Abstract
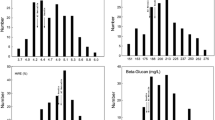
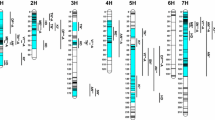
Malting quality is genetically determined by the complex interaction of numerous traits which are expressed prior to and, in particular, during the malting process. Here, we applied the advanced backcross quantitative trait locus (AB-QTL) strategy (Tanksley and Nelson, Theor Appl Genet 92:191–203, 1996), to detect QTLs for malting quality traits and, in addition, to identify favourable exotic alleles for the improvement of malting quality. For this, the BC2DH population S42 was generated from a cross between the spring barley cultivar Scarlett and the wild barley accession ISR42-8 (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum). A QTL analysis in S42 for seven malting parameters measured in two different environments yielded 48 QTLs. The exotic genotype improved the trait performance at 18 (37.5%) of 48 QTLs. These favourable exotic alleles were detected, in particular, on the chromosome arms 3HL, 4HS, 4HL and 6HL. The exotic allele on 4HL, for example, improved α-amylase activity by 16.3%, fermentability by 0.8% and reduced raw protein by 2.4%. On chromosome 6HL, the exotic allele increased α-amylase by 16.0%, fermentability by 1.3%, friability by 7.3% and reduced viscosity by 2.9%. Favourable transgressive segregation, i.e. S42 lines exhibiting significantly better performance than the recurrent parent Scarlett, was recorded for four traits. For α-amylase, fermentability, fine-grind extract and VZ45 20, 16, 2 and 26 S42 lines, respectively, surpassed the recurrent parent Scarlett. The present study hence demonstrates that wild barley does harbour valuable alleles, which can enrich the genetic basis of cultivated barley and improve malting quality traits.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahokas H, Naskali L (1990a) Geographic variation of α-amylase, β-amylase, β-glucanase, pullulanase and chitinase activity in germinating Hordeum spontaneum barley from Israel and Jordan. Genetica 82:73–78
Ahokas N, Naskali L (1990b) Variation of α-amylase, β-amylase, β-glucanase, pullulanase, proteinase and chitinase activity in germinated samples of the wild progenitor of barley. J Inst Brew 96:27–31
Baek HJ, Beharav A, Nevo E (2003) Ecological-genomic diversity of microsatellites in wild barley, Hordeum spontaneum, populations in Jordan. Theor Appl Genet 106:397–410
Barr AR, Jefferies SP, Broughton S, Chalmers KJ, Kretschmer JM, Boyd WJR, Collins HM, Roumeliotis S, Logue SJ, Coventry SJ, Moody DB, Read BJ, Poulsen D, Lance RCM, Platz GJ, Park RF, Panozzo JF, Karakousis A, Lim P, Verbyla AP, Eckermann PJ (2003a) Map** and QTL analysis of the barley population Alexis × Sloop. Aust J Agric Res 54:1117–1123
Barr AR, Karakousis A, Lance RCM, Logue SJ, Manning S, Chalmers KJ, Kretschmer JM, Boyd WJR, Collins HM, Roumeliotis S, Coventry SJ, Moody DB, Read BJ, Poulsen D, Li CD, Platz GJ, Inkerman PA, Panozzo JF, Cullis BR, Smith AB, Lim P, Langridge P (2003b) Map** and QTL analysis of the barley population Chebec × Harrington. Aust J Agric Res 54:1125–1130
Benjamini J, Yekutieli B (2005) Quantitative trait loci analysis using the false discovery rate. Genetics 171:783–790
Collins HM, Panozzo JF, Logue SJ, Jefferies SP, Barr AR (2003) Map** and validation of chromosome regions associated with high malt extract in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Aust J Agric Res 54:1223–1240
Coventry SJ, Collins HM, Barr AR, Jefferies SP, Chalmers KJ, Logue SJ, Langridge P (2003) Use of putative QTLs and structural genes in marker assisted selection for diastatic power in malting barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Aust J Agric Res 54:1241–1250
Choi DW, Koag MC, Close TJ (2000) Map locations of barley Dhn genes determined by gene-specific PCR. Theor Appl Genet 101:350–354
Choi DW, Rodriguez EM, Close TJ (2002) Barley Cbf3 gene identification, expression pattern, and map location. Plant Physiol 129:1781–1787
Costa JM, Corey A, Hayes PM, Jobet C, Kleinhofs A, Kopisch-Obusch A, Kramer SF, Kudrna D, Li M, Riera-Lizarazu O, Sato K, Szucs P, Too**da T, Vales MJ, Wolfe RI (2001) Molecular map** of the Oregon Wolfe barleys: a phenotypically polymorphic doubled-haploid population. Theor Appl Genet 103:415–424
Crosatti C, Nevo E, Stanca AM, Cattivelli L (1996) Genetic analysis of the accumulation of COR14 proteins in wild (Hordeum spontaneum) and cultivated (Hordeum vulgare) barley. Theor Appl Genet 93:975–981
EBC, European Brewery Convention (2005) Analytica-EBC. Fachverlag Hans Carl, Nürnberg, Germany, ISBN: 3-418-00759-7
Eglington JK, Langridge P, Everson EH (1998) Thermostability variation in alleles of barley β-amylase. J Cereal Sci 28:301–309
Erkkilä MJ, Leah R, Ahokas H, Cameron-Mills V (1998) Allele-dependent barley grain α-amylase activity. Plant Physiol 117:679–685
Evans DE, Collins H, Eglinton J, Wilhelmson A (2005) Assessing the impact of the level of diastatic power enzymes and their thermostability on the hydrolysis of starch during wort production to predict malt fermentability. J Am Soc Brew Chem 63:185–198
Forster BP, Russell JR, Ellis RP, Handley LL, Robinson D, Hackett CA, Nevo E, Waugh R, Gordon DC, Keith R, Powell W (1997) Locating genotypes and gene for abiotic stress tolerance in barley: a strategy using maps, markers and the wild species. New Phytol 137:141–147
Fox GP, Panozzo JF, Li CD, Lance RCM, Inkerman PA, Henry RJ (2003) Molecular basis of barley quality. Aust J Agric Res 54:1081–1101
Gao W, Clancy JA, Han F, Jones BL, Budde A, Wesenberg DM, Kleinhofs A, Ullrich SE (2004) Fine map** of a malting-quality QTL complex near the chromosome 4H S telomere in barley. Theor Appl Genet 109:750–760
Grando S, Ceccarelli S (1995) Seminal root morphology and coleoptile length in wild (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum) and cultivated (Hordeum vulgare ssp. vulgare) barley. Euphytica 86:73–80
Han F, Ullrich SE, Chirat S, Menteur S, Jesting L, Sarrafi O, Hayes MP, Jones BL, Blake TK, Wessenberg D, Kleinhofs A, Kilian A (1995) Map** of β-glucan content and β glucanase activity loci in barley grain and malt. Theor Appl Genet 91:921–927
Han F, Romagosa I, Ullrich SE, Jones BL, Hayes PM, Wesenberg DM (1997) Molecular marker-assisted selection for malting quality traits in barley. Mol Breed 3:427–437
Han F, Clancy JA, Jones BL, Wesenberg DM, Kleinhofs A, Ullrich SE (2004) Dissection of a malting quality QTL region on chromosome 1 (7H) of barley. Mol Breed 14:339–347
Hayes PM, Liu BH, Knapp SJ, Chen F, Jones B, Blake T, Franckowiak J, Rasmusson D, Sorrells M, Ullrich SE, Wesenberg D, Kleinhofs A (1993) Quantitative trait locus effects and environmental interaction in a sample of North American barley germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 87:392–401
Hayes PM, Costro A, Marquez-Cedillo L, Corey A, Henson CA, Jones BL, Kling J (2003) Genetic diversity for quantitatively inherited agronomic and malting quality traits. In: Von Bothmer R, Van Hintum T, Knupffer H, Sato K (eds) Diversity in barley (Hordeum vulgare), Elsevier Press, New York, pp 147–169
Karakousis A, Barr AR, Kretschmer JM, Manning S, Logue SJ, Roumeliotis S, Collins HM, Chalmers KJ, Li CD, Lance RCM, Langridge P (2003) Map** and QTL analysis of the barley population Galleon × Haruna Nijo. Aust J Agric Res 54:1131–1135
Kleinhofs A, Graner A (2001) An integrated map of the barley genome. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 187–199
Laurie DA, Pratchett N, Bezant JH, Snape JW (1995) RFLP map** of five major genes and eight quantitative trait loci controlling flowering time in a winter × spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cross. Genome 38:575–585
Li JZ, Huang XQ, Heinrichs F, Ganal MW, Röder MS (2005) Analysis of QTLs for yield, yield components, and malting quality in a BC3-DH population of spring barley. Theor Appl Genet 110:356–363
MEBAK, Mitteleuropäische Brautechnische Analysenkommission (1997) Methodensammlung der Mitteleuropäischen Analysenkommission. Band I, 3. Auflage: Rohstoffe–Wasser, Gerste, Rohfrucht, Malz, Hopfen und Hopfenprodukte, ISBN 3-9805814-0-3
Maestri E, Klueva N, Perrotta C, Gulli M, Nguyen HT, Marmiroli N (2002) Molecular genetics of heat tolerance and heat shock proteins in cereals. Plant Mol Biol 48:667–681
Marquez-Cedillo LA, Hayes PM, Jones BL, Kleinhofs A, Legge WG, Rossnagel BG, Sato K, Ullrich E, Wesenberg DM, The North American Barley (2000) QTL analysis of malting quality in barley based on the doubled-haploid progeny of two elite North American varieties representing different germplasm groups. Theor Appl Genet 101:173–184
Mather DE, Tinker NA, LaBerge DE, Edney M, Jones BL, Rossnagel BG, Legge WG, Briggs KG, Irvine RB, Falk DE, Kasha KJ (1997) Regions of the genome that affect grain and malt quality in a North American two-row barley cross. Crop Sci 37:544–554
Oziel A, Hayes P, Chen F, Jones B (1996) Application of quantitative trait locus map** to the development of winter-habit barley. Plant Breed 115:43–51
Paris M, Jones MGK, Eglington JK (2002) Genoty** single nucleotide polymorphisms for selection of barley α-amylase alleles. Plant Mol Biol Rep 20:149–159
Pillen K, Zacharias A, Léon J (2003) Advanced backcross QTL analysis in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 107:340–352
Read BJ, Raman H, McMichael G, Chalmers KJ, Ablett GA, Platz GJ, Raman R, Genger RK, Boyd WJR, Li CD, Grime CR, Park RF, Wallwork H, Pragnell R, Lance RCM (2003) Map** and QTL analysis of the barley population Sloop × Halcyon. Aust J Agric Res 54:1145–1153
SAS Institute (2003) The SAS system for Windows, release 9.1. SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA
Tanksley SD, Nelson JC (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis: a method of the simultaneous discovery and transfer of valuable QTLs from unadapted germplasm into elite breeding lines. Theor Appl Genet 92:191–203
Tatham A, Shewry P (1995) The S-poor prolamins of wheat, barley and rye. J Cereal Sci 22:1–16
Thomas WTB, Powell W, Swanson JS, Ellis RP, Chalmers KJ, Barua UM, Jack P, Lea V, Forster BP, Waugh R, Smith DB (1996) Quantitative trait loci for germination and malting quality characters in a spring barley cross. Crop Sci 36:265–273
von Korff M, Wang H, Léon J, Pillen K (2004) Development of candidate introgression lines using an exotic barley accession (H. vulgare ssp. spontaneum) as donor. Theor Appl Genet 109:1736–1745
von Korff M, Wang H, Léon J, Pillen K (2005) Detection of resistance genes against powdery mildew, leaf rust and scald introgressed from wild barley (H. vulgare ssp. spontaneum). Theor Appl Genet 111:583–590
von Korff M, Wang H, Léon J, Pillen K (2006) AB-QTL analysis in spring barley: II. Detection of favourable exotic alleles for agronomic traits introgressed from wild barley (H. vulgare ssp. spontaneum). Theor Appl Genet 112:1221–1231
Zale JM, Clancy JA, Ullrich SE, Jones BL, Hayes PM (2000) The North American barley genome map** project summary of barley malting QTLs mapped in various populations. Barley Genet Newsl 30:44
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Eberhard Laubach (Nordsaat Saatzucht) and his team for conducting the field experiment at Gudow. We are greatly indebted to Dr. Lissy Kuntze (Nordsaat Saatzucht, Böhnshausen) for the analysis of malting parameters. The excellent technical assistance of Merle Noschinski, Carsten Golletz, and the team of the Dikopshof Research Station in Wesseling is appreciated. This work was funded by the German Plant Genome Research Initiative (GABI) of the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF, project 0312278A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Korff, M., Wang, H., Léon, J. et al. AB-QTL analysis in spring barley: III. Identification of exotic alleles for the improvement of malting quality in spring barley (H. vulgare ssp. spontaneum). Mol Breeding 21, 81–93 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-007-9110-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-007-9110-1