Abstract
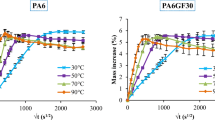
Hygrothermal ageing of polyamide 6 (PA6) and polyamide 6 reinforced with 30 wt% of glass fibers (PA6GF30) was undertaken. Immersion was conducted in distilled water at 90 °C and 100% relative humidity (RH) for up to 80 days (1920 h). Results revealed a noteworthy decrease either in glass transition temperature Tg or in tensile properties, at early stage of ageing, for both studied materials. This decline was mainly caused by the plasticization effect of water and the weakness of the interfacial interactions leading as a consequence to a loss of adhesion between fiber and matrix. Afterwards, physical and mechanical properties decrease monotonically testifying the occurrence of exhaustive damages and chemical reaction phenomena. Such phenomena were yellowing and crazing formation which were observed for both materials after 1920 h of conditioning. The former is caused by the thermo- oxidation whereas the latter results from the release of internal stresses induced by water sorption. These chemical reactions were monitored by infrared spectroscopy. Thus, an increase of the free N-H stretch and the carbonyl groups (imides) was noted. Accordingly, it seems that long term immersion in distilled water at high temperature induces chemical reactions which indicate the severity of the damage.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thomason JL (2008) The influence of fibre length, diameter and concentration on the strength and strain to failure of glass fibre-reinforced polyamide 6,6. Compos Part A 39:1618–1624
Bernasconi A, Davoli P, Basile A, Filippi A (2007) Effect of fibre orientation on the fatigue behaviour of a short glass fibre reinforced polyamide-6. Int J Fatigue 29:199–208
Teixeira D, Giovanela M, Gonella LB, Crespo JS (2013) Influence of flow restriction on the microstructure and mechanical properties of long glass fiber-reinforced polyamide 6.6 composites for automotive applications. Mater Des 47:287–294
Lim LT, Britt IJ, Tung MA (1999) Sorption and transport of water vapor in nylon 6,6 film. J Appl Polym Sci 7:197–206
Mohd Ishak ZA, Berry JP (1994) Effect of moisture absorption on the dynamic mechanical properties of short carbon fiber reinforced nylon 6,6. Polym Compos 15:223–230
Mohd Ishak ZA, Berry JP (1994) Hygrothermal aging studies of short carbon fiber reinforced nylon 6.6. J Appl Polym Sci 51:2145–2155
Bergeret A, Pires I, Foulc MP, Abadie B, Ferry L, Crespy A (2001) The hygrothermal behaviour of glass-fibre-reinforced thermoplastic composites: a prediction of the composite lifetime. Polym Test 20:753–763
Carrascal I, Casado JA, Polanco JA, Gutiérrez-Solana F (2005) Absorption and diffusion of humidity in fiber glass- reinforced polyamide. Polym Compos 26:580–586. doi:10.1002/pc.20134
Gonçalves ES, Poulsen L, Ogilby PR (2007) Mechanism of the temperature-dependent degradation of polyamide 66 films exposed to water. Polym Degrad Stab 92:1977–1985
El-Mazry C, Correc O, Colin X (2012) A new kinetic model for predicting polyamide 6-6 hydrolysis and its mechanical embrittlement. Polym Degrad Stab 97:1049–1059
Regrain C (2009) comportement, endommagement et fissuration par fluage du polyamide 6 etude experimentale et modelisation: Ph.D.Thesis, Mines Paris Tech
Miri V, Persyn O, Lefebvre J-M, Seguela R (2009) Effect of water absorption on the plastic deformation behavior of nylon 6. Eur Polym J 45:757–762
Pillay S, Vaidya UK, Janowski GM (2009) Effects of moisture and UV exposure on liquid molded carbon fabric reinforced nylon 6 composite laminates. Compos Sci Technol 69:839–846
Vlasveld DPN, Groenewold J, Bersee HEN, Picken SJ (2005) Moisture absorption in polyamide-6 silicate nanocomposites and its influence on the mechanical properties. Polymer 46:12567–12576
Rajeesh KR, Gnanamoorthy R, Velmurugan R (2010) Effect of humidity on the indentation hardness and flexural fatigue behavior of polyamide 6 nanocomposite. Material Science and Engineering A 527:2826–2830
Haddar N, Ksouri I, Kallel T, Mnif N (2014) Effect of hygrothermal ageing on the monotonic and cyclic loading of glass fiber reinforced polyamide. Polym Compos 35:501–508
Ferreño D, Carrascal I, Ruiz E, Casado JA (2011) Characterisation by means of a finite element model of the influence of moisture content on the mechanical and fracture properties of the polyamide 6 reinforced with short glass fibre. Polymer Testing 30:420–428
Bernasconi A, Davoli P, Rossin D, Armanni C (2007) Effect of reprocessing on the fatigue strength of a fiberglass reinforced polyamide. Composites Part: A 38:710–718
Foulc MP, Bergeret A, Ferry L, Ienny P, Crespy A (2005) Study of hygrothermal ageing of glass fibre reinforced PET composites. Polym Degrad Stab 89:461–470
Mercier J, Bunsell A, Castaing P, Renard J (2008) Characterisation and modelling of aging of composites. Compos Part A 39:428–438
Scida D, Assarar M, Poilâne C, Ayad R (2013) Influence of hygrothermal ageing on the damage mechanisms of flax-fibre reinforced epoxy composite. Compos Part B 48:51–58
Simar A, Gigliotti M, Grandidier JC, Ammar-Khodja I (2014) Evidence of thermo-oxidation phenomena occurring during hygrothermal aging of thermosetting resins for RTM composite applications. Compos Part A 66:175–182
Mezghani K (2012) Long term environmental effects on physical properties of vinylester composite pipes. Polym Test 31:76–82
B. Ledieu (2010) vieillissement en milieu eau/glycol du polyamide 66 renforcé fibres de verres courtes pour l’application boîte à eau de radiateur de refroidissement moteur: Ph.D.Thesis, École Nationale Supérieure d'Arts et Métiers
Chaupart N, Serpe G, Verdu J (1998) Molecular weight distribution and mass changes during polyamide hydrolysis. Polymer 39:1375–1380
Chevali VS, Dean DR, Janowski GM (2010) Effect of environmental weathering on flexural creep behavior of long fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites. Polym Degrad Stab 95:2628–2640
Thomason JL (2007) Structure-property relationships in glass-reinforced polyamide, part 3: effects of hydrolysis ageing on the dimensional stability and performance of short glass-fiber-reinforced polyamide 66. Polym Compos 28:344–354
Rudzinski S, Häussler L, Harnisch C, Mäder E, Heinrich G (2011) Glass fibre reinforced polyamide composites: Thermal behaviour of sizings. Composites: Part A 42:157–164
El-Mazry C, Ben Hassine M, Correc O, Colin X (2013) Thermal oxidation kinetics of additive free polyamide 6–6. Polymer Degradation and Stability 98:22–36
M.N. Grigg (2006) Thermo-oxydative Degradation of Polyamide 6: Ph.D.Thesis, School of Physical and Chemical Sciences Queensland University of Technology
Li R, Hu X (1998) Study on discoloration mechanism of polyamide 6 during thermo-oxidative degradation. Polym Degrad Stab 62:523–528
Bergeret A, Ferry L, Ienny P (2009) Influence of the fibre/matrix interface on ageing mechanisms of glass fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites (PA-6,6, PET, PBT) in a hygrothermal environment. Polym Degrad Stab 94:1315–1324
Thomason JL, Ali JZ, Anderson J (2010) The thermo-mechanical performance of glass-fibre reinforced polyamide 66 during glycol–water hydrolysis conditioning. Compos Part A 41:820–826
Wu Q, Liu X, Berglund LA (2002) FT-IR spectroscopic study of hydrogen bonding in PA6/clay nanocomposites. Polymer 43:2445–2449
Dong W, Gijsman P (2010) Influence of temperature on the thermo-oxidative degradation of polyamide 6 films. Polym Degrad Stab 95:1054–1062
Cerruti P, Lavorgnac M, Carfagna C, Nicolais L (2005) Comparison of photo-oxidative degradation of polyamide 6,6 films stabilized with HALS and CuCl2+KI mixtures. Polymer 46:4571–4583
Cerruti P, Carfagna C (2010) Thermal-oxidative degradation of polyamide 6,6 containing metal salts. Polymer Degradation and Stability 95:2405–2412
Diogo OO, Richaud E, Verdu J, Fernagut F, Guilment J, Fayolle B (2015) Molecular and macromolecular structure changes in polyamide 11 during thermal oxidation e kinetic modeling. Polym Degrad Stab 120:76–87
Jha A, Bhowmick AK (1998) Thermal degradation and ageing behaviour of novel thermoplastic elastomeric nylon-6/acrylate rubber reactive blends. Polym Degrad Stab 62:575–586
Su KH, Lin JH, Lin CC (2007) Influence of reprocessing on the mechanical properties and structure of polyamide 6. J Mater Process Technol 192–193:532–538
Taktak R, Guermazi N, Derbeli J, Haddar N (2015) Effect of hygrothermal aging on the mechanical properties and ductile fracture of polyamide 6: experimental and numerical approaches. Eng Fract Mech 148:122–133
Phua YJ, Chow WS, Mohd Ishak ZA (2011) The hydrolytic effect of moisture and hygrothermal aging on poly(butylene succinate)/organo-montmorillonite nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stab 96:1194–1203
Ksouri I, Guermazi N, Haddar N, Ferid Ayedi H (2016) Effects of processing steps and hygrothermal ageing on mechanical performance of PA6GF30 composite: interfacial shear strength. Polym Compos. doi: 10.1002/pc.23961
Athijayamani A, Thiruchitrambalam M, Natarajan U, Pazhanivel B (2009) Effect of moisture absorption on the mechanical properties of randomly oriented natural fibers/polyester hybrid. Mater Sci Eng A 517:344–353
Ray BC (2006) Temperature effect during humid ageing on interfaces of glass and carbon fibers reinforced epoxy composites. Journal of Colloid Interface Science 298:111–117
Bergeret A, Ferry L, Ienny P (2009) Influence of the fibre/matrix interface on ageing mechanisms of glass fibre reinforced thermoplastic composites (PA-6,6, PET, PBT) in a hygrothermal environment. Polym Degrad Stab 94:1315–1324
Q.N. THI THUY (2013) Identification des propriétés morphologiques et hygrothermiques hétérogènes de nouveaux composites hautes performances soumis à des cycles de vieillissement thermo-hygro-mécaniques: Ph.D.Thesis, École Nationale Supérieure Saint-Étienne
Mohd Ishak ZA, Ishiaku US, Karger-Kocsis J (2000) Hygrothermal aging and fracture behavior of short-glass-fiber- reinforced rubber-toughened poly(butylene terephthalate) composites. Compos Sci Technol 60:803–815
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the helpful discussions and suggestions provided by Dr. Noamen Guermazi. Authors would like also to thank ICA team (EMAC-France) especially Pr. Thierry Cutard, E. Ramirez, S. Tovar,V. Vidal, and K. Choquet, for their help provided for this research project. This work was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research- Tunisia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ksouri, I., De Almeida, O. & Haddar, N. Long term ageing of polyamide 6 and polyamide 6 reinforced with 30% of glass fibers: physicochemical, mechanical and morphological characterization. J Polym Res 24, 133 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1292-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1292-6