Abstract
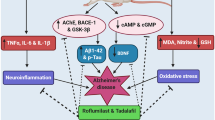
Phosphodiesterase type 4 (PDE4) inhibitors can prevent the breakdown of the second messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and improve cognitive performances in several animal models of cognition. However, the clinical development of PDE4 inhibitors has been seriously hampered by severe side effects, such as vomiting and nausea. In this study, we investigated the effect and mechanism of roflumilast, an FDA-approved PDE4 inhibitor for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), on learning and memory abilities in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). APP/PS1 transgenic mice received 3 intragastric doses of roflumilast (0.1, 0.2 and 0.4 mg/kg) daily for 3 weeks followed by behavioral tests. Chronic administration of roflumilast significantly improved the learning and memory abilities of APP/PS1 transgenic mice in the novel object recognition task, Morris water maze, and the step-down passive avoidance task. In addition, roflumilast increased the cAMP, phosphorylated cAMP response-element binding protein (p-CREB) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels, and reduced the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) p65, and proinflammatory cytokine (IL-6, TNF-a and IL-1β) levels in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 transgenic mice. In conclusion, these findings suggest that roflumilast can enhance cognitive function in APP/PS1 transgenic mice, which may be related to its stimulation of the cAMP/CREB/BDNF pathway and anti-neuroinflammatory effects.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akar F, Mutlu O, Celikyurt IK, Bektas E, Tanyeri MH, Ulak G, Tanyeri P, Erden F (2014) Effects of zaprinast and rolipram on olfactory and visual memory in the social transmission of food preference and novel object recognition tests in mice. Drug Target Insights 8:23–29
Akar F, Mutlu O, Celikyurt IK, Ulak G, Erden F, Bektas E, Tanyeri P (2015) Effects of rolipram and zaprinast on learning and memory in the Morris water maze and radial arm maze tests in naive mice. Drug Res (Stuttg) 65:86–90
Bambah-Mukku D, Travaglia A, Chen DY, Pollonini G, Alberini CM (2014) A positive autoregulatory BDNF feedback loop via C/EBPbeta mediates hippocampal memory consolidation. J Neurosci 34:12547–12559
Barage SH, Sonawane KD (2015) Amyloid cascade hypothesis: pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropeptides 52:1–18
Bolos M, Perea JR, Avila J (2017) Alzheimer's disease as an inflammatory disease. Biomol Concepts 8:37–43
Bruce-Keller AJ, Gupta S, Knight AG, Beckett TL, McMullen JM, Davis PR, Murphy MP, van Eldik LJ, St Clair D, Keller JN (2011) Cognitive impairment in humanized APPxPS1 mice is linked to Abeta (1-42) and NOX activation. Neurobiol Dis 44:317–326
Chong J, Leung B, Poole P (2017) Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 9:CD002309
Daniilidou M, Koutroumani M, Tsolaki M (2011) Epigenetic mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Med Chem 18:1751–1756
Dansokho C, Heneka MT (2017) Neuroinflammatory responses in Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 125:771–779
Dewapriya P, Li YX, Himaya SW, Pangestuti R, Kim SK (2013) Neoechinulin a suppresses amyloid-beta oligomer-induced microglia activation and thereby protects PC-12 cells from inflammation-mediated toxicity. Neurotoxicology 35:30–40
Dworkin S, Mantamadiotis T (2010) Targeting CREB signalling in neurogenesis. Expert Opin Ther Targets 14:869–879
Garcia-Osta A, Cuadrado-Tejedor M, Garcia-Barroso C, Oyarzabal J, Franco R (2012) Phosphodiesterases as therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 3:832–844
Gong B, Vitolo OV, Trinchese F, Liu S, Shelanski M, Arancio O (2004) Persistent improvement in synaptic and cognitive functions in an Alzheimer mouse model after rolipram treatment. J Clin Invest 114:1624–1634
Guo HB, Y F C, Wu JG et al (2015) Donepezil improves learning and memory deficits in APP/PS1 mice by inhibition of microglial activation. Neuroscience 290:530–542
Guo H, Cheng Y, Wang C, Wu J, Zou Z, Niu B, Yu H, Wang H, Xu J (2017) FFPM, a PDE4 inhibitor, reverses learning and memory deficits in APP/PS1 transgenic mice via cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling and anti-inflammatory effects. Neuropharmacology 116:260–269
Haraguchi S, Good RA, Day NK (1995) Immunosuppressive retroviral peptides: cAMP and cytokine patterns. Immunol Today 16:595–603
Jabaris SG, Sumathy H, Kumar RS et al (2015) Effects of rolipram and roflumilast, phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors, on hypertension-induced defects in memory function in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 746:138–147
Jiang LI, Sternweis PC, Wang JE (2013) Zymosan activates protein kinase a via adenylyl cyclase VII to modulate innate immune responses during inflammation. Mol Immunol 54:14–22
Josselyn SA, Nguyen PV (2005) CREB, synapses and memory disorders: past progress and future challenges. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 4:481–497
Kandel ER (2012) The molecular biology of memory: cAMP, PKA, CRE, CREB-1, CREB-2, and CPEB. Mol Brain 5:14
Karran E, Mercken M, De Strooper B (2011) The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer's disease: an appraisal for the development of therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:698–712
Lakics V, Karran EH, Boess FG (2010) Quantitative comparison of phosphodiesterase mRNA distribution in human brain and peripheral tissues. Neuropharmacology 59:367–374
Liu M, Wei Y, Yang Y et al (2017) Effects and mechanism of Huannao Yicong decoction extract on the ethology of transgenic APP/PS1 mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017:9502067
Lonze BE, Ginty DD (2002) Function and regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous system. Neuron 35:605–623
Lopez-Gonzalez I, Schluter A, Aso E et al (2015) Neuroinflammatory signals in Alzheimer disease and APP/PS1 transgenic mice: correlations with plaques, tangles, and oligomeric species. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 74:319–344
Luccarini I, Grossi C, Traini C, Fiorentini A, Ed Dami T, Casamenti F (2012) Abeta plaque-associated glial reaction as a determinant of apoptotic neuronal death and cortical gliogenesis: a study in APP mutant mice. Neurosci Lett 506:94–99
Nagakura A, Shitaka Y, Yarimizu J, Matsuoka N (2013) Characterization of cognitive deficits in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease and effects of donepezil and memantine. Eur J Pharmacol 703:53–61
Pan XD, Chen XC, Zhu YG, Chen LM, Zhang J, Huang TW, Ye QY, Huang HP (2009) Tripchlorolide protects neuronal cells from microglia-mediated beta-amyloid neurotoxicity through inhibiting NF-kappaB and JNK signaling. Glia 57:1227–1238
Pinner NA, Hamilton LA, Hughes A (2012) Roflumilast: a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor for the treatment of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Ther 34:56–66
Poole RM, Ballantyne AD (2014) Apremilast: first global approval. Drugs 74:825–837
Press NJ, Banner KH (2009) PDE4 inhibitors - a review of the current field. Prog Med Chem 47:37–74
Puzzo D, Vitolo O, Trinchese F et al (2005) Amyloid-beta peptide inhibits activation of the nitric oxide/cGMP/cAMP-responsive element-binding protein pathway during hippocampal synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 25:6887–6897
Robichaud A, Savoie C, Stamatiou PB, Lachance N, Jolicoeur P, Rasori R, Chan CC (2002) Assessing the emetic potential of PDE4 inhibitors in rats. Br J Pharmacol 135:113–118
Rutten K, Prickaerts J, Blokland A (2006) Rolipram reverses scopolamine-induced and time-dependent memory deficits in object recognition by different mechanisms of action. Neurobiol Learn Mem 85:132–138
Rutten K, Lieben C, Smits L, Blokland A (2007) The PDE4 inhibitor rolipram reverses object memory impairment induced by acute tryptophan depletion in the rat. Psychopharmacology 192:275–282
Saura CA, Valero J (2011) The role of CREB signaling in Alzheimer's disease and other cognitive disorders. Rev Neurosci 22:153–169
Scearce-Levie K (2011) Monitoring spatial learning and memory in Alzheimer's disease mouse models using the Morris water maze. Methods Mol Biol 670:191–205
Sierksma AS, van den Hove DL, Pfau F et al (2014) Improvement of spatial memory function in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice after chronic inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 4D. Neuropharmacology 77:120–130
Smith DL, Pozueta J, Gong B, Arancio O, Shelanski M (2009) Reversal of long-term dendritic spine alterations in Alzheimer disease models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:16877–16882
Swerdlow RH (2012) Alzheimer's disease pathologic cascades: who comes first, what drives what. Neurotox Res 22:182–194
Van Duinen MA, Sambeth A, Heckman P et al (2018) Acute administration of roflumilast enhances immediate recall of verbal word memory in healthy young adults. Neuropharmacology 131:31–38
Vanmierlo T, Creemers P, Akkerman S, van Duinen M, Sambeth A, de Vry J, Uz T, Blokland A, Prickaerts J (2016) The PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast improves memory in rodents at non-emetic doses. Behav Brain Res 303:26–33
Veremeyko T, Yung A, Dukhinova M et al (2018) Cyclic AMP pathway suppress autoimmune neuroinflammation by inhibiting functions of encephalitogenic CD4 T cells and enhancing M2 macrophage polarization at the site of inflammation. Front Immunol 9:50
Wang C, Yang XM, Zhuo YY, Zhou H, Lin HB, Cheng YF, Xu JP, Zhang HT (2012) The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor rolipram reverses Abeta-induced cognitive impairment and neuroinflammatory and apoptotic responses in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15:749–766
Wang G, Chen L, Pan X, Chen J, Wang L, Wang W, Cheng R, Wu F, Feng X, Yu Y, Zhang HT, O'Donnell JM, Xu Y (2016) The effect of resveratrol on beta amyloid-induced memory impairment involves inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 related signaling. Oncotarget 7:17380–17392
Webster SJ, Bachstetter AD, Van Eldik LJ (2013) Comprehensive behavioral characterization of an APP/PS-1 double knock-in mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 5:28
Wengenack TM, Whelan S, Curran GL, Duff KE, Poduslo JF (2000) Quantitative histological analysis of amyloid deposition in Alzheimer's double transgenic mouse brain. Neuroscience 101:939–944
Wortmann M (2012) Dementia: a global health priority - highlights from an ADI and World Health Organization report. Alzheimers Res Ther 4:40
Yamamoto M, Gotz ME, Ozawa H et al (2000) Hippocampal level of neural specific adenylyl cyclase type I is decreased in Alzheimer's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1535:60–68
Yamamoto-Sasaki M, Ozawa H, Saito T, Rosler M, Riederer P (1999) Impaired phosphorylation of cyclic AMP response element binding protein in the hippocampus of dementia of the Alzheimer type. Brain Res 824:300–303
Yamashima T (2012) 'PUFA-GPR40-CREB signaling' hypothesis for the adult primate neurogenesis. Prog Lipid Res 51:221–231
Zemek F, Drtinova L, Nepovimova E et al (2014) Outcomes of Alzheimer's disease therapy with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and memantine. Expert Opin Drug Saf 13:759–774
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, H., Wang, C., He, W. et al. Roflumilast ameliorates cognitive impairment in APP/PS1 mice via cAMP/CREB/BDNF signaling and anti-neuroinflammatory effects. Metab Brain Dis 34, 583–591 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0374-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0374-4