Abstract
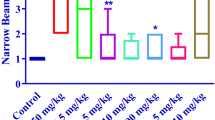
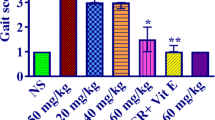
Acrylamide (ACR) is extensively used in industrial areas and has been demonstrated to induce neurotoxicity via oxidative stress and apoptosis. In this study, we assessed the probable protective effects of thymoquinone (TQ), an active constituent of Nigella sativa, against ACR-induced neurotoxicity. ACR (50 mg/kg, i.p., for 11 days) and TQ (2.5, 5 and 10 mg/kg, i.p., for 11 days) were administered to rats. On 12th day, gait score was examined and rats were sacrificed. Malondialdehyde (MDA) and reduced glutathione (GSH) contents were determined in sciatic nerve. Furthermore, western blotting was conducted. The exposure of rats to ACR caused severe gait disabilities. The MDA and GSH contents were increased and decreased, respectively. ACR decreased P-ERK/ERK ratio and myelin basic protein (MBP) content, but significantly increased P-JNK/JNK, P-P38/P38, Bax/Bcl-2 ratios and caspase 3 and 9 levels. Concurrently administration of TQ (5 and 10 mg/kg) with ACR, prevented gait abnormalities and meaningfully reduced MDA and elevated the GSH contents. Furthermore, TQ (5 mg/kg) elevated the P-ERK/ERK ratio and MBP content while reduced the P-JNK/JNK, P-P38/P38 ratios and apoptotic markers. MAP kinase and apoptosis signaling pathways were involved in ACR-induced neurotoxicity in rat sciatic nerve and TQ significantly reduced ACR neurotoxicity. TQ afforded neuroprotection, in part, due to its anti-oxidative stress and anti-apoptotic mechanisms.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Żyżelewicz D, Nebesny E, Oracz J (2010) Acrylamide-formation, physicochemical and biological properties. Bromatol Chem Toksykol 43:415–427
Jankowska JHJ, Potocki A (2009) Acrylamide as a foreign substance in food (in Polish). Problemy Higieny i Epidemiologii 90:171–174
Dybing E, Sanner T (2003) Risk assessment of acrylamide in foods. Toxicol Sci 75:7–15
Organization WH (2002) FAO/WHO consultation on the health implications of acrylamide in food. Summary report of a meeting held in Geneva, 25–27 June 2002. World Health Organization, Geneva
Grob K, Biedermann M, Biedermann-Brem S, Noti A, Imhof D, Amrein T, Pfefferle A, Bazzocco D (2003) French fries with less than 100 µg/kg acrylamide. A collaboration between cooks and analysts. Eur Food Res Technol 217:185–194
Cummins E, Butler F, Brunton N, Gormley R (2006) Factors affecting acrylamide formation in processed potato products a simulation approach. In: 13th World Congress of Food Science & Technology 2006, Nantes, pp 719–719
Pennisi M, Malaguarnera G, Puglisi V, Vinciguerra L, Vacante M, Malaguarnera M (2013) Neurotoxicity of acrylamide in exposed workers. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:3843
LoPachin RM (2005) Acrylamide neurotoxicity: neurological, morhological and molecular endpoints in animal models. In: Chemistry and safety of acrylamide in food. Springer, Boston, pp 21–37
Mehri S, Abnous K, Khooei A, Mousavi SH, Shariaty VM, Hosseinzadeh H (2015) Crocin reduced acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in Wistar rat through inhibition of oxidative stress. Iran J Basic Med Sci 18:902–908
Zhu YJ, Zeng T, Zhu YB, Yu SF, Wang QS, Zhang LP, Guo X, **e KQ (2008) Effects of acrylamide on the nervous tissue antioxidant system and sciatic nerve electrophysiology in the rat. Neurochem Res 33:2310–2317
LoPachin RM, Barber DS, Geohagen BC, Gavin T, He D, Das S (2007) Structure-toxicity analysis of type-2 alkenes: in vitro neurotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 95:136–146
Arroyo EJ, Scherer SS (2000) On the molecular architecture of myelinated fibers. Histochem Cell Biol 113:1–18
LoPachin RM, Castiglia CM, Saubermann AJ (1992) Acrylamide disrupts elemental composition and water content of rat tibial nerve: I. myelinated axons. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 115:21–34
Peter K, Santiago L (2000) Regulation of protein function by S-glutathiolation in response to oxidative and nitrosative stress. Eur J Biochem 267:4928–4944
Altinoz E, Turkoz Y (2014) The protective role of n-acetylcysteine against acrylamide-induced genotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Gene Ther Mol Biol 16:35–43
Kopańska M, Lukáč N, Kapusta E, Formicki G (2015) Acrylamide influence on activity of acetylcholinesterase, thiol groups, and malondialdehyde content in the brain of swiss mice. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 29:472–478
Johnson GL, Lapadat R (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science 298:1911–1912
Kim K-H, Park B, Rhee D-K, Pyo S (2015) Acrylamide induces senescence in macrophages through a process involving ATF3, ROS, p38/JNK, and a telomerase-independent pathway. Chem Res Toxicol 28:71–86
Pan X, Yan D, Wang D, Wu X, Zhao W, Lu Q, Yan H (2017) Mitochondrion-mediated apoptosis induced by acrylamide is regulated by a balance between Nrf2 antioxidant and MAPK signaling pathways in PC12 Cells. Mol Neurobiol 54:4781–4794
Lakshmi D, Gopinath K, Jayanthy G, Anjum S, Prakash D, Sudhandiran G (2012) Ameliorating effect of fish oil on acrylamide induced oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral cortex. Neurochem Res 37:1859–1867
Mehri S, Abnous K, Mousavi SH, Shariaty VM, Hosseinzadeh H (2012) Neuroprotective effect of crocin on acrylamide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:227–235
Sumizawa T, Igisu H (2007) Apoptosis induced by acrylamide in SH-SY5Y cells. Arch Toxicol 81:279–282
Li S-x, Cui N, Zhang C-l, Zhao X-l, Yu S-f, **e K-q (2006) Effect of subchronic exposure to acrylamide induced on the expression of bcl-2, bax and caspase-3 in the rat nervous system. Toxicology 217:46–53
Menéndez R, García T, Garateix A, Morales RA, Regalado EL, Laguna A, Valdés O, Fernández MD (2014) Neuroprotective and antioxidant effects of Thalassia testudinum extract BM-21, against acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in mice. J Pharm Pharmacogn Res 2:53–62
Esmaeelpanah E, Rahmatkhah A, Poormahmood N, Razavi BM, Vahdati Hasani F, Hosseinzadeh H (2015) Protective effect of green tea aqueous extract on acrylamide induced neurotoxicity. Jundishapur J Nat Pharm Prod 10:e18406
Hosseinzadeh H, Tabeshpur J, Mehri S (2014) Effect of saffron extract on acrylamide-induced toxicity: in vitro and in vivo assessment. Chin J Integr Med (In Press)
Motamedshariaty VS, Amel Farzad S, Nassiri-Asl M, Hosseinzadeh H (2014) Effects of rutin on acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity. DARU J Pharm Sci 22:27
Mehri S, Veis Karami H, Vahdati Hassani F, Hosseinzadeh H (2014) Chrysin reduced acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in both in vitro and in vivo assessments. Iran Biomed J 18:101–106
Mehri S, Meshki MA, Hosseinzadeh H (2015) Linalool as a neuroprotective agent against acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in Wistar rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 38:162–166
Ahmad A, Husain A, Mujeeb M, Khan SA, Najmi AK, Siddique NA, Damanhouri ZA, Anwar F (2013) A review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa: A miracle herb. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 3:337–352
Goreja W (2003) Black seed: nature’s miracle remedy. Amazing Herbs Press, New York
Kanter M, Coskun O, Uysal H (2006) The antioxidative and antihistaminic effect of Nigella sativa and its major constituent, thymoquinone on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage. Arch Toxicol 80:217–224
Hosseinzadeh H, Parvardeh S, Asl MN, Sadeghnia HR, Ziaee T (2007) Effect of thymoquinone and Nigella sativa seeds oil on lipid peroxidation level during global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat hippocampus. Phytomedicine 14:621–627
Abd El-Ghany RM, Sharaf NM, Kassem LA, Mahran LG, Heikal OA (2009) Thymoquinone triggers anti-apoptotic signaling targeting death ligand and apoptotic regulators in a model of hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury. Drug Discov Ther 3:296–306
Al-Ghamdi MS (2001) The anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activity of Nigella sativa. J Ethnopharmacol 76:45–48
Ebrahimi SS, Oryan S, Izadpanah E, Hassanzadeh K (2017) Thymoquinone exerts neuroprotective effect in animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol Lett 276:108–114
Oguz S, Kanter M, Erboga M, Erenoglu C (2012) Protective effects of thymoquinone against cholestatic oxidative stress and hepatic damage after biliary obstruction in rats. J Mol Histol 43:151–159
Mollazadeh H, Hosseinzadeh H (2014) The protective effect of Nigella sativa against liver injury: a review. Iran J Basic Med Sci 17:958–966
Boskabady MH, Mohsenpoor N, Takaloo L (2010) Antiasthmatic effect of Nigella sativa in airways of asthmatic patients. Phytomedicine 17:707–713
Abdel-Sater KA (2009) Gastroprotective effects of Nigella sativa oil on the formation of stress gastritis in hypothyroidal rats. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 1:143–149
Hosseinian S, Hadjzadeh M-A-R, Roshan N, Khazaei M, Shahraki S, Mohebbati R, Rad A (2018) Renoprotective effect of Nigella sativa against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rat. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 29:19–29
Agbaria R, Gabarin A, Dahan A, Ben-Shabat S (2015) Anticancer activity of Nigella sativa (black seed) and its relationship with the thermal processing and quinone composition of the seed. Drug Des Devel Ther 9:3119–3124
Mollazadeh H, Afshari AR, Hosseinzadeh H (2017) Review on the potential therapeutic roles of Nigella sativa in the treatment of patients with cancer: involvement of apoptosis: black cumin and cancer. J Pharmacopunct 20:158–172
Tavakkoli A, Mahdian V, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H (2017) Review on clinical trials of black seed (Nigella sativa) and its active constituent, thymoquinone. J Pharmacopunct 20:179–193
Mehri S, Shahi M, Razavi BM, Hassani FV, Hosseinzadeh H (2014) Neuroprotective effect of thymoquinone in acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in Wistar rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 17:1007–1011
Tavakkoli A, Ahmadi A, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H (2017) Black seed (Nigella sativa) and its constituent thymoquinone as an antidote or a protective agent against natural or chemical toxicities. Iran J Pharm Res 16:2–23
Hosseini SM, Taghiabadi E, Abnous K, Hariri AT, Pourbakhsh H, Hosseinzadeh H (2017) Protective effect of thymoquinone, the active constituent of Nigella sativa fixed oil, against ethanol toxicity in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 20:927–939
Pourbakhsh H, Taghiabadi E, Abnous K, Hariri AT, Hosseini SM, Hosseinzadeh H (2014) Effect of Nigella sativa fixed oil on ethanol toxicity in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 17:1020–1031
Aboul Ezz HS, Khadrawy YA, Noor NA (2011) The neuroprotective effect of curcumin and Nigella sativa oil against oxidative stress in the pilocarpine model of epilepsy: a comparison with valproate. Neurochem Res 36:2195
Farkhondeh T, Samarghandian S, Shahri AMP, Samini F (2018) The neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone: a review. Dose-Response 16:1559325818761455–1559325818761455
Radad K, Hassanein K, Al-Shraim M, Moldzio R, Rausch W-D (2014) Thymoquinone ameliorates lead-induced brain damage in Sprague Dawley rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 66:13–17
Erboga M, Kanter M, Aktas C, Sener U, Fidanol Erboga Z, Bozdemir Donmez Y, Gurel A (2016) Thymoquinone ameliorates cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in rats is based on its anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidant properties. Biol Trace Elem Res 170:165–172
Yang Y, Bai T, Sun P, Lian L-H, Yao Y-L, Zheng H-X, Li X, Li J-B, Wu Y-L, Nan J-X (2015) Thymoquinone, a bioactive component of Nigella sativa Linn seeds or traditional spice, attenuates acute hepatic failure and blocks apoptosis via the MAPK signaling pathway in mice. RSC Adv 5:7285–7290
Ismail N, Ismail M, Mazlan M, Latiff LA, Imam MU, Iqbal S, Azmi NH, Ghafar SAA, Chan KW (2013) Thymoquinone prevents β-amyloid neurotoxicity in primary cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33:1159–1169
Ullah I, Ullah N, Naseer MI, Lee HY, Kim MO (2012) Neuroprotection with metformin and thymoquinone against ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in prenatal rat cortical neurons. BMC Neurosci 13:11
Ismail N, Ismail M, Azmi NH, Abu Bakar MF, Basri H, Abdullah MA (2016) Modulation of hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human neuronal cells by thymoquinone-rich fraction and thymoquinone via transcriptomic regulation of antioxidant and apoptotic signaling genes. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:15
Limón-Pacheco JH, Hernández NA, Fanjul-Moles ML, Gonsebatt ME (2007) Glutathione depletion activates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways that display organ-specific responses and brain protection in mice. Free Radic Biol Med 43:1335–1347
Dodelet-Devillers A, Zullian C, Vachon P, Beaudry F (2016) Assessment of stability of ketamine-xylazine preparations with or without acepromazine using high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Can J Vet Res 80:86–89
Islam MS, Oliveira MC, Wang Y, Henry FP, Randolph MA, Park BH, de Boer JF (2012) Extracting structural features of rat sciatic nerve using polarization-sensitive spectral domain optical coherence tomography. J Biomed Opt 17:056012–056012
Draper HH, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. In: Methods in enzymol. Academic Press, New York, pp 421–431
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205
Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B (1979) Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 582:67–78
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Shukla PK, Khanna VK, Ali MM, Maurya RR, Handa SS, Srimal RC (2002) Protective effect of Acorus calamus against acrylamide induced neurotoxicity. Phytother Res 16:256–260
Al-Majed AA, Al-Omar FA, Nagi MN (2006) Neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone against transient forebrain ischemia in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol 543:40–47
Cotgreave IA, Gerdes RG (1998) Recent trends in glutathione biochemistry–glutathione-protein interactions: a molecular link between oxidative stress and cell proliferation? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 242:1–9
Gökce EC, Kahveci R, Gökce A, Cemil B, Aksoy N, Sargon MF, Kısa Ü, Erdoğan B, Güvenç Y, Alagöz F, Kahveci O (2016) Neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuation of inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. J Neurosurg Spine 24:949–959
Chen J-H, Yang C-H, Wang Y-S, Lee J-G, Cheng C-H, Chou C-C (2013) Acrylamide-induced mitochondria collapse and apoptosis in human astrocytoma cells. Food Chem Toxicol 51:446–452
Prasad SN, Muralidhara (2013) Neuroprotective efficacy of eugenol and isoeugenol in acrylamide-induced neuropathy in rats: behavioral and biochemical evidence. Neurochem Res 38:330–345
Kim EK, Choi E-J (2015) Compromised MAPK signaling in human diseases: an update. Arch Toxicol 89:867–882
Kim K, Rhee D-K, Pyo S (2011) Acrylamide induces cellular senescence in macrophage through ROS-MAPK signaling pathway. FASEB J 25:615.615–615.615
Mendilcioglu I, Karaveli S, Erdogan G, Simsek M, Taskin O, Ozekinci M (2011) Apoptosis and expression of Bcl-2, Bax, p53, caspase-3, and Fas, Fas ligand in placentas complicated by preeclampsia. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 38:38–42
Kekre N, Griffin C, McNulty J, Pandey S (2005) Pancratistatin causes early activation of caspase-3 and the flip** of phosphatidyl serine followed by rapid apoptosis specifically in human lymphoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 56:29–38
Salvesen GS, Dixit VM (1999) Caspase activation: the induced-proximity model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:10964–10967
Jiang G, Zhang L, Wang H, Chen Q, Wu X, Yan X, Chen Y, **e M (2018) Protective effects of a Ganoderma atrum polysaccharide against acrylamide induced oxidative damage via a mitochondria mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathway in IEC-6 cells. Food Funct 9:1133–1143
Lee J-G, Wang Y-S, Chou C-C (2014) Acrylamide-induced apoptosis in rat primary astrocytes and human astrocytoma cell lines. Toxicol In Vitro 28:562–570
Garbay B, Heape AM, Sargueil F, Cassagne C (2000) Myelin synthesis in the peripheral nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 61:267–304
Al-Gholam MA, Nooh HZ, El-Mehi AE, El-Barbary Ael M, Fokar AZ (2016) Protective effect of rosemary on acrylamide motor neurotoxicity in spinal cord of rat offspring: postnatal follow-up study. Anat Cell Biol 49:34–49
Elgholam M, Elbarbary A-M, Zolfakar A, Nooh H, El-Mehi A (2015) The role of rosemary against acrylamide developmental toxicity on the white matter of the rat spinal cord. Menoufia Med J 28:765–773
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the Vice Chancellor of Research, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran for financial support. The data reported in this article are part of a Ph.D. thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabeshpour, J., Mehri, S., Abnous, K. et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Thymoquinone in Acrylamide-Induced Peripheral Nervous System Toxicity Through MAPKinase and Apoptosis Pathways in Rat. Neurochem Res 44, 1101–1112 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02741-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02741-4