Abstract
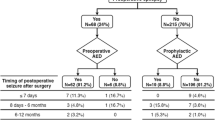
Low grade tumors are associated with a high risk of seizures. Prolonged use of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) is associated with morbidity. Determining which patients can safely discontinue AEDs perioperatively is difficult. We examined patients with low grade supratentorial brain tumors to determine characteristics of patients who underwent AED withdrawal. A retrospective chart review was performed in patients who underwent resection between 1/1/2004 and 12/31/2005 at a single center. Data were collected regarding the use of postoperative AEDs, occurrence of postoperative seizures, and patient/tumor characteristics. We examined 169 patients with a median follow-up of 3.1 years. AEDs were withdrawn or never started in 111 patients; post-withdrawal seizures occurred in 11 (9.9%). The rate was similar between meningiomas and primary brain tumors. No independent risk factors for post-withdrawal seizures were found. Of 58 patients whose AEDs were not withdrawn, postoperative seizures occurred in 28 (48%). Predictors of AED continuation included existence of preoperative seizures, temporal tumor location, tumor recurrence, incomplete resection, and male sex. The decision to continue AEDs was predictive for postoperative seizures even after controlling for known risk factors. Although clinicians are able to identify patients at high risk for postoperative seizures, treatment with AEDs is ineffective in many patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Antiepileptic drug:
-
AED
References
van Breemen MS, Wilms EB, Vecht CJ (2007) Epilepsy in patients with brain tumours: epidemiology, mechanisms, and management. Lancet Neurol 6:421–430. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70103-5
Lynam LM, Lyons MK, Drazkowski JF, Sirven JI, Noe KH, Zimmerman RS, Wilkens JA (2007) Frequency of seizures in patients with newly diagnosed brain tumors: a retrospective review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 109:634–638. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2007.05.017
Vertosick FT Jr, Selker RG, Arena VC (1991) Survival of patients with well-differentiated astrocytomas diagnosed in the era of computed tomography. Neurosurgery 28:496–501
Lieu AS, Howng SL (2000) Intracranial meningiomas and epilepsy: incidence, prognosis and influencing factors. Epilepsy Res 38:45–52
Glantz MJ, Coleman RE, Forsyth PA, Recht LD, Wen PY, Chamberlain MC, Grossman SA, Cairncross JG (2000) Practice parameter: anticonvulsant prophylaxis in patients with newly diagnosed brain tumors. Neurology 54:1886–1893
Rosati A, Buttolo L, Stefini R, Todeschini A, Cenzato M, Padovani A (2010) Efficacy and safety of levetiracetam in patients with glioma: a clinical prospective study. Arch Neurol 67(3):343–346. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2009.335
Siomin V, Angelov L, Li L, Vogelbaum MA (2005) Results of a survey of neurosurgical practice patterns regarding the prophylactic use of anti-epilepsy drugs in patients with brain tumors. J Neurooncol 74:211–215. doi:10.1007/s11060-004-6912-4
Karceski S, Morrell MJ, Carpenter D (2005) Treatment of epilepsy in adults: expert opinion, 2005. Epilepsy Behav 7(Suppl 1):S1–S64
Arif H, Buchsbaum R, Weintraub D, Pierro J, Resor SR Jr, Hirsch LJ (2009) Patient-reported cognitive side effects of antiepileptic drugs: predictors and comparison of all commonly used antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsy Behav 14:202–209. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2008.10.017
Kennedy GM, Lhatoo SD (2008) CNS adverse events associated with antiepileptic drugs. CNS Drugs 22:739–760
Ahmed I, Reichenberg J, Lucas A, Shehan JM (2004) Erythema multiforme associated with phenytoin and cranial radiation therapy: a report of three patients and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol 43:67–73
Aguiar D, Pazo R, Duran I, Terrasa J, Arrivi A, Manzano H, Martin J, Rifa J (2004) Toxic epidermal necrolysis in patients receiving anticonvulsants and cranial irradiation: a risk to consider. J Neurooncol 66:345–350
Page RL 2nd, O’Neil MG, Yarbrough DR 3rd, Conradi S (1998) Fatal toxic epidermal necrolysis related to lamotrigine administration. Pharmacotherapy 18:392–398
Correa DD, DeAngelis LM, Shi W, Thaler HT, Lin M, Abrey LE (2007) Cognitive functions in low-grade gliomas: disease and treatment effects. J Neurooncol 81:175–184. doi:10.1007/s11060-006-9212-3
Klein M, Engelberts NH, van der Ploeg HM, Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenite DG, Aaronson NK, Taphoorn MJ, Baaijen H, Vandertop WP, Muller M, Postma TJ, Heimans JJ (2003) Epilepsy in low-grade gliomas: the impact on cognitive function and quality of life. Ann Neurol 54:514–520. doi:10.1002/ana.10712
Bourg V, Lebrun C, Chichmanian RM, Thomas P, Frenay M (2001) Nitroso-urea-cisplatin-based chemotherapy associated with valproate: increase of haematologic toxicity. Ann Oncol 12:217–219
Oberndorfer S, Piribauer M, Marosi C, Lahrmann H, Hitzenberger P, Grisold W (2005) P450 enzyme inducing and non-enzyme inducing antiepileptics in glioblastoma patients treated with standard chemotherapy. J Neurooncol 72:255–260. doi:10.1007/s11060-004-2338-2
Vecht CJ, van Breemen M (2006) Optimizing therapy of seizures in patients with brain tumors. Neurology 67:S10–S13
Chadwick D (2006) Starting and stop** treatment for seizures and epilepsy. Epilepsia 47(Suppl 1):58–61. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00662.x
Taphoorn MJ (2003) Neurocognitive sequelae in the treatment of low-grade gliomas. Semin Oncol 30:45–48
Luyken C, Blumcke I, Fimmers R, Urbach H, Elger CE, Wiestler OD, Schramm J (2003) The spectrum of long-term epilepsy-associated tumors: long-term seizure and tumor outcome and neurosurgical aspects. Epilepsia 44:822–830
Khan RB, Onar A (2006) Seizure recurrence and risk factors after antiepilepsy drug withdrawal in children with brain tumors. Epilepsia 47:375–379. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00431.x
Chang EF, Potts MB, Keles GE, Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Barbaro NM, Berger MS (2008) Seizure characteristics and control following resection in 332 patients with low-grade gliomas. J Neurosurg 108:227–235. doi:10.3171/JNS/2008/108/2/0227
Rajneesh KF, Binder DK (2009) Tumor-associated epilepsy. Neurosurg Focus 27:E4. doi:10.3171/2009.5.FOCUS09101
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, R.R., Artsy, E., Hurwitz, S. et al. Outcomes after discontinuation of antiepileptic drugs after surgery in patients with low grade brain tumors and meningiomas. J Neurooncol 107, 565–570 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0779-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0779-y