Abstract
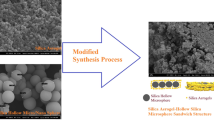
In twentieth century, nations are dealing with several problems related to fresh water availability that needs to be addressed at the earliest. Adsorption desalination by employing inorganic caged silica could be a feasible approach to address this pressing issue. Caged Silica is an inorganic sorbent that is widely employed in a variety of applications, including catalysts, thermal insulation, energy storage batteries, and as an adsorbent in the extraction of fresh water. Researchers have devised several techniques to prepare mono-dispersed caged silica with standard morphology. Template synthesis is quite prominent due to its structural stability and versatility. In this article, we present synthesis of caged silica microsphere via hard template synthesis by employing the process of calcination and subsequent drying. Emulsion polymerization was utilized to develop the polystyrene required in the procedure. This study also looks at how different parameters like silica precursor, surfactant, and catalyst affect silica morphology. We also impregnated Caged silica with 9% of hygroscopic salts (CaCl2 and LiCl) and it showed substantial uptake improvement. Preliminary results showed that LiCl impregnated caged silica is more efficient at water uptake compared to CaCl2.The proposed composite adsorbent (Si-9-Li & Si-9-Ca) could be a step** stone for improvement in the field of desalination, specifically in adsorbent development, and open new doors to exploration and reliability.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 February 2024
The original online version of this article was revised: The email address of the author Muhammad Wakil Shahzad has been changed.
References
M.A. Eltawil, Z. Zhengming, L. Yuan, A review of renewable energy technologies integrated with desalination systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 13(9), 2245–2262 (2009)
M.M. Mekonnen, A.Y. Hoekstra, Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2(2), e1500323 (2016)
Miller, J. E. (2003). Review of water resources and desalination technologies (No. SAND2003–0800). Sandia National Lab.(SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States); Sandia National Lab.(SNL-CA), Livermore, CA (United States).
A. Shahmirzadi, S.S. Hosseini, Environmental aspects of brine management in seawater desalination. Iran-Water Resour. Res. 10(3), 104–112 (2014)
K. Yang, Y. Shi, M. Wu, W. Wang, Y. **, R. Li, P. Wang, Hollow spherical SiO 2 micro-container encapsulation of LiCl for high-performance simultaneous heat reallocation and seawater desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 8(4), 1887–1895 (2020)
M. Nemiwal, D. Kumar, Metal organic frameworks as water harvester from air: hydrolytic stability and adsorption isotherms. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 122, 108279 (2020)
L.G. Gordeeva, Y.D. Tu, Q. Pan, M.L. Palash, B.B. Saha, Y.I. Aristov, R.Z. Wang, Metal-organic frameworks for energy conversion and water harvesting: a bridge between thermal engineering and material science. Nano Energy 84, 105946 (2021)
N. Yu, R.Z. Wang, L.W. Wang, Sorption thermal storage for solar energy. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 39(5), 489–514 (2013)
X. Wang, X. Li, G. Liu, J. Li, X. Hu, N. Xu, J. Zhu, An interfacial solar heating assisted liquid sorbent atmospheric water generator. Angew. Chem. 131(35), 12182–12186 (2019)
H. Qi, T. Wei, W. Zhao, B. Zhu, G. Liu, P. Wang, J. Zhu, An interfacial solar-driven atmospheric water generator based on a liquid sorbent with simultaneous adsorption–desorption. Adv. Mater. 31(43), 1903378 (2019)
J. Xu, T. Li, J. Chao, S. Wu, T. Yan, W. Li, R. Wang, Efficient solar-driven water harvesting from arid air with metal–organic frameworks modified by hygroscopic salt. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59(13), 5202–5210 (2020)
Y.I. Aristov, G. Restuccia, G. Cacciola, V.N. Parmon, A family of new working materials for solid sorption air conditioning systems. Appl. Therm. Eng. 22(2), 191–204 (2002)
L.G. Gordeeva, A.D. Grekova, T.A. Krieger, Y.I. Aristov, Adsorption properties of composite materials (LiCl+ LiBr)/silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 126(3), 262–267 (2009)
Y.I. Aristov, Challenging offers of material science for adsorption heat transformation: a review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 50(2), 1610–1618 (2013)
N. Yu, R.Z. Wang, Z.S. Lu, L.W. Wang, Study on consolidated composite sorbents impregnated with LiCl for thermal energy storage. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 84, 660–670 (2015)
X. Zheng, L.W. Wang, R.Z. Wang, T.S. Ge, T.F. Ishugah, Thermal conductivity, pore structure and adsorption performance of compact composite silica gel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 68, 435–443 (2014)
X. Zheng, R.Z. Wang, T.S. Ge, Experimental study and performance predication of carbon based composite desiccants for desiccant coated heat exchangers. Int. J. Refrig 72, 124–131 (2016)
M.O. Abdullah, I.A.W. Tan, L.S. Lim, Automobile adsorption air-conditioning system using oil palm biomass-based activated carbon: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15(4), 2061–2072 (2011)
R. Li, Y. Shi, M. Alsaedi, M. Wu, L. Shi, P. Wang, Hybrid hydrogel with high water vapor harvesting capacity for deployable solar-driven atmospheric water generator. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52(19), 11367–11377 (2018)
F. Zhao, X. Zhou, Y. Liu, Y. Shi, Y. Dai, G. Yu, Super moisture-absorbent gels for all-weather atmospheric water harvesting. Adv. Mater. 31(10), 1806446 (2019)
R.M. Anisur, J. Shin, H.H. Choi, K.M. Yeo, E.J. Kang, I.S. Lee, Hollow silica nanosphere having functionalized interior surface with thin manganese oxide layer: nanoreactor framework for size-selective Lewis acid catalysis. J. Mater. Chem. 20(47), 10615–10621 (2010)
H. Wang, M. Tang, K. Zhang, D. Cai, W. Huang, R. Chen, C. Yu, Functionalized hollow siliceous spheres for VOCs removal with high efficiency and stability. J. Hazard. Mater. 268, 115–123 (2014)
A. Shkatulov, L.G. Gordeeva, I.S. Girnik, H. Huinink, Y.I. Aristov, Novel adsorption method for moisture and heat recuperation in ventilation: composites “LiCl/matrix” tailored for cold climate. Energy 201, 117595 (2020)
A. Frazzica, V. Brancato, A. Caprì, C. Cannilla, L.G. Gordeeva, Y.I. Aristov, Development of “salt in porous matrix” composites based on LiCl for sorption thermal energy storage. Energy 208, 118338 (2020)
J.Y. Wang, J.Y. Liu, R.Z. Wang, L.W. Wang, Experimental research of composite solid sorbents for fresh water production driven by solar energy. Appl. Therm. Eng. 121, 941–950 (2017)
J.Y. Wang, R.Z. Wang, L.W. Wang, Water vapor sorption performance of ACF-CaCl2 and silica gel-CaCl2 composite adsorbents. Appl. Therm. Eng. 100, 893–901 (2016)
X.Y. Liu, W.W. Wang, S.T. **e, Q.W. Pan, Performance characterization and application of composite adsorbent LiCl@ ACFF for moisture harvesting. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 14412 (2021)
D. Deepika, J. PonnanEttiyappan, Synthesis and characterization of microporous hollow core-shell silica nanoparticles (HCSNs) of tunable thickness for controlled release of doxorubicin. J. Nanopart. Res. 20, 1–15 (2018)
J. Ke, Y. Wang, L. Wang, B. Yang, K. Gou, Y. Qin, H. Li, Synthesis and characterization of core-shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles with various shell thickness as indomethacin carriers: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 297, 110043 (2020)
M.N. Yeasmin, M. Sultana, A. Siddika, S. Tabassum, S.M. Ullah, M.S. Bashar, Structural, optical, and morphological characterization of silica nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel process. J. Turk. Chem. Soc. Sect. A: Chem. 9(4), 1323–1334 (2022)
X. Jiang, X. Tang, L. Tang, B. Zhang, H. Mao, Synthesis and formation mechanism of amorphous silica particles via sol–gel process with tetraethylorthosilicate. Ceram. Int. 45(6), 7673–7680 (2019)
G. Yang, Q. Guo, D. Yang, P. Peng, J. Li, Disperse ultrafine amorphous SiO2 nanoparticles synthesized via precipitation and calcination. Colloids Surf., A 568, 445–454 (2019)
G. Su, C. Yang, J.J. Zhu, Fabrication of gold nanorods with tunable longitudinal surface plasmon resonance peaks by reductive dopamine. Langmuir 31(2), 817–823 (2015)
Gordeeva, L. G., & Aristov, Y. I. (2009). Nanocomposites (salt inside porous matrix) for methanol sorption: design of phase composition and sorption properties, practical applications. Sorbent: Prop., Mater. Appl.
A. Shkatulov, R. Joosten, H. Fischer, H. Huinink, Core–shell encapsulation of salt hydrates into mesoporous silica shells for thermochemical energy storage. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 3(7), 6860–6869 (2020)
M. Takeuchi, R. Kurosawa, J. Ryu, M. Matsuoka, Hydration of LiOH and LiCl─ near-infrared spectroscopic analysis. ACS Omega 6(48), 33075–33084 (2021)
J. Fang, Y. Xuan, Q. Li, Preparation of polystyrene spheres in different particle sizes and assembly of the PS colloidal crystals. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 53, 3088–3093 (2010)
V. Herman, H. Takacs, F. Duclairoir, O. Renault, J.H. Tortai, B. Viala, Core double–shell cobalt/graphene/polystyrene magnetic nanocomposites synthesized by in situ sonochemical polymerization. RSC Adv. 5(63), 51371–51381 (2015)
A.N. Sabbar, H.S. Mohammed, A.R. Ibrahim, H.R. Saud, Thermal and optical properties of polystyrene nanocomposites reinforced with soot. Orient. J. Chem. 35(1), 455 (2019)
M. Agrawal et al., Synthesis of novel tantalum oxide sub-micrometer hollow spheres with tailored shell thickness. Langmuir 24(3), 1013–1018 (2008)
Z. Deng, M. Chen, S. Zhou, B. You, L. Wu, A novel method for the fabrication of monodisperse hollow silica spheres. Langmuir 22(14), 6403–6407 (2006)
N. Shukla, A. Debnath, S. Banerjee, Sonochemical synthesis of silica supported iron nanoparticles for enhanced removal of Cr (VI) species from aqueous medium. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 7, 1–12 (2022)
X. Chen, H. Xu, C. Hua, J. Zhao, Y. Li, Y. Song, Synthesis of silica microspheres—inspired by the formation of ice crystals—With high homogeneous particle sizes and their applications in photonic crystals. Materials 11(10), 2017 (2018)
R. Ellerbrock, M. Stein, J. Schaller, Comparing amorphous silica, short-range-ordered silicates and silicic acid species by FTIR. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 11708 (2022)
M.M. Baig, M.A. Yousuf, I.A. Alsafari, M. Ali, P.O. Agboola, I. Shakir, M.F. Warsi, New mesostructured origami silica matrix: a nano-platform for highly retentive and pH-controlled delivery system. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 15(1), 133–144 (2021)
L.I.U. Chun, H.B. Yin, A.L. Wang, Z.A. Wu, W.U. Gang, T. Jiang, T.S. Jiang, Size-controlled preparation of hollow silica spheres and glyphosate release. Trans. Nonferrous Metals Soc. China 22(5), 1161–1168 (2012)
B.U. Yoo, M.H. Han, H.H. Nersisyan, J.H. Yoon, K.J. Lee, J.H. Lee, Self-templated synthesis of hollow silica microspheres using Na2SiO3 precursor. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 190, 139–145 (2014)
C.M. Hoo, N. Starostin, P. West, M.L. Mecartney, A comparison of atomic force microscopy (AFM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) methods to characterize nanoparticle size distributions. J. Nanopart. Res. 10, 89–96 (2008)
J. Yuan, T. Zhou, H. Pu, Nano-sized silica hollow spheres: preparation, mechanism analysis and its water retention property. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71(7), 1013–1019 (2010)
I. Park, S.H. Ko, Y.S. An, K.H. Choi, H. Chun, S. Lee, G. Kim, Monodisperse polystyrene-silica core-shell particles and silica hollow spheres prepared by the stöber method. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9(12), 7224–7228 (2009)
D. Niu, Z. Ma, Y. Li, J. Shi, Synthesis of core− shell structured dual-mesoporous silica spheres with tunable pore size and controllable shell thickness. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(43), 15144–15147 (2010)
C. Wang, B. Yang, X. Ji, R. Zhang, H. Wu, Study on activated carbon/silica gel/lithium chloride composite desiccant for solid dehumidification. Energy 251, 123874 (2022)
R.H. Mohammed, E. Rashad, R. Huo, M. Su, L.C. Chow, Pore-size engineered nanoporous silica for efficient adsorption cooling and desalination cycle. npj Clean Water 4(1), 38 (2021)
M.W. Shahzad, D. Ybyraiymkul, Q. Chen, M. Burhan, M. Kumja, K.C. Ng, B.B. Xu, Pressure driven adsorption cycle integrated with thermal desalination. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 41, 102608 (2023)
K.C. Ng, M. Burhan, Q. Chen, D. Ybyraiymkul, F.H. Akhtar, M. Kumja, M.W. Shahzad, A thermodynamic platform for evaluating the energy efficiency of combined power generation and desalination plants. npj Clean Water 4(1), 25 (2021)
H.S. Son, M.W. Shahzad, N. Ghaffour, K.C. Ng, Pilot studies on synergetic impacts of energy utilization in hybrid desalination system: multi-effect distillation and adsorption cycle (MED-AD). Desalination 477, 114266 (2020)
M.W. Shahzad, M. Burhan, N. Ghaffour, K.C. Ng, A multi evaporator desalination system operated with thermocline energy for future sustainability. Desalination 435, 268–277 (2018)
M.W. Shahzad, M. Burhan, K.C. Ng, Pushing desalination recovery to the maximum limit: membrane and thermal processes integration. Desalination 416, 54–64 (2017)
M.W. Shahzad, M. Burhan, L. Ang, K.C. Ng, Energy-water-environment nexus underpinning future desalination sustainability. Desalination 413, 52–64 (2017)
M.W. Shahzad, K.C. Ng, An improved multievaporator adsorption desalination cycle for gulf cooperation council countries. Energ. Technol. 5(9), 1663–1669 (2017)
M.W. Shahzad, K. Thu, Y.D. Kim, K.C. Ng, An experimental investigation on MEDAD hybrid desalination cycle. Appl. Energy 148, 273–281 (2015)
K. Thu, Y.D. Kim, M.W. Shahzad, J. Saththasivam, K.C. Ng, Performance investigation of an advanced multi-effect adsorption desalination (MEAD) cycle. Appl. Energy 159, 469–477 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank RAEng / Leverhulme Trust Research Fellowships Tranche 19 for FAM project (LTRF2223-19-103), Northumbria University UK and Northern Accelerator Proof-of-Concept award for AD4DCs (NACCF-232) Awarded to Dr. Muhammad Wakil Shahzad. The authors also would like to thank to KAUST cooling initiative (REP/1/3988-01-01) for the support provided.
Funding
KAUST cooling initiative, REP/1/3988-01-01, Northumbria University UK and Northern Accelerator Proof-of-Concept award for AD4DCs, NACCF-232
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SK and JRK wrote the main manuscript. KCN and MKJ helped with the experimental results. MI and MWS provided the guidance for research. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khushnood, S., Khan, J.R., Ng, K.C. et al. Optimized caged silica synthesis with lithium chloride and calcium chloride impregnation for prospective desalination application. J Porous Mater 31, 625–641 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-023-01536-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-023-01536-x