Abstract
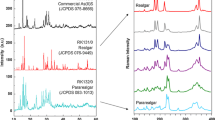
Arsenic nanoparticles are alternative for arsenic compounds currently used in medicine. The preparation of suitable arsenic nanoparticles could significantly reduce the doses of arsenic administered and thus eliminate negative side effects. A method for controlled synthesis of arsenic nanoparticles is proposed and described. The preparation of arsenic nanoparticles, based on the simple reduction of sodium arsenite by sodium tetraborohydride in aqueous solution, led to the production of amorphous, spherical nanoparticles with diameters between 50 and 90 nm. Diameter was controlled simply by varying the pH value of the solution within the range of 5.5–11.0. The addition of cetyl trimethylammonium bromide into the reaction mixture allowed the preparation of small crystalline arsenic nanoparticles with an average diameter of approximately 4 nm, and the addition of bovine serum albumin led to bottle-like amorphous arsenic nanoparticles. The prepared nanoparticles were characterised using the single-particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry method, ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy and electron microscopy.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anwari NS, Aini N, Hardian A, Suendo V, Prasetyo A (2019) The effect of temperature to CTAB-assisted solvothermal synthesis of TiO2. Iop Conf Ser-Mat Sci 546:042003
Chakraborty S, Bhar K, Saha S, Chakrabarti R, Pal A, Siddhanta A (2014) Novel arsenic nanoparticles are more effective and less toxic than As (III) to inhibit extracellular and intracellular proliferation of Leishmania donovani. J Parasitol Res 2014:187640
Chakraborty I, Feliu N, Roy S, Dawson K, Parak WJ (2018) Protein-mediated shape control of silver nanoparticles. Bioconjugate Chem 29(4):1261–1265
Henke K (2009) Arsenic: environmental chemistry, health threats and waste treatment. John Wiley & Sons Ltd
Hosnedlova B, Kepinska M, Skalickova S, Fernandez C, Ruttkay-Nedecky B, Peng QM, Baron M, Melcova M, Opatrilova R, Zidkova J, Bjorklund G, Sochor J, Kizek R (2018) Nano-selenium and its nanomedicine applications: a critical review. Int J Nanomed 13:2107–2128
Huang W, Zeng YC (2019) A candidate for lung cancer treatment: arsenic trioxide. Clin Transl Oncol 21(9):1115–1126
Huang P, Zhang YH, Zheng XW, Liu YJ, Zhang H, Fang L, Zhang YW, Yang C, Islam K, Wang C, Naranmandura H (2017) Phenylarsine oxide (PAO) induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells via ROS-mediated mitochondria and ER-stress dependent signaling pathways. Metallomics 9(12):1756–1764
Jana NR, Gearheart L, Murphy CJ (2001) Wet chemical synthesis of silver nanorods and nanowires of controllable aspect ratio. Chem Commun 7:617–618
Jeevanandam J, Barhoum A, Chan YS, Dufresne A, Danquah MK (2018) Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: history, sources, toxicity and regulations. Beilstein J Nanotech 9:1050–1074
**dal AB (2017) The effect of particle shape on cellular interaction and drug delivery applications of micro- and nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 532(1):450–465
Kalyan I, Pal T, Pal A (2019) Time and temperature dependent formation of hollow gold nanoparticles via galvanic replacement reaction of As(0) and its catalytic application. MRS Communications 9:270–279
Khan Z, Al-Thabaiti SA, Obaid AY, Khan ZA, Al-Youbi AAO (2012) Shape-directing role of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide in the preparation of silver nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 367:101–108
Laborda F, Bolea E, Jimenez-Lamana J (2014) Single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: a powerful tool for nanoanalysis. Anal Chem 86(5):2270–2278
Lahtinen RM, Mertens SFL, East E, Kiely CJ, Schiffrin DJ (2004) Silver halide colloid precursors for the synthesis of monolayer-protected clusters. Langmuir 20(8):3289–3296
Lee O, Jeong SH, Shin WU, Lee G, Oh C, Son SW (2013) Influence of surface charge of gold nanorods on skin penetration. Skin Res Technol 19(1):E390–E396
Liu B, Pan SG, Dong XS, Qiao HQ, Jiang HC, Krissansen GW, Sun XY (2006) Opposing effects of arsenic trioxide on hepatocellular carcinomas in mice. Cancer Sci 97(7):675–681
Loula M, Kana A, Mestek O (2019) Non-spectral interferences in single-particle ICP-MS analysis: an underestimated phenomenon. Talanta 202:565–571
Mandal G, Orta J, Sharma M, Mukhopadhyay R (2013) Trypanosomatid aquaporins: roles in physiology and drug response. Diseases 2(1):3–23
Mehta A, Shaha C (2006) Mechanism of metalloid-induced death in Leishmania spp.: role of iron, reactive oxygen species, Ca2+, and glutathione. Free Radic Biol Med 40(10):1857–68
Naujokas MF, Anderson B, Ahsan AHV, Graziano JH, Thompson C, Suk WA (2013) The broad scope of health effects from chronic arsenic exposure: update on a worldwide public health problem. Environ Health Perspect 121(3):295–302
Okuda M, Kobayashi Y, Suzuki K, Sonoda K, Kondoh T, Wagawa A, Kondo A, Yoshimura H (2005) Self-organized inorganic nanoparticle arrays on protein lattices. Nano Lett 5(5):991–993
Pal A, Saha S, Maji SK, Kundu M, Kundu A (2012) Wet-chemical synthesis of spherical arsenic nanoparticles by a simple reduction method and its characterisation. Adv Mat Lett 3(3):177–180
Platzbecker U, Avvisati G, Cicconi L, Thiede C, Paoloni F, Vignetti M, Ferrara F, Divona M, Albano F, Efficace F, Fazi P, Sborgia M, Di Bona E, Breccia M, Borlenghi E, Cairoli R, Rambaldi A, Melillo L, La Nasa G, Fiedler W, Brossart P, Hertenstein B, Salih HR, Wattad M, Lubbert M, Brandts CH, Hanel M, Rollig C, Schmitz N, Link H, Frairia C, Pogliani EM, Fozza C, D’Arco AM, Di Renzo N, Cortelezzi A, Fabbiano F, Dohner K, Ganser A, Dohner H, Amadori S, Mandelli F, Ehninger G, Schlenk RF, Lo-Coco F (2017) Improved outcomes with retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide compared with retinoic acid and chemotherapy in non-high-risk acute promyelocytic leukemia: final results of the randomized Italian-German APL0406 Trial. J Clin Oncol 35(6):605–612
Sanchez-Martinez D, Gomez-Solis C, Torres-Martinez LM (2015) CTAB-assisted ultrasonic synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic properties of WO3. Mater Res Bull 61:165–172
Shen SW, Li XF, Cullen WR, Weinfeld M, Le XC (2013) Arsenic binding to proteins. Chem Rev 113(10):7769–7792
Singh Z, Singh I (2019) CTAB surfactant assisted and high pH nano-formulations of CuO nanoparticles pose greater cytotoxic and genotoxic effects. Sci Rep-Uk 9:5880
Singh N, Wadhawan M, Tiwari S, Kumar R, Rathaur S (2016) Inhibition of Setaria cervi protein tyrosine phosphatases by phenylarsine oxide: a proteomic and biochemical study. Acta Trop 159:20–28
Sodhi KK, Kumar M, Agrawal PK, Singh DK (2019) Perspectives on arsenic toxicity, carcinogenicity and its systemic remediation strategies. Environ Technol Innov 16:100462
Subbarayan PR, Lima M, Ardalan B (2007) Arsenic trioxide/ascorbic acid therapy in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal carcinoma: a clinical experience. Acta Oncol 46(4):557–561
Subastri A, Arun V, Sharma P, PreediaBabu E, Suyavaran A, Nithyananthan S, Alshammari GM, Aristatile B, Dharuman V, Thirunavukkarasu C (2018) Synthesis and characterisation of arsenic nanoparticles and its interaction with DNA and cytotoxic potential on breast cancer cells. Chem Biol Interact 295:73–83
Tan YN, Lee JY, Wang DIC (2010) Uncovering the design rules for peptide synthesis of metal nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 132(16):5677–5686
Wang ZY (2001) Arsenic compounds as anticancer agents. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 48:S72–S76
Yoshimura H (2006) Protein-assisted nanoparticle synthesis. Colloid Surface A 282:464–470
Zhang J, Song BC, Peng WT, Feng YL, Xu B (2010) CTAB-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of nano-sized tetragonal zirconium dioxide. Mater Chem Phys 123(2–3):606–609
Zhang J, Tang H, Liu ZF, Chen BA (2017) Effects of major parameters of nanoparticles on their physical and chemical properties and recent application of nanodrug delivery system in targeted chemotherapy. Int J Nanomed 12:8483–8493
Zhao HY, Jiang QP, Li YH (2013) Surfactant CTAB-assisted synthesis and gas-sensing characteristics of SnO2 nanomaterials. Adv Mater Res-Switz 750–752:241–244
Zhou Q, ** SH (2018) A review on arsenic carcinogenesis: epidemiology, metabolism, genotoxicity and epigenetic changes. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 99:78–88
Funding
This work was supported from the grant of Specific university research—Grant No. A1_FCHI_2021_003, the Operational Programme Prague Competitiveness (CZ.2.16/3.1.00/24501) and National Program of Sustainability (NPU I LO1613) MSMT-43760/2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest for this study.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaňa, A., Loula, M. & Mestek, O. Controlled preparation of arsenic nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 23, 239 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05356-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05356-5