Abstract
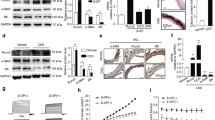
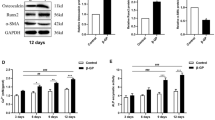
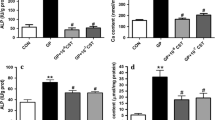
Vascular calcification is associated with cardiovascular disease as a complication of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and chronic kidney disease. Vitamin K2 (VK2) delays vascular calcification by an unclear mechanism. Moreover, apoptosis modulates vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) calcification. This paper aimed to study VK2-modified VSMC calcification and survival cell signaling mediated by growth arrest-specific gene 6 (Gas6) and its tyrosine kinase receptor Axl. Primary-cultured VSMCs were dose-dependently treated with VK2 in the presence of calcification medium for 8 days, or pre-treated for 1 h with/without the Axl inhibitor R428 (2 μmol/L) or the caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-fmk (20 μmol/L) followed by treatment with VK2 (10 μmol/L) or rmGas6 (200 nmol/L) in calcification medium for 8 days. Calcium deposition was determined by the o-cresolphthalein complexone assay and Alizarin Red S staining. Apoptosis was determined by TUNEL and flow cytometry using Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide staining. Western blotting detected the expressions of Axl, Gas6, p-Akt, Akt, and Bcl2. VK2 significantly inhibited CaCl2- and β-sodium glycerophosphate (β-GP)-induced VSMC calcification and apoptosis, which was dependent on restored Gas6 expression and activated downstream signaling by Axl, p-Akt, and Bcl2. Z-VAD-fmk significantly inhibited CaCl2- and β-GP-induced VSMC calcification and apoptosis. Augmented recombinant mouse Gas6 protein (rmGas6) expression significantly reduced VSMC calcification and apoptosis. Furthermore, the Gas6/Axl interaction was inhibited by R428, which abolished the preventive effect of VK2 on CaCl2- and β-GP-induced apoptosis and calcification. These results suggest that Gas6 is critical in VK2-mediated functions that attenuate CaCl2- and β-GP-induced VSMC calcification by blocking apoptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liberman M, Pesaro AEP, Carmo LS, Serrano CV Jr (2013) Vascular calcification: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 11(3):376–382
Dalmeijer GW, van der Schouw YT, Vermeer C, Magdeleyns EJ, Schurgers LJ, Beulens JW (2013) Circulating matrix Gla protein is associated with coronary artery calcification and vitamin K status in healthy women. J Nutr Biochem 24(4):624–628
Sage AP, Tintut Y, Demer LL (2010) Regulatory mechanisms in vascular calcification. Nat Rev Cardiol 7(9):528–536
Wu M, Rementer C, Giachelli CM (2013) Vascular calcification: an update on mechanisms and challenges in treatment. Calcif Tissue Int 93(4):365–373
Burton D, Matsubara H, Ikeda K (2010) Pathophysiology of vascular calcification: pivotal role of cellular senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp Gerontol 45(11):819–824
Liao X-B, Peng Y-Q, Zhou X-M, Yang B, Zheng Z, Liu L-M, Song F-L, Li J-M, Zhou K, Meng J-C (2010) Taurine restores Axl/Gas6 expression in vascular smooth muscle cell calcification model. Amino Acids 39(2):375–383
Proudfoot D, Skepper JN, Hegyi L, Bennett MR, Shanahan CM, Weissberg PL (2000) Apoptosis regulates human vascular calcification in vitro evidence for initiation of vascular calcification by apoptotic bodies. Circ Res 87(11):1055–1062
Son B-K, Kozaki K, Iijima K, Eto M, Kojima T, Ota H, Senda Y, Maemura K, Nakano T, Akishita M (2006) Statins protect human aortic smooth muscle cells from inorganic phosphate-induced calcification by restoring Gas6-Axl survival pathway. Circ Res 98(8):1024–1031
Dam H (1935) The antihaemorrhagic vitamin of the chick. Biochem J 29(6):1273
Dam H, Schönheyder F (1934) A deficiency disease in chicks resembling scurvy. Biochem J 28(4):1355
Schønheyder F (1936) The quantitative determination of vitamin K. I. Biochem J 30(5):890
Dam H, Schønheyder F (1936) The occurrence and chemical nature of vitamin K. Biochem J 30(5):897
El Asmar MS, Naoum JJ, Arbid EJ (2014) Vitamin k dependent proteins and the role of vitamin k2 in the modulation of vascular calcification: a review. Oman Med J 29(3):172
Schurgers LJ (2013) Vitamin K: key vitamin in controlling vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 83(5):782–784
Flore R, Ponziani FR, Di Rienzo TA, Zocco MA, Flex A, Gerardino L, Lupascu A, Santoro L, Santoliquido A, Di Stasio E (2013) Something more to say about calcium homeostasis: the role of vitamin K2 in vascular calcification and osteoporosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 17(18):2433–2440
Clauser S, Meilhac O, Bieche I, Raynal P, Bruneval P, Michel J-B, Borgel D (2012) Increased secretion of Gas6 by smooth muscle cells in human atherosclerotic carotid plaques. Thromb Haemost 107(1):140–149
Jiang X, Tao H, Qiu C, Ma X, Li S, Guo X, Lv A, Li H (2016) Vitamin K2 regression aortic calcification induced by warfarin via Gas6/Axl survival pathway in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 786:10–18
Melaragno MG, Cavet ME, Yan C, Tai L-K, ** Z-G, Haendeler J, Berk BC (2004) Gas6 inhibits apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle: role of Axl kinase and Akt. J Mol Cell Cardiol 37(4):881–887
Hasanbasic I, Rajotte I, Blostein M (2005) The role of γ-carboxylation in the anti-apoptotic function of gas6. J Thromb Haemost 3(12):2790–2797
Kim H, Kim HJ, Lee K, Kim JM, Kim HS, Kim JR, Ha CM, Choi YK, Lee SJ, Kim JY (2012) α-Lipoic acid attenuates vascular calcification via reversal of mitochondrial function and restoration of Gas6/Axl/Akt survival pathway. J Cell Mol Med 16(2):273–286
Kaesler N, Immendorf S, Ouyang C, Herfs M, Drummen N, Carmeliet P, Vermeer C, Floege J, Krüger T, Schlieper G (2016) Gas6 protein: its role in cardiovascular calcification. BMC Nephrol 17(1):1
Danziger J (2008) Vitamin K-dependent proteins, warfarin, and vascular calcification. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3(5):1504–1510
Li H, Tao Hr HuT, Fan Yh, Rq Zhang, Jia G, Hc Wang (2010) Atorvastatin reduces calcification in rat arteries and vascular smooth muscle cells. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 107(4):798–802
Chang X, Zhang B, Lihua L, Feng Z (2016) T3 inhibits the calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells and the potential mechanism. Am J Transl Res 8(11):4694–4704
Chang JR, Duan XH, Zhang BH, Teng X, Zhou YB, Liu Y, Yu YR, Zhu Y, Tang CS, Qi YF (2013) Intermedin1-53 attenuates vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress via cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 238(10):1136–1146. doi:10.1177/1535370213502619
Schurgers L, Spronk H, Skepper J, Hackeng T, Shanahan C, Vermeer C, Weissberg P, Proudfoot D (2007) Post-translational modifications regulate matrix Gla protein function: importance for inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. J Thromb Haemost 5(12):2503–2511
Konishi A, Aizawa T, Mohan A, Korshunov VA, Berk BC (2004) Hydrogen peroxide activates the Gas6-Axl pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 279(27):28766–28770
Reynolds JL, Joannides AJ, Skepper JN, McNair R, Schurgers LJ, Proudfoot D, Jahnen-Dechent W, Weissberg PL, Shanahan CM (2004) Human vascular smooth muscle cells undergo vesicle-mediated calcification in response to changes in extracellular calcium and phosphate concentrations: a potential mechanism for accelerated vascular calcification in ESRD. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(11):2857–2867
Persy V, D’Haese P (2009) Vascular calcification and bone disease: the calcification paradox. Trends Mol Med 15(9):405–416
Cao X, Li H, Tao H, Wu N, Yu L, Zhang D, Lu X, Zhu J, Lu Z, Zhu Q (2013) Metformin inhibits vascular calcification in female rat aortic smooth muscle cells via the AMPK-eNOS-NO pathway. Endocrinology 154(10):3680–3689
Shanahan CM, Crouthamel MH, Kapustin A, Giachelli CM (2011) Arterial calcification in chronic kidney disease: key roles for calcium and phosphate. Circ Res 109(6):697–711
Crouthamel MH, Lau WL, Leaf EM, Chavkin NW, Wallingford MC, Peterson DF, Li X, Liu Y, Chin MT, Levi M (2013) Sodium-dependent phosphate cotransporters and phosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells redundant roles for PiT-1 and PiT-2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(11):2625–2632
Takemura A, Iijima K, Ota H, Son B-K, Ito Y, Ogawa S, Eto M, Akishita M, Ouchi Y (2011) Sirtuin 1 retards hyperphosphatemia-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31(9):2054–2062
Watanabe Y, Suzuki M, Oyama Y, Kusano E, Tamba K, Iimura O, Ito C, Imai M, Asano Y (2002) Cellular component of vascular calcification. Nephron 92(4):840–845
Saito E, Wachi H, Sato F, Sugitani H, Seyama Y (2007) Treatment with vitamin K2 combined with bisphosphonates synergistically inhibits calcification in cultured smooth muscle cells. J Atheroscler Thromb 14(6):317–324
Shroff RC, McNair R, Skepper JN, Figg N, Schurgers LJ, Deanfield J, Rees L, Shanahan CM (2010) Chronic mineral dysregulation promotes vascular smooth muscle cell adaptation and extracellular matrix calcification. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(1):103–112
Llacuna L, Bárcena C, Bellido-Martín L, Fernández L, Stefanovic M, Marí M, García-Ruiz C, Fernández-Checa JC, García de Frutos P, Morales A (2010) Growth arrest–specific protein 6 is hepatoprotective against murine ischemia/reperfusion injury. Hepatology 52(4):1371–1379
Goruppi S, Ruaro E, Varnum B, Schneider C (1999) Gas6-mediated survival in NIH3T3 cells activates stress signalling cascade and is independent of Ras. Oncogene 18(29):4224–4236
Goruppi S, Ruaro E, Schneider C (1996) Gas6, the ligand of Axl tyrosine kinase receptor, has mitogenic and survival activities for serum starved NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Oncogene 12(3):471–480
Zuo P-Y, Chen X-L, Lei Y-H, Liu C-Y, Liu Y-W (2014) Growth arrest-specific gene 6 protein promotes the proliferation and migration of endothelial progenitor cells through the PI3 K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med 34(1):299–306
Lijnen HR, Christiaens V (2011) Growth arrest-specific protein 6 receptor antagonism impairs adipocyte differentiation and adipose tissue development in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 337(2):457–464
Holland SJ, Pan A, Franci C, Hu Y, Chang B, Li W, Duan M, Torneros A, Yu J, Heckrodt TJ (2010) R428, a selective small molecule inhibitor of Axl kinase, blocks tumor spread and prolongs survival in models of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res 70(4):1544–1554
Ghosh AK, Secreto C, Boysen J, Sassoon T, Shanafelt TD, Mukhopadhyay D, Kay NE (2011) The novel receptor tyrosine kinase Axl is constitutively active in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acts as a docking site of nonreceptor kinases: implications for therapy. Blood 117(6):1928–1937
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81170256 and 81070698) and the Development Project of Scientific and Technological Research of Shanxi Province (2009K13-01).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81170256 and 81070698) and the Development Project of Scientific and Technological Research of Shanxi Province (No. 2009K13-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The experiments were performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Fourth Military Medical University.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, C., Zheng, H., Tao, H. et al. Vitamin K2 inhibits rat vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by restoring the Gas6/Axl/Akt anti-apoptotic pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 433, 149–159 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3023-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3023-z