Abstract
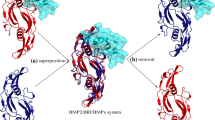
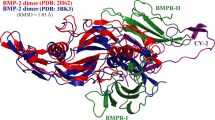
Human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP2) plays an important role in the development of bone and cartilage, which functions as bone growth factor by interacting with its cognate type-I and type-II receptors (BMPR-I and BMPR-II) through conformational wrist epitope and linear knuckle epitope, respectively. Here, the intermolecular interaction between the BMP2 knuckle epitope and BMPR-II is investigated at structural level, from which a binding hotspot region is identified that is primarily responsible for the epitope recognition by BMPR-II. A KEH peptide covering the hotspot region exhibits a weak binding affinity (Kd = 78.6 ± 13.5 µM) to BMPR-II and a moderate osteogenic activity on human BMSCs (ALP = 135 ± 17% and 164 ± 21% at peptide concentrations 0.01 and 0.1 µg/ml, respectively). Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) is used to guide the rational optimization of KEH peptide. The strategy focuses on systematic design of the peptide’s non-key residues to derive a series of its promising mutants, which are then evaluated rigorously by using dynamics simulation and energetic analysis. Consequently, totally ten designed peptide mutants are tested in vitro at molecular and cellular levels; most of them are determined to exhibit an increased or comparable affinity/activity relative to the native KEH peptide and knuckle epitope. In particular, the KEH-p7 peptide is found to have a satisfactory profile with Kd = 9.6 ± 1.2 µM and ALP = 178 ± 24% and 235 ± 32% at peptide concentrations 0.01 and 0.1 µg/ml, respectively. Structural analysis reveals a complicated noncovalent network of hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic forces and stacking interactions across the complex interface of BMPR-II with KEH-p7, conferring both stability and specificity to the receptor–peptide interaction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assaf RB, Fayyad-Kazan M, Al-Nemer F, Makki R, Fayyad-Kazan H, Badran B, Berbéri A (2019) A evaluation of the osteogenic potential of different scaffolds embedded with human stem cells originated from Schneiderian membrane: an in vitro study. Biomed Res Int 2019:2868673
Bai Z, Hou S, Zhang S, Li Z, Zhou P (2017) Targeting self-binding peptides as a novel strategy to regulate protein activity and function: a case study on the proto-oncogene tyrosine protein kinase c-Src. J Chem Inf Model 57:835–845
Brown NP, Leroy C, Sander C (1998) MView: a web-compatible database search or multiple alignment viewer. Bioinformatics 14:380–381
Brown MA, Zhao Q, Baker KA, Naik C, Chen C, Pukac L, Singh M, Tsareva T, Parice Y, Mahoney A, Roschke V, Sanyal I, Choe S (2005) Crystal structure of BMP-9 and functional interactions with pro-region and receptors. J Biol Chem 280:25111–25118
Case DA, Cheatham TE, Darden T, Gohlke H, Luo R, Merz KM, Onufriev A, Simmerling C, Wang B, Woods RJ (2005) The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J Comput Chem 26:1668–1688
Chen D, Zhao M, Mundy GR (2004) Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors 22:233–241
Chen Z, Yu X, Zhang A, Wang F, **ng (2020) De novo hydrocarbon-stapling design of single-turn α-helical antimicrobial peptides. Int J Pept Res Ther. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-019-0996-47
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L (1983) Particale mesh Ewald and N.log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98:10089–10092
Esposito M, Lucariello A, Riccio I, Riccio V, Esposito V, Riccardi G (2012) Differentiation of human osteoprogenitor cells increases after treatment with pulsed electromagnetic fields. In Vivo 26:299–304
Falcigno L, D’Auria G, Calvanese L, Marasco D, Iacobelli R, Scognamiglio PL, Brun P, Danesin R, Pasqualin M, Castagliuolo I, Dettin M (2015) Osteogenic properties of a short BMP-2 chimera peptide. J Pept Sci 21:700–709
Fan X, **a H, Liu X, Li B, Fang J (2019) Rational design of type-IA receptor-derived cyclic peptides to target human bone morphogenic protein 2. J Biosci 44:130
Golub E, Boesze-Battaglia K (2007) The role of alkaline phosphatase in mineralization. Curr Opin Orthop 18:444–448
Kanie K, Kurimoto R, Tian J, Ebisawa K, Narita Y, Honda H, Kato R (2016) Screening of osteogenic-enhancing short peptides from BMPs for biomimetic material applications. Materials 9:e730
Katagiri T, Watabe T (2016) Bone morphogenetic proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 8:a021899
Katritzky AR, Jain R, Lomaka A, Petrukhin R, Karelson M, Visser AE, Rogers RD (2002) Correlation of the melting points of potential ionic liquids (imidazolium bromides and benzimidazolium bromides) using the CODESSA program. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 42:225–231
Kirsch T, Nickel J, Sebald W (2000) BMP-2 antagonists emerge from alterations in the low-affinity binding epitope for receptor BMPR-II. EMBO J 19:3314–3324
Lauzon MA, Faucheux N (2018) A small peptide derived from BMP-9 can increase the effect of bFGF and NGF on SH-SY5Y cells differentiation. Mol Cell Neurosci 88:83–92
Lauzon MA, Drevelle O, Faucheux N (2017) Peptides derived from the knuckle epitope of BMP-9 induce the cholinergic differentiation and inactivate GSk3β in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Sci Rep 7:4695
Lauzon MA, Marcos B, Faucheux N (2018) Characterization of alginate/chitosan-based nanoparticles and mathematical modeling of their SpBMP-9 release inducing neuronal differentiation of human SH-SY5Y cells. Carbohydr Polym 181:801–811
Lee JS, Kim ME, Seon JK, Kang JY, Yoon TR, Park YD, Kim HK (2018) Bone-forming peptide-3 induces osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells via regulation of the ERK1/2 and Smad1/5/8 pathways. Stem Cell Res 26:28–35
Li Z, Yan F, Miao Q, Meng Y, Wen L, Jiang Q, Zhou P (2019) Self-binding peptides: binding-upon-folding versus folding-upon-binding. J Theor Biol 469:25–34
Li Z, Miao Q, Yan F, Meng Y, Zhou P (2019) Machine learning in quantitative protein-peptide affinity prediction: implications for therapeutic peptide design. Curr Drug Metab 20:170–176
Liu L, He D, Yang S, Xu Y (2010) Applying chemometrics approaches to model and predict the binding affinities between the human amphiphysin SH3 domain and its peptide ligands. Protein Pept Lett 17:246–253
Liu H, Zhang R, Chen D, Oyajobi BO, Zhao M (2012) Functional redundancy of type II BMP receptor and type IIB activin receptor in BMP2-induced osteoblast differentiation. J Cell Physiol 227:952–963
Liu M, Xu H, Ma Y, Cheng J, Hua Z, Huang G (2017) Osteoblasts proliferation and differentiation stimulating activities of the main components of Epimedii folium. Pharmacogn Mag 13:90–94
Luo H, Du T, Zhou P, Yang L, Mei H, Ng H, Zhang W, Shu M, Tong W, Shi L, Mendrick DL, Hong H (2015) Molecular docking to identify associations between drugs and class I human leukocyte antigens for predicting idiosyncratic drug reactions. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 18:296–304
Ren Y, Chen X, Feng M, Wang Q, Zhou P (2011) Gaussian process: a promising approach for the modeling and prediction of peptide binding affinity to MHC proteins. Protein Pept Lett 18:670–678
Ryckaert JP, Ciccotti G, Berendsen HJC (1997) Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J Comput Phys 23:327–341
Saito A, Suzuki Y, Ogata SI, Ohtsuki C, Tanihara M (2003) Activation of osteo-progenitor cells by a novel synthetic peptide derived from the bone morphogenetic protein-2 knuckle epitope. Biochim Biophys Acta 1651:60–67
Senta H, Park H, Bergeron E, Drevelle O, Fong D, Leblanc E, Cabana F, Roux S, Grenier G, Faucheux N (2009) Cell responses to bone morphogenetic proteins and peptides derived from them: biomedical applications and limitations. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 20:213–222
Senta H, Bergeron E, Drevelle O, Park H, Faucheux N (2011) Combination of synthetic peptides derived from bone morphogenetic proteins and biomaterials for medical applications. Can J Chem Eng 89:227–239
Tian F, Yang L, Lv F, Yang Q, Zhou P (2009) In silico quantitative prediction of peptides binding affinity to human MHC molecule: an intuitive quantitative structure-activity relationship approach. Amino Acids 36:535–554
Tian F, Lv Y, Zhou P, Yang L (2011) Characterization of PDZ domain-peptide interactions using an integrated protocol of QM/MM, PB/SA, and CFEA analyses. J Comput Aided Mol Des 25:947–958
Tian F, Tan R, Guo T, Zhou P, Yang L (2013) Fast and reliable prediction of domain-peptide binding affinity using coarse-grained structure models. Biosystems 113:40–49
Tian F, Yang C, Wang C, Guo T, Zhou P (2014) Mutatomics analysis of the systematic thermostability profile of Bacillus subtilis lipase A. J Mol Model 20:2257
UniProt C (2019) UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D506–D515
Wang RN, Green J, Wang Z, Deng Y, Qiao M, Peabody M, Zhang Q, Ye J, Yan Z, Denduluri S, Idowu O, Li M, Shen C, Hu A, Haydon RC, Kang R, Mok J, Lee MJ, Luu HL, Shi LL (2014) Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling in development and human diseases. Genes Dis 1:87–105
Wang Y, Yang YJ, Chen YN, Zhao HY, Zhang S (2016) Computer-aided design, structural dynamics analysis, and in vitro susceptibility test of antibacterial peptides incorporating unnatural amino acids against microbial infections. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 134:215–223
Weber D, Kotzsch A, Nickel J, Harth S, Seher A, Mueller U, Sebald W, Mueller TD (2007) A silent H-bond can be mutationally activated for high-affinity interaction of BMP-2 and activin type IIB receptor. BMC Struct Biol 7:6
Yang C, Zhang S, He P, Wang C, Huang J, Zhou P (2015a) Self-binding peptides: folding or binding. J Chem Inf Model 55:329–342
Yang C, Wang C, Zhang S, Huang J, Zhou P (2015b) Structural and energetic insights into the intermolecular interaction among human leukocyte antigens, clinical hypersensitive drugs and antigenic peptides. Mol Simul 41:741–751
Yang C, Zhang S, Bai Z, Hou S, Wu D, Huang J, Zhou P (2016) A two-step binding mechanism for the self-binding peptide recognition of target domains. Mol Biosyst 12:1201–1213
Yu H, Zhou P, Deng M, Shang Z (2014) Indirect readout in protein-peptide recognition: a different story from classical biomolecular recognition. J Chem Inf Model 54:2022–2032
Zhang W, Liu J, Shan H, Yin F, Zhong B, Zhang C, Yu X (2019) Machine learning-guided evolution of BMP-derived osteogenic peptides to target receptor. J Drug Targ 28:416–419
Zhou P, Wang C, Tian F, Ren Y, Yang C, Huang J (2013) Biomacromolecular quantitative structure-activity relationship (BioQSAR): a proof-of-concept study on the modeling, prediction and interpretation of protein-protein binding affinity. J Comput Aided Mol Des 27:67–78
Zhou P, Yang C, Ren Y, Wang C, Tian F (2013) What are the ideal properties for functional food peptides with antihypertensive effect? A computational peptidology approach. Food Chem 141:2967–2973
Zhou P, Zhang S, Wang Y, Yang C, Huang J (2016) Structural modeling of HLA-B*1502 peptide carbamazepine T-cell receptor complex architecture: implication for the molecular mechanism of carbamazepine-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Biomol Struct Dyn 34:1806–1817
Zhou P, Hou S, Bai Z, Li Z, Wang H, Chen Z, Meng Y (2018) Disrupting the intramolecular interaction between proto-oncogene c-Src SH3 domain and its self-binding peptide PPII with rationally designed peptide ligands. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:1122–1131
Zhou P, Miao Q, Yan F, Li Z, Jiang Q, Wen L, Meng Y (2019) Is protein context responsible for peptide-mediated interactions? Mol Omics 15:280–295
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the YCH foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors decalred that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, A., Chen, Z., Yu, X. et al. Rational Derivation of Osteogenic Peptides from Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Knuckle Epitope by Integrating In Silico Analysis and In Vitro Assay. Int J Pept Res Ther 27, 25–35 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10058-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10058-y