Abstract
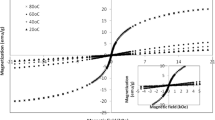
The influence of the precipitant and ferric concentration on the magnetic properties of coprecipitated zinc ferrite nanoparticles has been investigated. The nanoparticles were characterized using X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscope, and vibrating sample magnetometer techniques. The results showed that the single-phase zinc ferrite with partially inverse spinel structures can be formed at high concentrations. The inversion coefficient calculated by the Rietveld method decreases with increasing of the concentrations, may be due to the crystal growth. The magnetic measurements exhibited that the coprecipitated zinc ferrite nanoparticles were superparamagnet and magnetization decreases with increasing of the concentrations through decreasing of inversion coefficient.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikenaga, N., Ohgaito, Y., Matsushima, H., Suzuki, T.: Preparation of zinc ferrite in the presence of carbon material and its application to hot-gas cleaning. Fuel 83, 661–669 (2004)
Jung, C.W., Jacobs, P.: Physical and chemical properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide MR contrast agents: ferumoxides, ferumoxtran, ferumoxsil. Magn. Reson. Imaging 13, 661–674 (1995)
Liu, J.P., et al. (eds.): Nanoscale Magnetic Materials and Applications. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Brusentsov, N.A., Gogosov, V., Brusentsova, T., Sergeev, A., Jurchenko, N., Kuznetsov, A.A., Kuznetsov, O.A., Shumakov, L.: Evaluation of ferromagnetic fluids and suspensions for the site-specific radiofrequency-induced hyperthermia of MX11 sarcoma cells in vitro. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 225, 113–117 (2001)
Atif, M., Hasanain, S.K., Nadeem, M.: Magnetization of sol–gel prepared zinc ferrite nanoparticles: effects of inversion and particle size. Solid State Commun. 138, 416–421 (2006)
Kamiyama, T., Haneda, K., Sato, T., Ikeda, S., Asano, H.: Cation distribution in ZnFe2O4 fine particles studied by neutron powder diffraction. Solid State Commun. 81, 563 (1992)
Sato, T., Haneda, K., Seki, N., Iijima, T.: Morphology and magnetic properties of ultrafine ZnFe2O4 particles. Appl. Phys. A 50, 13 (1990)
Jayadevan, B., Tohji, K., Nakatsuka, K.: Structure analysis of coprecipitated ZnFe2O4 by extended X-ray absorption fine structure. J. Appl. Phys. 76, 6325 (1994)
Oliver, S.A., Harris, V.G., Hamdeh, H., Ho, J.C.: Large zinc cation occupancy of octahedral sites in mechanically activated zinc ferrite powders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2761 (2000)
Chinnasamy, C.N., Narayanasamy, A., Ponpandian, N., Chat-topadhyay, K., Guérault, H., Greneche, J.-M.: Ferrimagnetic ordering in nanostructured zinc ferrite. Scr. Mater. 44, 1407 (2001)
Yao, C., Zeng, Q., Goya, G., Torres, T., Liu, J., Wu, H., Ge, M., Zeng, Y., Wang, Y., Jiang, J.: ZnFe2O4 nanocrystals: synthesis and magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 12274–12278 (2007)
Wang, L., Zhou, Q., Li, F.: Onic disorder and Yaffet–Kittel angle in nanoparticles of ZnFe2O4 prepared by sol-gel method. Phys. Status Solidi, B Basic Res. 241, 377–382 (2004)
Kundu, A., Upadhyay, C., Verma, H.: Magnetic properties of a partially inverted zinc ferrite synthesized by a new coprecipitation technique using urea. Phys. Lett. A 311, 410–415 (2003)
Hu, X., Guan, P., Yan, X.: Hydrothermal synthesis of nano-meter microporous zinc ferrite. China Particuology 2, 135–137 (2004)
Zhang, R., Huang, J., Zhao, J., Sun, Z., Wang, Y.: Sol–gel auto-combustion synthesis of zinc ferrite for moderate temperature desulfurization. Energy Fuels 21, 2682–2687 (2007)
Reddy, B.R., Sivasankar, T., Sivakumar, M., Moholkar, V.S.: Physical facets of ultrasonic cavitational synthesis of zinc ferrite particles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 17, 416–426 (2010)
Raeisi Shahraki, R., et al.: Structural characterization and magnetic properties of superparamagnetic zinc ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by the coprecipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 3762–3765 (2012)
Rietveld, H.M.: A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2, 65–71 (1969)
Bid, S., Pradhan, S.K.: Preparation of zinc ferrite by high-energy ball-milling and microstructure characterization by Rietveld’s analysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 82, 27–37 (2003)
Kim, D.K., Mikhaylova, M., Zhang, Y., Muhammed, M.: Protective coating of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 15, 1617 (2003)
Jolivet, J.P., Chanéac, C., Tronc, E.: Iron oxide chemistry. From molecular clusters to extended solid networks. Chem. Commun. 5, 481–483 (2004)
Tao, K., Dou, H., Sun, K.: Interfacial coprecipitation to prepare magnetite nanoparticles: concentration and temperature dependence. Colloids Surf. A, Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 320, 115–122 (2008)
Cushing, B.L., Kolesnichenko, V.L., O’Connor, C.J.: Recent advances in the liquid-phase syntheses of inorganic nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 104, 3893 (2004)
Massart, R., Roger, J., Cabuil, V.: New trends in chemistry of magnetic colloids: polar and non polar magnetic fluids, emulsions, capsules and vesicles. Braz. J. Phys. 25, 135–141 (1995)
Chinnasamy, C.N., Narayanasamy, A., Ponpandian, N., Chattopadhyay, K., Guérault, H., Greneche, J.-M.: J. Phys. Condens. Matter 12, 7795–7805 (2000)
Bean, C.P., Livingston, J.D.: Superparamagnetism. J. Appl. Phys. 30, 120S (1959)
Kumar, V., Rana, A., Yadav, M.S., Pant, R.P.: Size-induced effect on nano-crystalline CoFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 1729–1734 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimi, M., Raeisi Shahraki, R., Seyyed Ebrahimi, S.A. et al. Magnetic Properties of Zinc Ferrite Nanoparticles Synthesized by Coprecipitation Method. J Supercond Nov Magn 27, 1587–1592 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2485-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2485-4