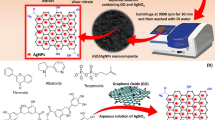
Abstract
In the present work, the synthesis of novel nanocomposite adsorbent based on graft copolymer of Poly(AA)/GG incorporated silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) has been carried out for the elimination of Methylene blue (MB) dye from the aqueous phase. The characterization of synthesized nanocomposite has been carried out by using various analytical techniques such as UV–Vis, FTIR, XRD, FE-SEM, EDX, DLS and BET studies. The UV–Vis, DLS and XRD studies revealed the stable formation of AgNPs inside the polymer matrix with an average size of 100 ± 1 nm. The − 26.40 mV value of Zeta potential also confirms the stability of AgNPs inside the polymer matrix. Furthermore, the resultant adsorbent with an improved adsorption capacity is used to eliminate the MB dye from liquid phase. The parameters such as adsorbent dose and pH of dye solution in adsorption process are optimized. Moreover, the study of the adsorption kinetics and isotherm indicate that the pseudo-second-order kinetics and Langmuir isotherm model is more suitable for describing the experimental adsorption data having maximum adsorption capacity of 833.33 mg/g. Further, the positive values of enthalpy and entropy change specify that the adsorption of MB dye onto the surface of AgNPs/GG/Poly(AA) is endothermic, spontaneous and favorable process. Hence, In-situ synthesis of AgNPs inside polymer and grafting of AA as monomer onto GG has proven to be accountable for the substantial changes in adsorption capacity for removal of MB dye from aqueous phase. Therefore, the resultant AgNPs/GG/Poly(AA) nanocomposite may prove to be a noble adsorbent for the removal of MB dye from the liquid phase.
Graphic Abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramezani S, Zahedi P, Bahrami SH, Nemati Y (2019) Microfluidic fabrication of nanoparticles based on ethyl acrylate-functionalized chitosan for adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. J Polym Environ 27:1653–1665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01463-6
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2010) Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater 177:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.047
Sen TK, Afroze S, Ang HM (2011) Equilibrium, kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption onto pine cone biomass of Pinus radiata. Water Air Soil Pollut 218:499–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0663-y
Zollinger H (2003) Color chemistry: syntheses, properties, and applications of organic. Dyes Pigment. https://doi.org/10.1002/col.5080130314
Liu Y, Chen X, Li J, Burda C (2005) Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes by nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanocatalysts. Chemosphere 61:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.069
Singh J, Dhaliwal AS (2018) Plasmon-induced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye using biosynthesized silver nanoparticles as photocatalyst. Environ Technol (United Kingdom). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1540663
Khan MI, Akhtar S, Zafar S et al (2015) Removal of Congo Red from aqueous solution by anion exchange membrane (EBTAC): adsorption kinetics and themodynamics. Materials (Basel) 8:4147–4161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8074147
Akbari A, Remigy JC, Aptel P (2002) Treatment of textile dye effluent using a polyamide-based nanofiltration membrane. Chem Eng Process 41:601–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0255-2701(01)00181-7
Zhu MX, Lee L, Wang HH, Wang Z (2007) Removal of an anionic dye by adsorption/precipitation processes using alkaline white mud. J Hazard Mater 149:735–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.04.037
Rastgar M, Zolfaghari AR, Mortaheb HR et al (2013) Photocatalytic/adsorptive removal of methylene blue dye by electrophoretic nanostructured TiO2/montmorillonite composite films. J Adv Oxid Technol 16:292–297. https://doi.org/10.1515/jaots-2013-0211
Wang S, Zhu ZH (2005) Sonochemical treatment of fly ash for dye removal from wastewater. J Hazard Mater 126:91–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.06.009
Fernandes A, Morao A, Magrinho M et al (2004) Electrochemical degradation of C. I. Acid Orange 7. Dye Pigment 61:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2003.11.008
Pelekani C, Snoeyink VL (2001) Kinetic and equilibrium study of competitive adsorption between atrazine and Congo red dye on activated carbon: the importance of pore size distribution. Carbon N Y 39:25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(00)00078-6
Pendleton P, Wu SH (2003) Kinetics of dodecanoic acid adsorption from caustic solution by activated carbon. J Colloid Interface Sci 266:245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9797(03)00575-7
Faria PCC, Orfao JJM, Pereira MFR (2004) Adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes on activated carbons with different surface chemistries. Water Res 38:2043–2052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2004.01.034
Ai L, Li M, Li L (2011) Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution with activated carbon/cobalt ferrite/alginate composite beads: kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamics. J Chem Eng Data 56:3475–3483. https://doi.org/10.1021/je200536h
Baek MH, Ijagbemi CO, Se-** O, Kim DS (2010) Removal of Malachite Green from aqueous solution using degreased coffee bean. J Hazard Mater 176:820–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.110
Zhao M, Tang Z, Liu P (2008) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution with silica nano-sheets derived from vermiculite. J Hazard Mater 158:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.031
Attia AA, Girgis BS, Fathy NA (2008) Removal of methylene blue by carbons derived from peach stones by H3PO4 activation: batch and column studies. Dye Pigment 76:282–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.08.039
Hajati S, Ghaedi M, Mazaheri H (2016) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by walnut carbon: optimization using response surface methodology. Desalin Water Treat 57:3179–3193. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.981217
Ahmad S, Ahmad M, Manzoor K et al (2019) A review on latest innovations in natural gums based hydrogels: preparations & applications. Int J Biol Macromol 136:870–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.113
Mittal H, **dal R, Kaith BS et al (2014) Synthesis and flocculation properties of gum ghatti and poly(acrylamide-co-acrylonitrile) based biodegradable hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym 114:321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.08.029
Singh J, Dhaliwal AS (2019) Novel green synthesis and characterization of the antioxidant activity of silver nanoparticles prepared from Nepeta leucophylla root extract. Anal Lett 52:213–230. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2018.1454936
Ghorai S, Sarkar A, Raoufi M et al (2014) Enhanced removal of methylene blue and methyl violet dyes from aqueous solution using a nanocomposite of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide grafted xanthan gum and incorporated nanosilica. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:4766–4777. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4055657
Singh J, Kumar S, Dhaliwal AS (2020) Journal of drug delivery science and technology controlled release of amoxicillin and antioxidant potential of gold nanoparticles-xanthan gum/poly (Acrylic acid) biodegradable nanocomposite. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 55:101384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101384
Ghimici L, Nichifor M (2010) Novel biodegradable flocculanting agents based on cationic amphiphilic polysaccharides. Bioresour Technol 101:8549–8554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.049
Manzoor K, Ahmad M, Ahmad S, Ikram S (2019) Synthesis, characterization, kinetics, and thermodynamics of EDTA-modified chitosan-carboxymethyl cellulose as Cu(II) ion adsorbent. ACS Omega 4:17425–17437. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b02214
Paulino AT, Belfiore LA, Kubota LT et al (2011) Efficiency of hydrogels based on natural polysaccharides in the removal of Cd2+ ions from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 168:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.037
Mittal H, Maity A, Ray SS (2016) Gum karaya based hydrogel nanocomposites for the effective removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions. Appl Surf Sci 364:917–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.12.241
Manatunga DC, De Silva RM, De Silva KMN, Ratnaweera R (2016) Natural polysaccharides leading to super adsorbent hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for the removal of heavy metals and dyes from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 6:105618–105630. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra22662k
Lessa EF, Medina AL, Ribeiro AS, Fajardo AR (2020) Removal of multi-metals from water using reusable pectin/cellulose microfibers composite beads. Arab J Chem 13:709–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.07.011
Crini G (2005) Recent developments in polysaccharide-based materials used as adsorbents in wastewater treatment. Prog Polym Sci 30:38–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2004.11.002
Manzoor K, Ahmad M, Ahmad S, Ikram S (2019) Removal of Pb(ii) and Cd(ii) from wastewater using arginine cross-linked chitosan-carboxymethyl cellulose beads as green adsorbent. RSC Adv 9:7890–7902. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9RA00356H
Yan L, Chang PR, Zheng P, Ma X (2012) Characterization of magnetic guar gum-grafted carbon nanotubes and the adsorption of the dyes. Carbohydr Polym 87:1919–1924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.09.086
Sharma R, Kalia S, Kaith BS, Srivastava MK (2016) Synthesis of guar gum-acrylic acid graft copolymers based biodegradable adsorbents for cationic dye removal. Int J Plast Technol 20:294–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12588-016-9156-1
Mittal H, Maity A, Ray SS (2015) Effective removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution using gum ghatti-based biodegradable hydrogel. Int J Biol Macromol 79:8–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.04.045
Kumar N, Mittal H, Parashar V et al (2016) Efficient removal of rhodamine 6G dye from aqueous solution using nickel sulphide incorporated polyacrylamide grafted gum karaya bionanocomposite hydrogel. RSC Adv 6:21929–21939. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA24299A
Kera NH, Bhaumik M, Ballav N et al (2016) Selective removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by polypyrrole/2,5-diaminobenzene sulfonic acid composite. J Colloid Interface Sci 476:144–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.05.011
Shankar SS, Rai A, Ahmad A, Sastry M (2004) Rapid synthesis of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au core-Ag shell nanoparticles using Neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf broth. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:496–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.03.003
Mittal AK, Bhaumik J, Kumar S, Banerjee UC (2014) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles: elucidation of prospective mechanism and therapeutic potential. J Colloid Interface Sci 415:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.10.018
Singh J, Dhaliwal AS (2019) Water retention and controlled release of KCl by using microwave—assisted green synthesis of xanthan gum—cl - poly ( acrylic acid )/AgNPs hydrogel nanocomposite. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02990-x
Sharma R, Kaith BS, Kalia S et al (2015) Biodegradable and conducting hydrogels based on Guar gum polysaccharide for antibacterial and dye removal applications. J Environ Manag 162:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.07.044
Pandey S, Goswami GK, Nanda KK (2013) Green synthesis of polysaccharide/gold nanoparticle nanocomposite: an efficient ammonia sensor. Carbohydr Polym 94:229–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.009
Singh J, Dhaliwal AS (2018) Synthesis, characterization and swelling behavior of silver nanoparticles containing superabsorbent based on grafted copolymer of polyacrylic acid/Guar gum. Vacuum 157:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.08.017
Vieira AP, Santana SAA, Bezerra CWB et al (2009) Kinetics and thermodynamics of textile dye adsorption from aqueous solutions using babassu coconut mesocarp. J Hazard Mater 166:1272–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.043
Pathania D, Sharma S, Singh P (2017) Removal of methylene blue by adsorption onto activated carbon developed from Ficus carica bast. Arab J Chem 10:S1445–S1451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.04.021
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents. Process Saf Environ Prot 76:332–340. https://doi.org/10.1205/095758298529696
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02268a002
Ozmen EY, Yilmaz M (2007) Use of β-cyclodextrin and starch based polymers for sorption of Congo red from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 148:303–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.02.042
Freundlich H, Heller W (1939) The Adsorption of cis - and trans -Azobenzene. J Am Chem Soc 61:2228–2230. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01877a071
Khan TA, Dahiya S, Ali I (2012) Use of kaolinite as adsorbent: equilibrium, dynamics and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution. Appl Clay Sci 69:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2012.09.001
Liu C, Omer AM, Ouyang X (2017) Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue dye using carboxymethyl cellulose/k-carrageenan/activated montmorillonite composite beads: isotherm and kinetic studies. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.084
Gong G, Zhang F, Cheng Z, Zhou L (2015) Facile fabrication of magnetic carboxymethyl starch/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite gel for methylene blue removal. Int J Biol Macromol 81:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.07.061
Ge F, Ye H, Li M-M, Zhao B-X (2012) Efficient removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by polymer-modified magnetic nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 198–199:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.074
Sun XF, Liu B, **g Z, Wang H (2015) Preparation and adsorption property of xylan/poly(acrylic acid) magnetic nanocomposite hydrogel adsorbent. Carbohydr Polym 118:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.11.013
Hou C, Ma K, Jiao T et al (2016) Preparation and dye removal capacities of porous silver nanoparticle-containing composite hydrogels: via poly(acrylic acid) and silver ions. RSC Adv 6:110799–110807. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra23371f
Liu Y, Hou C, Jiao T et al (2018) Self-assembled AgNP-containing nanocomposites constructed by electrospinning as efficient dye photocatalyst materials for wastewater treatment. Nanomaterials. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8010035
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the MHRD (Govt. of India), New Delhi, and Sant Longowal Institute of Engineering and Technology, Longowal (SLIET), for providing the essential research facilities. The author (Jagdeep Singh) is also very thankful to the Sophisticated Analytical Instrumentation Facility (SAIF), Panjab University, Chandigarh and central facility of SLIET, Longowal for analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, J., Dhaliwal, A.S. Effective Removal of Methylene Blue Dye Using Silver Nanoparticles Containing Grafted Polymer of Guar Gum/Acrylic Acid as Novel Adsorbent. J Polym Environ 29, 71–88 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01859-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-020-01859-9