NeuroToxicol 62:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2017.05.006
Verkhratsky A, Zorec R, Parpura V (2017) Stratification of astrocytes in healthy and diseased brain. Brain Pathol 27:629–644. https://doi.org/10.1111/bpa.12537
Verkhratsky A, Nedergaard M (2018) Physiology of astroglia. Physiol Rev 98:239–389. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00042.2016
Butterworth RF (2002) Glutamate transporters in hyperammonemia. Neurochem Int 41:81–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-0186(02)00027-x
Rovira A, Alonso J, Córdoba J (2008) MR imaging findings in hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Neuroradiol 29:1612–1621. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1139
Jaeger V, DeMorrow S, McMillin M (2019) The direct contribution of astrocytes and microglia to the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. J Clin Transl Hepatol 7:352–361. https://doi.org/10.14218/JCTH.2019.00025
Rose CF, Verkhratsky A, Parpura V (2013) Astrocyte glutamine synthetase: pivotal in health and disease. Biochem Soc Trans 41:1518–1524. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20130237
Thumburu KK, Dhiman RK, Vasishta RK et al (2014) Expression of astrocytic genes coding for proteins implicated in neural excitation and brain edema is altered after acute liver failure. J Neurochem 128:617–627. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12511
Chastre A, Jiang W, Desjardins P, Butterworth RF (2010) Ammonia and proinflammatory cytokines modify expression of genes coding for astrocytic proteins implicated in brain edema in acute liver failure. Metab Brain Dis 25:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-010-9185-y
Jayakumar AR, Tong XY, Curtis KM et al (2014) Decreased astrocytic thrombospondin-1 secretion after chronic ammonia treatment reduces the level of synaptic proteins: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Neurochem 131:333–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12810
Norenberg MD (1987) The role of astrocytes in hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Pathol 6:13–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02833599
Jover R, Rodrigo R, Felipo V et al (2006) Brain edema and inflammatory activation in bile duct ligated rats with diet-induced hyperammonemia: a model of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis. Hepatology 43:1257–1266. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21180
Görg B, Karababa A, Häussinger D (2018) Hepatic encephalopathy and astrocyte senescence. J Clin Exp Hepatol 8:294–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jceh.2018.05.003
Görg B, Karababa A, Shafigullina A et al (2015) Ammonia-induced senescence in cultured rat astrocytes and in human cerebral cortex in hepatic encephalopathy: hepatic encephalopathy and senescence. Glia 63:37–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22731
Murthy CR, Rama Rao KV, Bai G, Norenberg MD (2001) Ammonia-induced production of free radicals in primary cultures of rat astrocytes. J Neurosci Res 66:282–288. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.1222
Mederos S, González-Arias C, Perea G (2018) Astrocyte–neuron networks: a multilane highway of signaling for homeostatic brain function. Front Synaptic Neurosci 10:45. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsyn.2018.00045
Oberheim NA, Takano T, Han X et al (2009) Uniquely hominid features of adult human astrocytes. J Neurosci 29:3276–3287. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4707-08.2009
Lemberg A, Fernández MA (2009) Hepatic encephalopathy, ammonia, glutamate, glutamine and oxidative stress. Ann Hepatol 8:95–102
Kritis AA, Stamoula EG, Paniskaki KA, Vavilis TD (2015) Researching glutamate – induced cytotoxicity in different cell lines: a comparative/collective analysis/study. Front Cell Neurosci 9:91. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2015.00091
Vaquero J, Butterworth RF (2006) The brain glutamate system in liver failure. J Neurochem 98:661–669. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03918.x
Kimelberg HK (2005) Astrocytic swelling in cerebral ischemia as a possible cause of injury and target for therapy. Glia 50:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20174
Rodrigo R, Cauli O, Boix J et al (2009) Role of NMDA receptors in acute liver failure and ammonia toxicity: therapeutical implications. Neurochem Int 55:113–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2009.01.007
Ahmadi S, Poureidi M, Rostamzadeh J (2015) Hepatic encephalopathy induces site-specific changes in gene expression of GluN1 subunit of NMDA receptor in rat brain. Metab Brain Dis 30:1035–1041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-015-9669-x
Felipo V (2006) Contribution of altered signal transduction associated to glutamate receptors in brain to the neurological alterations of hepatic encephalopathy. World J Gastroenterol 12:7737–7743. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i48.7737
Hermenegildo C, Monfort P, Felipo V (2000) Activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat brain in vivo following acute ammonia intoxication: characterization by in vivo brain microdialysis. Hepatology 31:709–715. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.510310322
Li Y, Maher P, Schubert D (1997) Requirement for cGMP in nerve cell death caused by glutathione depletion. J Cell Biol 139:1317–1324. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.139.5.1317
Montoliu C, Llansola M, Monfort P et al (2001) Role of nitric oxide and cyclic GMP in glutamate-induced neuronal death. Neurotox Res 3:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033190
Lavoie J, Giguère J-F, Layrargues GP, Butterworth RF (1987) Activities of neuronal and astrocytic marker enzymes in autopsied brain tissue from patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 2:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00999698
Rackayova V, Braissant O, Rougemont A-L et al (2020) Longitudinal osmotic and neurometabolic changes in young rats with chronic cholestatic liver disease. Sci Rep 10:7536. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64416-3
Bosoi CR, Rose CF (2013) Brain edema in acute liver failure and chronic liver disease: similarities and differences. Neurochem Int 62:446–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2013.01.015
Häussinger D, Kircheis G, Fischer R et al (2000) Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: a clinical manifestation of astrocyte swelling and low-grade cerebral edema? J Hepatol 32:1035–1038. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(00)80110-5
Ventura-Cots M, Carmona I, Moreno C et al (2017) Duration of the acute hepatic encephalopathy episode determines survival in cirrhotic patients. Ther Adv Gastroenterol 11:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756283X17743419
Patwardhan VR, Jiang ZG, Risech-Neiman Y et al (2016) Serum ammonia is associated with transplant-free survival in hospitalized patients with acutely decompensated cirrhosis [corrected]. J Clin Gastroenterol 50:345–350. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0000000000000443
Mookerjee RP, Sheikh SM, Agarwal B et al (2019) Prognostic role of ammonia in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 70:982–994. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30534
Vierling JM, Mokhtarani M, Brown RS et al (2016) Fasting blood ammonia predicts risk and frequency of hepatic encephalopathy episodes in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:903-906.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2015.11.018
Dasarathy S, Mookerjee RP, Rackayova V et al (2017) Ammonia toxicity: from head to toe? Metab Brain Dis 32:529–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9938-3
Lucidi C, Ginanni Corradini S, Abraldes JG et al (2016) Hepatic encephalopathy expands the predictivity of model for end-stage liver disease in liver transplant setting: evidence by means of 2 independent cohorts. Liver Transplant 22:1333–1342. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.24517
Chavarria L, Alonso J, García-Martínez R et al (2011) Biexponential analysis of diffusion-tensor imaging of the brain in patients with cirrhosis before and after liver transplantation. Am J Neuroradiol 32:1510–1517. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2533
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR). Figures are created with BioRender.com.
Funding
Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RO, FT, and CFR, contributed to the review concept and wrote the manuscript review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Special issue: In Honor of Vladimir Parpura.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ochoa-Sanchez, R., Tamnanloo, F. & Rose, C.F. Hepatic Encephalopathy: From Metabolic to Neurodegenerative. Neurochem Res 46, 2612–2625 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03372-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03372-4