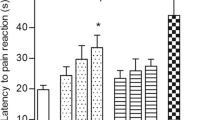
Experiments carried out on mice demonstrated that administration of a platinum-based drug, cisplatin, extensively used in anticancer chemotherapy, exerts significant hyperalgesic effects; it intensifies both phases of pain behavioral reactions induced in the formalin test. When introduction of cisplatin was combined with i.p. injections of 100 mg/kg of an aqueous-alcoholic extract from the leaves of Salvia officinalis, the second phase of cisplatin-enhanced pain in the formalin test was effectively suppressed; the effect was comparable with that provided by injections of morphine or even more intense.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Kelland, “The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy,” Nat. Rev. Cancer, 7, No. 8, 573-584 (2007).
C. Tournigand, T. Andre, E. Achille, et al., “FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced colorectal cancer: a randomized GERCOR study,” J. Clin. Oncol., 22, No. 2, 229-237 (2004).
A. Bhagra and R. D. Rao, “Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy,” Curr. Oncol. Rep., 9, No. 4, 290-299 (2007).
G. Kannarkat, E. E. Lasher, and D. Schiff, “Neurologic complications of chemotherapy agents,” Curr. Opin. Neurol., 20, No. 6, 719-725 (2007).
Y. Pan and M. S. Kao, “Discordance of clinical symptoms and electrophysiologic findings in taxane plus platinum-induced neuropathy,” Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer, 17, No. 2, 394-397 (2007).
E. Gamelin, L. Gamelin, L. Bossi, and S. Quasthoff, “Clinical aspects and molecular basis of oxaliplatin neurotoxicity: current management and development of preventive measures,” Sem. Oncol., 29, No. 5, Suppl. 15, 21-33 (2002).
M. Murata, Y. Yamaji, H. Futami, et al., “Peripheral neuropathy caused by cisplatin in patients with lung cancer,” Gan To Kagaku Ryoho, 16, No. 6, 2283-2288 (1989).
P. Gauchan, T. Andoh, K. Ikeda, et al., “Mechanical allodynia induced by paclitaxel, oxaliplatin and vincristine: different effectiveness of gabapentin and different expression of voltage-dependent calcium channel alpha(2) delta-1 subunit,” Biol. Pharm. Bull., 32, No. 4, 732-734 (2009).
O. Ghirardi, P. Lo Giudice, C. Pisano, et al., “Acetyl-L-Carnitine prevents and reverts experimental chronic neurotoxicity induced by oxaliplatin, without altering its antitumor properties,” Anticancer Res., 25, No. 4, 2681-2687 (2005).
A. Grothey, “Oxaliplatin-safety profile: neurotoxicity,” Sem. Oncol., 30, No. 4, Suppl. 15, 5-13 (2003).
E. K. Joseph, X. Chen, O. Bogen, and J. D. Levine, “Oxaliplatin acts on IB4-positive nociceptors to induce an oxidative stress-dependent acute painful peripheral neuropathy,” J. Pain, 9, No. 5, 463-472 (2008).
C. Lersch, R. Schmelz, F. Eckel, et al., “Prevention of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral sensory neuropathy by carbamazepine in patients with advanced colorectal cancer,” Clin. Colorect. Cancer, 2, No. 1, 54-58 (2002).
B. Ling, N. Authier, D. Balayssac, et al., “Behavioral and pharmacological description of oxaliplatin-induced painful neuropathy in rat,” Pain, 128, No. 3, 225-234 (2007).
B. Ling, F. Coudore, L. Decalonne, et al., “Comparative antiallodynic activity of morphine, pregabalin and lidocaine in a rat model of neuropathic pain produced by one oxaliplatin injection,” Neuropharmacology, 55, No. 5, 724-728 (2008).
B. Ling, M. A. Coudore-Civiale, D. Balayssac, et al., “Behavioral and immunohistological assessment of painful neuropathy induced by a single oxaliplatin injection in the rat,” Toxicology, 234, No. 3, 176-184 (2007).
M. O’Hara, D. Kiefer, K. Farrell, and K. Kemper, “A review of 12 commonly used medicinal herbs,” Arch. Fam. Med., 7, No. 6, 523-536 (1998).
A. N. A. Abad, M. H. K. Nouri, A. Gharjanie, and F. Tavakoli, “Effect of Matricaria chamomilla hydroalcoholic extract on cisplatin-induced neuropathy in mice,” Chin. J. Nat. Med., 9, No. 2, 126-131 (2011).
A. Namvaran Abbas Abad and M. H. Khayate Nouri, “Interactions between Matricaria recutita and cisplatin on PTZ-induced seizure threshold in mice,” Feyz, 15, No. 3, 188-193 (2011).
A. Namvaran Abbas Abad, M. H. Khayate Nouri, and F. Tavakkoli, “Study of Matricaria recutita and vincristine effects on PTZ-induced seizure threshold in mice,” Res. J. Med. Sci., 5, No. 5, 247-251 (2011).
A. Namvaran Abbas Abad, M. H. Khayate Nouri, and F. Tavakkoli, “Effect of Salvia officinalis hydroalcoholic extract on vincristine-induced neuropathy in mice,” Chin. J. Natur. Med., 9, No. 5, 354-358 (2011).
A. Zargari, Medical Plants, Tehran Univ., Tehran (2003).
A. Rustayan, S. Masoudi, A. Monfared, and H. Komilizadeh, “Volatile constituents of three Salvia species grown wild in Iran,” Flavor Fragrance J., 14, 267-278 (1999).
C. Brickell, Encyclopedia of Garden Plants, London Dorl. Kindersley, London (1996).
M. Hernandez-Perez, R. M. Rabanal, M. C. de la Torre, and B. Rodriguez, “Analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and haematological effects of aethiopinone, an o-naphthoquinone diterpenoid from Salvia aethiopis roots and two hemisynthetic derivatives,” Planta Med., 61, No. 6, 505-509 (1995).
S. Wasser, J. M. Ho, H. K. Ang, and C. E. Tan, “Salvia miltiorrhiza reduces experimentally-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats,” J. Hepatol., 29, No. 5, 760-771 (1998).
J. Jimenez, S. Risco, T. Ruiz, and A. Zarzuelo, “Hypoglycemic activity of Salvia lavandulifolia,” Planta Med., 52, No. 4, 260-262 (1986).
W. G. Yu and L. N. Xu, “Effect of acetylsalvianolic acid A on platelet function,” Yao Xue Xue Bao, 29, No. 6, 412-416 (1994).
H. J. P. Dorman, S. G. Deans, and R. C. Noble, “Evaluation in vitro of plant essential oils as natural antioxidants,” J. Essent. Oil Res., 7, 645-651 (1995).
J. Hohmann, I. Zupko, D. Redei, et al., “Protective effects of the aerial parts of Salvia officinalis, Melissa officinalis and Lavandula angustifolia and their constituents against enzyme-dependent and enzyme-independent lipid peroxidation,” Planta Med., 65, No. 6, 576-578 (1999).
D. Malencic, O. Gasic, M. Popovic, and P. Boza, “Screening for antioxidant properties of Salvia reflexa hornem,” Phytother. Res., 14, No. 7, 546-548 (2000).
I. Zupko, J. Hohmann, D. Redei, et al., “Antioxidant activity of leaves of Salvia species in enzyme-dependent and enzyme-independent systems of lipid peroxidation and their phenolic constituents,” Planta Med., 67, No. 4, 366-268 (2001).
M. J. Howes, N. S. Perry, and P. J. Houghton, “Plants with traditional uses and activities, relevant to the management of Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive disorders,” Phytother. Res., 17, No. 1, 1-18 (2003).
C. N. Wang, C. W. Chi, Y. L. Lin, et al., “The neuroprotective effects of phytoestrogens on amyloid beta protein-induced toxicity are mediated by abrogating the activation of caspase cascade in rat cortical neurons,” J. Biol. Chem., 276, No. 7, 5287-5295 (2001).
Y. A. Maklad, E. A. Aboutabl, M. M. el-Sherei, and K. M. Meselhy, “Bioactivity studies of Salvia transsylvanica (Schur ex Griseb) grown in Egypt,” Phytother. Res., 13, No. 2, 147-150 (1999).
T. J. Coderre, A. L. Vaccarino, and R. Melzack, “Central nervous system plasticity in the tonic pain response to subcutaneous formalin injection,” Brain Res., 535, No. 1, 155-158 (1990).
K. J. Ivey, “Gastrointestinal intolerance and bleeding with non-narcotic analgesics,” Drugs, 32, Suppl. 4, 71-89 (1986).
M. D. Murray and D. C. Brater, “Renal toxicity of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,” Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 33, 435-465 (1993).
A. Eidi, K. Parivar, A. Mazouji, and Z. Akhtari, “Antinociceptive effects of essential oil of Salvia hypoleuca L. in mice,” Med. Sci. J. Islam. Azad Univ. Tehran Med. Branch, 16, 165-169 (2006).
E. K. Joseph and J. D. Levine, “Comparison of oxaliplatin- and cisplatin-induced painful peripheral neuropathy in the rat,” Pain, 10 (5), 534-541 (2009).
M. Shibata, T. Ohkubo, H. Takahashi, and R. Inoki, “Modified formalin test: characteristic biphasic pain response,” Pain, 38, No. 3, 347-352 (1989).
K. O. Aley and J. D. Levine, “Different peripheral mechanisms mediate enhanced nociception in metabolic/toxic and traumatic painful peripheral neuropathies in the rat,” Neuroscience, 111, No. 2, 389-397 (2002).
E. K. Joseph and J. D. Levine, “Caspase signalling in neuropathic and inflammatory pain in the rat,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 20, No. 11, 2896-2902 (2004).
E. K. Joseph and J. D. Levine, “Mitochondrial electron transport in models of neuropathic and inflammatory pain,” Pain, 121, Nos. 1/2, 105-114 (2006).
L. E. Abrey and D. D. Correa, “Treatment-related neurotoxicity,” Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North. Am., 19, No. 4, 729-738 (2005).
M. Stillman and J. P. Cata, “Management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy,” Curr. Pain Headache Rep., 10, No. 4, 279-287 (2006).
J. K. Sul and L. M. Deangelis, “Neurologic complications of cancer chemotherapy,” Sem. Oncol., 33, No. 3, 324-332 (2006).
A. Eastman, “Alkylating and platinum-based agents,” Curr. Opin. Oncol., 2, No. 6, 1109-1114 (1990).
W. P. Reed, “Intravenous access devices for supportive care of patients with cancer,” Curr. Opin. Oncol., 3, No. 4, 634-642 (1991).
B. Rosenberg, “Noble metal complexes in cancer chemotherapy,” Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 91, 129-150 (1977).
R. J. Cersosimo, “Oxaliplatin-associated neuropathy: a review,” Ann. Pharmacother., 39, No. 1, 128-135 (2005).
J. M. Extra, M. Marty, S. Brienza, and J. L. Misset, “Pharmacokinetics and safety profile of oxaliplatin,” Sem. Oncol., 25, No. 2, Suppl. 5, 13-22 (1998).
C. R. Culy, D. Clemett, and L. R. Wiseman, “Oxaliplatin. A review of its pharmacological properties and clinical efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer and its potential in other malignancies,” Drugs, 60, No. 4, 895-924 (2000).
T. L. Sahley and G. G. Berntson, “Antinociceptive effects of central and systemic administrations of nicotine in the rat,” Psychopharmacology, 65, No. 3, 279-283 (1979).
E. K. Joseph, X. Chen, S. G. Khasar, and J. D. Levine, “Novel mechanism of enhanced nociception in a model of AIDS therapy-induced painful peripheral neuropathy in the rat,” Pain, 107, Nos. 1/2, 147-158 (2004).
H. Adelsberger, S. Quasthoff, J. Grosskreutz, et al., “The chemotherapeutic oxaliplatin alters voltage-gated Na(+) channel kinetics on rat sensory neurons,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 406, No. 1, 25-32 (2000).
A. V. Krishnan, D. Goldstein, M. Friedlander, and M. C. Kiernan, “Oxaliplatin and axonal Na+ channel function in vivo,” Clin. Cancer Res., 12, No. 15, 4481-4484 (2006).
A. Binder, M. Stengel, R. Maag, et al., “Pain in oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy - sensitisation in the peripheral and central nociceptive system," Eur. J. Cancer., 43, No. 18, 2658-2663 (2007).
M. C. Kiernan and A. V. Krishnan, “The pathophysiology of oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity,” Curr. Med. Chem., 13, No. 24, 2901-2907 (2006).
A. V. Krishnan, D. Goldstein, M. Friedlander, and M. C. Kiernan, “Oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity and the development of neuropathy,” Muscle Nerve, 32, No. 1, 51-60 (2005).
N. Garrido, A. Perez-Martos, M. Faro, et al., “Cisplatin-mediated impairment of mitochondrial DNA metabolism inversely correlates with glutathione levels,” Biochem. J., 414, No. 1, 93-102 (2008).
J. Goodisman, D. Hagrman, K. A. Tacka, and A. K. Souid, “Analysis of cytotoxicities of platinum compounds,” Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol., 57, No. 2, 257-267 (2006).
M. L. Heaney, J. R. Gardner, N. Karasavvas, et al., “Vitamin C antagonizes the cytotoxic effects of antineoplastic drugs,” Cancer Res., 68, No. 19, 8031-8038 (2008).
C. H. Kim, S. U. Kang, J. Pyun, et al., “Epicatechin protects auditory cells against cisplatin-induced death,” Apoptosis, 13, No. 9, 1184-1194 (2008).
G. Melli, M. Taiana, F. Camozzi, et al., “Alpha-lipoic acid prevents mitochondrial damage and neurotoxicity in experimental chemotherapy neuropathy,” Exp. Neurol., 214, No. 2, 276-284 (2008).
S. J. Flatters and G. J. Bennett, “Studies of peripheral sensory nerves in paclitaxel-induced painful peripheral neuropathy: evidence for mitochondrial dysfunction,” Pain, 122, No. 3, 245-257 (2006).
M. Osio, F. Muscia, L. Zampini, et al., “Acetyl-l-carnitine in the treatment of painful antiretroviral toxic neuropathy in human immunodeficiency virus patients: an open label study,” J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst., 11, No. 1, 72-76 (2006).
E. Y. Qnais, M. Abu-Dieyeh, F. A. Abdulla, and S. S. Abdalla, “The antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of Salvia officinalis leaf aqueous and butanol extracts,” Pharm. Biol., 48, No. 10, 1149-1156 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Neirofiziologiya/Neurophysiology, Vol. 43, No. 6, pp. 527-533, November-December, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namvaran-Abbas-Abad, A., Tavakkoli, F. Antinociceptive Effect of Salvia Extract on Cisplatin-Induced Hyperalgesia in Mice. Neurophysiology 43, 452–458 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-012-9249-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-012-9249-1