Abstract
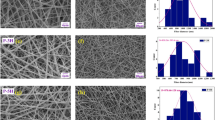
In this study, regarding the importance of optimal design and unique role of a scaffold in tissue regeneration and repair, poly(hydroxybutyrate) (PHB)/multiwalled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) nanocomposite scaffolds with different samples concentrations of CNTs (0, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, and 1.25% w/v) was prepared by electrospinning technique. Morphological evaluation of scaffolds by using scanning electron microscopy showed the pore volume in all the scaffolds was over 80% and the addition of CNTs increased the average fiber diameter, from 210 nm (neat PHB) to 500 nm at 1.0% CNTs. To evaluate the structural properties of scaffolds, transmission electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy were used and showed the presence of CNTs at along the fibers. The analysis of mechanical properties of the PHB/CNTs composites by using universal testing machine revealed great improvement over pure PHB scaffold, so that the tensile stress of the PHB/0.5%CNTs scaffolds was increased by 157%. The bioactivity of scaffolds was analyzed by placing them in simulated body fluid for 4 weeks and results showed that CNTs increase the bioactivity of scaffolds. The wettability of the scaffolds was evaluated with a conventional sessile drop method. The results of contact angles of surface showed that CNTs treatment increases the surface wettability. The attachment ability and viability of osteosarcoma cell lines MG-63 in presence of the scaffolds were also investigated. The attachment and proliferation of MG-63 were significantly increased in the PHB/CNTs scaffolds compared with the PHB control. Therefore, the PHB/CNTs composite scaffolds may be potentially useful in tissue engineering applications.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Abukawa, H. Terai, D. Hannouche, J.P. Vacanti, L.B. Kaban, M.J. Troulis, J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 61, 94 (2003)
D.J. Aframian, R. David, H. Ben-Bassat, E. Shai, D. Deutsch et al., Tissue Eng. 10, 914 (2004)
E. Alsberg, E.E. Hill, D.J. Mooney, Crit. Rev. Oral. Biol. Med. 12(1), 64 (2001)
F.A. Auger, F. Berthod, V. Moulin et al., Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 39(Pt 3), 263 (2004)
P.M. Bartold, C.A. McCulloch, A.S. Narayanan et al., Periodontology 24, 253 (2000)
B.J. Baum, D.J. Mooney, J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 131, 309 (2000)
C.M. Agrawal, R.B. Ray, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 55, 141 (2001)
L. Almany, D. Seliktar, Biomaterials 26, 2467 (2005)
G.H. Altman, F. Diaz, C. Jakuba et al., Silk-based biomaterials. Biomaterials 24, 401–416 (2003)
S.F. Badylak, Transpl. Immunol. 12, 367 (2004)
L.R. Sakaguchi, J.M. Powers, in Craig’s Restorative Dental Materials, 13th edn. Tissue engineering (Elsevier Mosby, St. Louis, MO, 2015), pp. 369–384
A. Hasan, A. Memic, N. Annabi, M. Hossain, A. Paul, R. Mehmet, F. Dehghani, A. Khademhosseini, Acta Biomater. 10(1), 11 (2013)
J. KucinskaLipka, I. Gubanska, H. Janik, M. Sienkiewicz, Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 46, 166 (2015)
T. Jiang, J.E. Carbone, C.T. Laurencin, Prog. Polym. Sci. (2014). doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2014.12.001
A.R. Unnithan, R.S. Arathyram, C.H.S. Kim, in Nanotechnology Applications for Tissue Engineering, Chap. 3 Electrospinning of Polymers for Tissue Engineering, (Elsevier Mosby, St. Louis, MO, 2015) pp. 45–55
M. Spasova, O. Stoilova, I. Manolova, I. Rashkov, J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 26, 48 (2011)
S.J. Hollister, R.D. Maddox, J.M. Taboas, Biomaterials 23, 4095 (2002)
X. Qi, Z. Mou, J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 102, 366 (2014)
S.H. Wua, X. Liu, W. Kelvin, K. Yeung, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 80, 1 (2014)
S. Ravindran, M. Kotecha, C.C. Huang, A. Ye, P. Pothirajan, Z. Yin, R. Magin, A. George, Biomaterials. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.08.030
N. Shadjou, M. Hasanzadeh, Mater. Sci. Eng. C (2015). doi:10.1016/j.msec.2015.05.027.
R.C. Younga, G. Terenghia, M. Wiberg, Br. J. Plast. Surg. 55, 235 (2002)
M. Niaounakis, Biopolymers: Applications and Trends—Processing and Part Fabrication. (Copyright© 2015 Elsevier B.V), p. 91
Niaounakis M (2015) Biopolymers: Applications and Trends—Definitions of Terms and Types of Biopolymers. (Copyright© 2015 Elsevier B.V), p. 1
H. Hajiali, S. Karbasi et al., J. Mater. Sci. 21, 2125 (2010)
R. Iron, M. Mehdikhani, S. Karbasi, 5th International Congress on Nanoscience & Nanotechnology. ICNN2014
N.W. Shi Kam, T.C. Jessop, P.A. Wender, H. Dai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126(22), 6850 (2004)
A. Bianco, K. Kostarelos, M. Prato, Chem. Commun. 37, 10182 (2011)
L. Zhuang, T. Scott, W. Kevin Hongjie, Nano Res. 2(2), 85 (2009)
B.S. Harrison, A. Atala, Biomaterials 28, 44 (2007)
A. Bianco, K. Kostarelos, C.D. Partidos, M. Prato, Chem. Commun. 1, 571 (2005)
S. Iijima, Nature 354, 56 (1991)
E.T. Thostenson, Z. Ren, T.W. Chou, Compos. Sci. Technol. 61, 1899 (2001)
P.G. Collins, P. Avouris, Sci. Am. 283, 62 (2000)
H. Zhang, J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 26(4), 347 (2011)
J.B. Yoo, J.S. Jeong, J.S. Moon, S.Y. Jeong, J.H. Park, J. Phys. Chem. Solids (2006). doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2006.10.058
Q. Chen, J.A. Roether, A.R. Boccaccini, in Topics in Tissue Engineering, vol 4, ed. by N. Asham makhi, R. Reis, F. Chiellini© 2008
H. Wang, Y. Li, Y. Zuo, J. Li, S. Ma, L. Cheng, Biomaterials 28, 3338 (2007)
L. Shor, S. Guceri, X. Wen, M. Gandhi, W. Sun, Biomaterials 28, 5291 (2007)
M.D. Kofron, J.R. Cooper, S.G. Kumbar, C.T. Laurencin, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 82, 415 (2007)
A. Bagchi, S.R. Meka, B.N. Rao, K. Chatterjee, Nanotechnology 25(48), 485101 (2014)
G.M. Kim, G.H. Michler, P. tschke, Polymer 46, 7346 (2005)
Y. Dror, W. Salalha, R.L. Khalfin, Y. Cohen, A.L. Yarin, E. Zussman, Langmuir 19, 7012 (2003)
Q.U. Song, W. Joseph, Y. **ao, Chem. Eur. J. 13(3), 723 (2007)
L. Ghasemi Mobarakeh, D. Semnani, M. Morshed, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 106, 2536 (2007)
ISO 1798:2008 Flexible cellular polymeric materials, Determination of tensile strength and elongation at break. Document published on: 2008-02-01. http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=41059.
S.M. Gubanski, A.E. mastos, IEEE Trans. Power Delivery 5(3), 1527 (1990)
J.M. Deitzel, J. Kleinmeyer, D. Harris, N.C. Beck Tan, Polymer 42, 261 (2001)
M. Naebe, T. Lin, X. Wang, in Nanofibers, ed by A. Kumar (InTech, Rijeka, Croatia, 2010), p. 309
E.D. Boland, D. Branch, P. Catherine, G. David, E. Gary, L. Gary, Acta Biomater. 1, 115 (2005)
C. Ayres, G.L. Bowlin, S.C. Henderson, L. Taylor, J. Shultz, J. Alexander, T.A. Telemeco, D.G. Simpson, Biomaterials 27(32), 5524 (2006)
J. Stephen, W. William, J. Roy. Soc. Interface 2, 309 (2005)
M.D. Landete-Ruiz, J.A. Martínez-Díez, M.A. Rodriguez-Perez, J.A. De Saja, J.M. Martin-Martínez, J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 16, 1073 (2002)
J. Amit, Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol (2016). doi:10.1590/1678-4324-2016150644
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarei, M., Karbasi, S. Evaluation of the effects of multiwalled carbon nanotubes on electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutirate) scaffold for tissue engineering applications. J Porous Mater 25, 259–272 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-017-0439-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-017-0439-5