Abstract
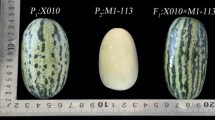
Melon (Cucumis melo L.) is one of the most popular and highly nutritious vegetable species within Cucurbitaceae. Because appearance is used as an important indicator of quality, the spotted to non-spotted trait associated with this product somewhat influences the buying habits of consumers. We tested a six-generation family to determine the inheritance and genetic basis of this trait. Genetic groups F1, F2, BC1P1, and BC1P2 were from a cross between “IM16559” (non-spotted) and “IM16553” (spotted). Our genetic analysis showed that the spotted to non-spotted trait was controlled by a single dominant gene that we named CmSp-1. Whole-genome resequencing-bulked segregant analysis (WG-BSA) demonstrated that this gene was located on the end of chromosome 2, in the intersections of 22,160,000 to 22,180,000 bp and 22,260,000 to 26,180,000 bp, an interval distance of 3.94 Mb. Insertion-deletion (InDel) markers designed based on WG-BSA data were used to map this gene. Using 13 InDel markers, we produced a genetic map indicating that CmSp-1 was tightly linked to markers I734-2 and I757, with genetic distances of 1.8 and 0.4 cM and an interval distance of 280.872 kb. The closest marker was I757. Testing of 107 different melon genotypes presented an accuracy of 84.11% in predicting the phenotype. By being able to locate CmSp-1 in melon, we can now use the findings to identify potential targets for further marker-assisted breeding and cloning projects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe A, Kosugi S, Yoshida K, Natsume S, Takagi H, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Yoshida K, Mitsuoka C, Tamiru M, Innan H, Cano L, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2012) Genome sequencing reveals agronomically important loci in rice using mutmap. Nat Biotechnol 30(2):174–178
Brotman Y, Silberstein L, Kovalski I, Perin C, Dogimont C, Pitrat M, Klingler J, Thompson GA, Perl-Treves R (2002) Resistance gene homologues in melon are linked to genetic loci conferring disease and pest resistance. Theor Appl Genet 104(6–7):1055–1063
Cingolani P, Platts A, Le LW, Coon M, Nguyen T, Luan W, Land SJ, Lu X, Ruden DM (2012) A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, Snpeff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 6(2):80–92
Cui JY, Miao H, Ding LH, Wehner TC, Liu PN, Wang Y, Zhang SP, Gu XF (2016) A new glabrous gene (csgl3) identified in trichome development in cucumber (Cucumis sativus l.). PLoS One 11(2):e0148422
Danin-Poleg Y, Tadmor Y, Tzuri G, Reis N, Hirschberg J, Katzir N (2002) Construction of a genetic map of melon with molecular markers and horticultural traits, and localization of genes associated with ZYMV resistance. Euphytica 125(3):373–384
Fekih R, Takagi H, Tamiru M, Abe A, Natsume S, Yaegashi H, Sharma S, Sharma S, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Saitoh MC, Utsushi H, Uemura A, Kanzaki E, Kosugi S, Yoshida K, Cano L, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2013) Mutmap+: genetic map** and mutant identification without crossing in rice. PLoS One 8(7):e68529
Han F, Yang C, Fang Z, Yang L, Zhuang M, Lv H, Liu Y, Li Z, Liu B, Yu H, Liu X, Zhang Y (2015) Inheritance and InDel markers closely linked to petal color gene (cpc-1) in Brassica oleracea. Mol Breed 35(8):160
Hill JT, Demarest BL, Bisgrove BW, Gorsi B, Su YC, Yost HJ (2013) MMAPPR: mutation map** analysis pipeline for pooled RNA-seq. Genome Res 23(4):687–697
Garcia-Mas J, Puigdomènech P (2012) The genome of melon (Cucumis melo L.). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(29):11872–11877
Gorohivets NA, Vedmedeva EV (2016) Inheritance of epidermis pigmentation in sunflower achenes. Cytol Genet 50(2):116–120
Gusmini G, Wehner TC (2006) Qualitative inheritance of rind pattern and flesh color in watermelon. J Hered 97(2):177–185
Kang H, Weng Y, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Zhang S, Mao Z, Cheng G, Gu X, Huang S, ** localizes cucumber scab resistance gene Ccu, into an R gene cluster. Theor Appl Genet 122(4):795–803
Kim H, Han D, Kang J, Choi Y, Levi A, Lee GP, Park Y (2015a) Sequence-characterized amplified polymorphism markers for selecting rind stripe pattern in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus L.). Hortic Environ Biotechnol 56(3):341–349
Kim KH, Ahn SG, Hwang JH, Choi YM, Moon HS, Park YH (2013) Inheritance of resistance to powdery mildew in the watermelon and development of a molecular marker for selecting resistant plants. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 54(2):134–140
Kim KH, Hwang JH, Han DY, Park M, Kim S, Choi D, Kim Y, Lee GP, Kim ST, Park YH (2015b) Major quantitative trait loci and putative candidate genes for powdery mildew resistance and fruit-related traits revealed by an intraspecific genetic map for watermelon (Citrullus lanatus var. lanatus). PLoS One 10(12):e0145665
Kim N, Oh J, Kim B, Choi EK, Hwang US, Kim N, Staub JE, Chung S, Park Y (2015c) The CmACS-7 gene provides sequence variation for development of DNA markers associated with monoecious sex expression in melon (Cucumis melo L.). Hortic Environ Biotechnol 56(4):535–545
Kosambi D (1943) The estimation of map distances from recombinant values. Ann Eugenics 12:172–175
Li B, Zhao Y, Zhu Q, Zhang Z, Fan C, Amanullah S, Gao P, Luan F (2017) Map** of powdery mildew resistance genes in melon (Cucumis melo L.) by bulked segregant analysis. Sci Hortic 220(16):160–167
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1750–1760
Lin P (2012) Comments on intraspecific classification of melon. China Cucur Veg 25(5):42–46 (in Chinese)
Liu R, Meng J (2003) Map Draw: a Microsoft Excel macro for drawing genetic linkage maps based on given genetic linkage data. Hereditas 25:317–321 (in Chinese)
Lv Y, Liu Y, Zhao H (2016) mInDel: a high-throughput and efficient pipeline for genome-wide InDel marker development. BMC Genomics 17(1):290
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo M (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20(9):1297–1303
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88(21):9828–9832
Murray H, Thompson W (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Natarajan S, Kim HT, Thamilarasan SK, Veerappan K, Park JI, Nou IS (2016) Whole genome re-sequencing and characterization of powdery mildew disease-associated allelic variation in melon. PLoS One 11(6):e0157524
Ntui V, Uyoh E (2005) Inheritance of stripe pattern on fruits and seed colour in “egusi” melon, Colocynthis citrullus L. Glob J Agric Sci 4(1):29–32
Paris HS (2000) Gene for broad, contiguous dark stripes in cocozelle squash (Cucurbita pepo). Euphytica 115(3):191–196
Paris HS (2002) Genetic control of irregular stri**, a new phenotype in Cucurbita pepo. Euphytica 129(1):119–126
Paris H, Burger Y (1989) Complementary genes for fruit stri** in summer squash. J Hered 80(6):489–493
Périn C, Dogimont C, Giovinazzo N, Besombes D, Guitton L, Hagen L, Pitrat M (1999) Genetic control and linkages of some fruit characters in melon. Cucurb Genet Coop Rep 22:16–18
Périn C, Hagen S, De CV, Katzir N, Danin-Poleg Y, Portnoy V, Baudracco-Arnas S, Chadoeuf J, Dogimont C, Pitrat M (2002) A reference map of Cucumis melo based on two recombinant inbred line populations. Theor Appl Genet 104(6–7):1017–1034
Pitrat M (2006) 2006 gene list for melon. Cucurb Genet Coop Rep 28–29:142–163
Ren L, Zhu BQ, Zhang YB, Wang HY, Li CY, Su YH, Ba CF (2004) The research of applying primer premier 5.0 to design PCR primer. J **zhou Med Coll 25(6):43–46 (in Chinese)
Takagi H, Abe A, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Natsume S, Mitsuoka C, Uemura A, Utsushi H, Tamiru M, Takuno S, Innan H, Cano LM, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2013) QTL-seq: rapid map** of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations. Plant J 74(1):174–183
Xu Q, Yang S, Yu T, Xu X, Yan Y, Qi X, Chen X (2016) Whole-genome resequencing of a cucumber chromosome segment substitution line and its recurrent parent to identify candidate genes governing powdery mildew resistance. PLoS One 11(10):e0164469
Yahiaoui N, Srichumpa P, Dudler R, Keller B (2004) Genome analysis at different ploidy levels allows cloning of the powdery mildew resistance gene pm3b from hexaploid wheat. Plant J 37(4):528–538
Yang HB, Sungwoo P, Younghoon P, Gungpyo L, Kang SC, Yongkwon K (2015) Linkage analysis of the three loci determining rind color and stripe pattern in watermelon. Korean J Hortic Sci Technol 33(4):559–565
Zhang H, Yi H, Wu M, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Li M, Wang G (2016) Map** the flavor contributing traits on “Fengwei Melon” (Cucumis melo L.) chromosomes using parent resequencing and super bulked-segregant analysis. PLoS One 11(2):e0148150
Zou C, Wang P, Xu Y (2016) Bulked sample analysis in genetics, genomics and crop improvement. Plant Biotechnol J 14(10):1941
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31201642 and 31471895), the China Agriculture Research System of Watermelon and Melon (CARS-25), and the Innovation Engineering Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, J., Fu, Q., Lai, Y. et al. Inheritance and gene map** of spotted to non-spotted trait gene CmSp-1 in melon (Cucumis melo L. var. chinensis Pangalo). Mol Breeding 38, 105 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-018-0860-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-018-0860-8