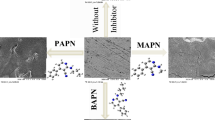
Abstract
Effect of an antibacterial drug, sulfacetamide, IUPAC name N-[(4-aminophenyl) sulfonyl] acetamide (APSA), on the corrosion products formed on carbon steel surface in 1.0 mol L−1 HCl solution has been investigated using mass loss, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and simultaneous thermal and differential scanning calorimetry/differential thermal analysis (TG/DSC/DTA). Mass loss measurements reveal that the corrosion rate of carbon steel is retarded by APSA and that the inhibition efficiency of this inhibitor increases with increasing the concentration. XPS analysis shows that, at this stage, the main product of corrosion is a non-stoichiometric Fe3+ oxyhydroxide, consisting of a mixture of FeO(OH) in anhydrous or hydrated forms, containing Cl− inclusions and adsorbed APSA molecules. The mechanism of inhibition was discussed in light of the chemical structure of the investigated inhibitor. The corrosion products were analyzed using TG/DSC/DTA technique.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larabi L, Harek Y, Traisnel M, Mansri A. Synergetic influence of poly(4-vinylpyridine) and potassium iodide on inhibition of corrosion of mild steel in 1 M HCl. J Appl Electrochem. 2004;34:833–9.
Samide A, Bibicu I, Rogalski M, Preda M. Study of the corrosion inhibition of carbon-steel in dilute ammoniacal media using N-cyclohexyl-benzothiazole-sulfenamide. Corros Sci. 2005;47:1119–27.
Subramania A, Kalyana Sundaram NT, Sathiya Priya R, Saminathan K, Muralidharan VS, Vasuedevan T. Aldimines—effective corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. J Appl Electrochem. 2004;34:1–4.
Samide A, Bibicu I. Kinetics corrosion process of mild steel in hydrochloric acid in absence and presence of 2-(cyclohexylaminomercapto) benzothiazole. Surf Interface Anal. 2008;40:944–52.
Abd El-Rehim SS, Refay SAM, Taha F, Saleh MB, Ahmed RA. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic medium using 2-amino thiophenol and 2-cyanomethyl benzothiazole. J Appl Electrochem. 2001;31:429–35.
Samide A, Bibicu I, Agiu M, Preda M. Mössbabauer spectroscopy study on the corrosion inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Mater Lett. 2008;62:320–2.
Hassan N, Holze R. A comparative electrochemical study of electrosorbed 2- and 4-mercaptopyridines and their application as corrosion inhibitors at C60 steel. J Chem Sci. 2009;121:693–701.
Samide A, Bibicu I, Rogalski MS, Preda M. A study of the corrosion inhibition of carbon steel in diluted ammonia media using 2-mercapto benzothiazole by Mössbauer spectrometry. Acta Chim Slov. 2004;51:127–36.
Samide A, Bibicu I, Turcanu E. Surface analysis of inhibitor films formed by N-(2-hydroxybenzylidene) thiosemicarbazide on carbon steel in acidic media. Chem Eng Commun. 2009;196:1008–17.
Samide A, Tutunaru B, Negrila C, Trandafir I, Maxut A. Effect of sulfacetamide on the composition of corrosion products formed onto carbon steel surface in hydrochloric acid. Dig J Nanomater Bios. 2011;6:663–73.
Ahamad I, Prasad R, Quraishi MA. Inhibition of mild steel corrosion in acid solution by pheniramine drug: experimental and theoretical study. Corros Sci. 2010;52:198–204.
Fonda AS, Mostafa HA, El-Abbasy HM. Antibacterial drugs as inhibitors for the corrosion of stainless steel type 304 in HCl solution. J Appl Electrochem. 2010;40:163–73.
Obot IB, Obi-Egbedi NO. 2,3-Diphenylbenzoquinoxaline: a new corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in sulphuric acid. Corros Sci. 2010;52:282–5.
Shukla SK, Singh AK, Ahamad I, Quraishi MA. Streptomycin: a commercially available drug as corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Mater Lett. 2009;63:819–22.
El-Naggar MM. Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in acidic medium by some sulfa drugs compounds. Corros Sci. 2007;49:2226–36.
Abdallah M. Antibacterial drugs as corrosion inhibitors for corrosion of aluminium in hydrochloric solution. Corros Sci. 2004;46:1981–96.
Ebenso EE, Arslan T, Kandemirli F, Love I, Ödretır C, Saracoğlu M, Umoren SA. Theoretical studies of some sulphonamides as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acidic medium. Int J Quantum Chem. 2010;110:2614–36.
Grosvenor AP, Kobe BA, Biesinger MC, McIntyre NS. Investigation of multiplet splitting of Fe 2p XPS spectra and bonding in iron compounds. Surf Interface Anal. 2004;36:1564–74.
Dupin JC, Gonbeau D, Vinatier P, Levasseur A. Systematic XPS studies of metal oxides, hydroxides and peroxides. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2000;2:1319–24.
Yi ZA, Xu YY, Zhu LP, Dong HB, Zhu BK. Hydrophilic modification of peak porous membranes via aqueous surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. Chin J Polym Sci. 2009;27:695–702.
Vinnichenko M, Chevolleau T, Pham MT, Poperenko L, Maitz MF. Spectroellipsometric, AFM and XPS probing of stainless steel surfaces subjected to biological influences. Appl Surf Sci. 2002;201:41–50.
Billon G, Ouddane B, Gengembre L, Boughriet A. On the chemical properties of sedimentary sulfur in estuarine environments. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2002;4:751–6.
Ait Chikh Z, Chebabe D, Dermaj A, Hajjaji N, Srhiri A, Montemor MF, Ferreira MGS, Bastos AC. Electrochemical and analytical study of corrosion inhibition on carbon steel in HCl medium by 1,12-bis(1,2,4-triazolyl)dodecane. Corros Sci. 2005;47:447–59.
Gece G. The use of quantum chemical methods in corrosion inhibitor studies. Corros Sci. 2008;50:2981–92.
El Ashry ESH, El Nemr A, Essawy SA, Ragab S. Corrosion inhibitors part 3: quantum chemical studies on the efficiencies of some aromatic hydrazides and Schiff bases as corrosion inhibitors of steel in acidic medium. Arkivoc. 2006;11:205–20.
Behpour M, Ghoreishi SM, Soltani N, Salavati-Niasari M, Hamadanian M, Gandomi A. Electrochemical and theoretical investigation on the corrosion inhibition of mild steel by thiosalicylaldehyde derivatives in hydrochloric acid solution. Corros Sci. 2008;50:2172–81.
Obot IB, Obi-Egbedi NO, Umoren SA. The synergistic inhibitive effect and some quantum chemical parameters of 2,3-diaminonaphthalene and iodide ions on the hydrochloric acid corrosion of aluminium. Corros Sci. 2009;51:276–82.
Jae-Yung Yu, Park M, Kim J. Solubilities of synthetic schwertmannite and ferrihydrite. Geochem J. 2002;36:119–32.
Prasad SVS, Sitakara Rao V. Thermal transformation of iron (111) oxide hydrate gel. J Mater Sci. 1984;19:3266–70.
Oliviera C, Marchetti GS, Do Carmo Rangel M. The effect the starting material on the thermal decomposition of iron oxyhydroxides. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2003;73:233–40.
Barron V, Torrent J, De Grave E. Hydromaghemite, an intermediate in the hydrothermal transformation of 2-line ferrihydrite into hematite. Am Mineral. 2003;88:1679–88.
Shah Singh S, Kodama H. Effect of the presence of aluminum ions in iron solutions on the formation of iron oxyhydroxides (FeOOH) at room temperature under acidic environment. Clay Clay Miner. 1994;42:606–13.
Gialanella S, Girardi F, Ischia G, Lonardelli I, Mattarelli M, Montagna M. On the goethite to hematite phase transformation. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;102:867–73.
Rivas Mercury JM, Cabral AA. Thermal behavior and evolution of the mineral phases of Brazilian red mud. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;104:635–43.
Dinesen AR, Pedersen CT, Bender Koch C. The thermal conversion of lepidocrocite (γ-FeOOH) revisited. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;64:1303–10.
Przepiera K, Przepiera A. Thermal transformations of selected transition metals oxyhydroxides. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2003;74:659–66.
Walter D, Buxbaum G. The mechanism of the thermal transformation from goethite to hematite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;63:733–48.
Przepiera K, Przepiera A. Kinetics of thermal transformations of precipitated magnetite and goethite. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;65:497–503.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by CNCSIS-UEFISCSU, project number PNII-IDEI 422/2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samide, A., Tutunaru, B., Dobritescu, A. et al. Study of the corrosion products formed on carbon steel surface in hydrochloric acid solution. J Therm Anal Calorim 110, 145–152 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-2186-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-2186-1