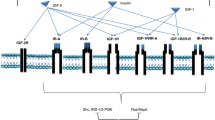
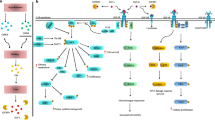
Abstract
The insulin-like growth factor pathway plays a major role in cancer cell proliferation, survival and resistance to anti-cancer therapies in many human malignancies, including breast cancer. As a key signaling component of IGF system, the IGF-1 receptor is the target of several investigational agents in clinical and pre-clinical development. This review will focus on the rationale for targeting the IGF-1 receptor and other components of the IGF-1 system. In addition, we will examine the role of IGF-1 signaling in resistance to clinically important breast cancer therapies, including cytotoxic chemotherapy, hormonal therapy and erbB targeted agents. We will also review the completed and ongoing clinical investigations with IGF-1 receptors inhibitors to date and the utility of these early data in designing future breast cancer studies with IGF-1 signaling inhibition strategies.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACC:
-
adrenocortical carcinoma
- ALL:
-
acute lymphocytic leukemia
- AST:
-
aspartate aminotransferase
- ASCO:
-
American Society of Clinical Oncology
- CDK4:
-
cyclin-dependent kinase 4
- CML:
-
chronic myelogenous leukemia
- CR:
-
complete response
- CRC:
-
colorectal cancer
- DLT:
-
dose limiting toxicity
- ER:
-
estrogen receptor
- FDG-PET:
-
14fluoro deoxyglucose-positron emission tomography
- FIH:
-
first in human
- GGT:
-
gamma-glutamyltransferase
- HER2:
-
human epidermal growth factors receptor 2
- H&N:
-
head and neck cancer
- HRPC:
-
hormone refractory prostate cancer
- IGFBP:
-
insulin-like growth factor binding protein
- IGF-1R:
-
insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
- IR:
-
insulin receptor
- mab:
-
monoclonal antibody
- MFD:
-
maximal feasible dose
- MFH:
-
malignant fibrous histiocytoma
- MR:
-
minor response
- NHL:
-
non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- NOS:
-
not otherwise specified
- NSCLCA:
-
non-small cell lung cancer
- PI3K:
-
phosphoinositidyl-3 kinase
- PNET:
-
peripheral neuroendocrine tumor
- PPP:
-
picropodophyllin
- PR:
-
partial response
- PSA:
-
prostate specific antigen
- RR:
-
response rate
- SD:
-
stable disease
- TKI:
-
tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Sell C, Rubini M, Rubin R, Liu JP, Efstratiadis A, Baserga R. Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen is unable to transform mouse embryonic fibroblasts lacking type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90 23:11217–21. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.23.11217.
Carboni JM, Lee AV, Hadsell DL, Rowley BR, Lee FY, Bol DK, et al. Tumor development by transgenic expression of a constitutively active insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Cancer Res. 2005;65 9:3781–7. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4602.
Lopez T, Hanahan D. Elevated levels of IGF-1 receptor convey invasive and metastatic capability in a mouse model of pancreatic islet tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2002;1 4:339–53. doi:10.1016/S1535-6108(02)00055-7.
Yakar S, Leroith D, Brodt P. The role of the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor axis in tumor growth and progression: lessons from animal models. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005;16 4–5:407–20. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2005.01.010.
Hartog H, Wesseling J, Boezen HM, van der Graaf WT. The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in cancer: old focus, new future. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43 13:1895–904. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2007.05.021.
Nielsen TO, Andrews HN, Cheang M, Kucab JE, Hsu FD, Ragaz J, et al. Expression of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor and urokinase plasminogen activator in breast cancer is associated with poor survival: potential for intervention with 17-allylamino geldanamycin. Cancer Res. 2004;64 1:286–91. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-1242.
Bonneterre J, Peyrat JP, Beuscart R, Demaille A. Prognostic significance of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990;50 21:6931–5.
Niedernhofer LJ, Garinis GA, Raams A, Lalai AS, Robinson AR, Appeldoorn E, et al. A new progeroid syndrome reveals that genotoxic stress suppresses the somatotroph axis. Nature 2006;444 7122:1038–43. doi:10.1038/nature05456.
Jones JI, Clemmons DR. Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev. 1995;16 1:3–34. doi:10.1210/er.16.1.3.
Lavoie JN, L'Allemain G, Brunet A, Muller R, Pouyssegur J. Cyclin D1 expression is regulated positively by the p42/p44MAPK and negatively by the p38/HOGMAPK pathway. J Biol Chem. 1996;271 34:20608–16. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.34.20608.
Rosenthal SM, Cheng ZQ. Opposing early and late effects of insulin-like growth factor I on differentiation and the cell cycle regulatory retinoblastoma protein in skeletal myoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92 22:10307–11. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.22.10307.
Hamelers IH, van Schaik RF, Sipkema J, Sussenbach JS, Steenbergh PH. Insulin-like growth factor I triggers nuclear accumulation of cyclin D1 in MCF-7S breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277 49:47645–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208727200.
Coats S, Flanagan WM, Nourse J, Roberts JM. Requirement of p27Kip1 for restriction point control of the fibroblast cell cycle. Science 1996;272 5263:877–80. doi:10.1126/science.272.5263.877.
Lu L, Katsaros D, Wiley A, de la Longrais IA, Puopolo M, Yu H. Klotho expression in epithelial ovarian cancer and its association with insulin-like growth factors and disease progression. Cancer Invest. 2008;26 2:185–92. doi:10.1080/07357900701638343.
Lu L, Katsaros D, Wiley A, Rigault de la Longrais IA, Puopolo M, Schwartz P, et al. Promoter-specific transcription of insulin-like growth factor-II in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;103 3:990–5. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2006.06.006.
Pasanisi P, Venturelli E, Morelli D, Fontana L, Secreto G, Berrino F. Serum insulin-like growth factor-I and platelet-derived growth factor as biomarkers of breast cancer prognosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17 7:1719–22. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0654.
Vadgama JV, Wu Y, Datta G, Khan H, Chillar R. Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and serum IGF-binding protein 3 can be associated with the progression of breast cancer, and predict the risk of recurrence and the probability of survival in African–American and Hispanic women. Oncology 1999;57 4:330–40. doi:10.1159/000012052.
Haluska P, Shaw H, Batzel GN, Molife LR, Adjei AA, Yap TA, et al. Phase I dose escalation study of the anti-IGF-1R monoclonal antibody CP-751,871 in patients with refractory solid tumors. ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2007;25 18_suppl:3586.
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, Andre F, Tordai A, Mejia JA, et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26 8:1275–81. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.4147.
Harris LN, You F, Schnitt SJ, Witkiewicz A, Lu X, Sgroi D, et al. Predictors of resistance to preoperative trastuzumab and vinorelbine for HER2-positive early breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13 4:1198–207. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1304.
Pandini G, Vigneri R, Costantino A, Frasca F, Ippolito A, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, et al. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptor overexpression in breast cancers leads to insulin/IGF-I hybrid receptor overexpression: evidence for a second mechanism of IGF-I signaling. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5 7:1935–44.
Pandini G, Frasca F, Mineo R, Sciacca L, Vigneri R, Belfiore A. Insulin/insulin-like growth factor I hybrid receptors have different biological characteristics depending on the insulin receptor isoform involved. J Biol Chem. 2002;277 42:39684–95. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202766200.
Kido Y, Nakae J, Accili D. Clinical review 125: the insulin receptor and its cellular targets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86 3:972–9. doi:10.1210/jc.86.3.972.
Frasca F, Pandini G, Scalia P, Sciacca L, Mineo R, Costantino A, et al. Insulin receptor isoform A, a newly recognized, high-affinity insulin-like growth factor II receptor in fetal and cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19 5:3278–88.
Pandini G, Wurch T, Akla B, Corvaia N, Belfiore A, Goetsch L. Functional responses and in vivo anti-tumour activity of h7C10: a humanised monoclonal antibody with neutralising activity against the insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptor and insulin/IGF-1 hybrid receptors. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43 8:1318–27. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2007.03.009.
Jenab M, Riboli E, Cleveland RJ, Norat T, Rinaldi S, Nieters A, et al. Serum C-peptide, IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-2 and risk of colon and rectal cancers in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Int J Cancer. 2007;121 2:368–76. doi:10.1002/ijc.22697.
Lukanova A, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Lundin E, Micheli A, Arslan AA, Rinaldi S, et al. Prediagnostic levels of C-peptide, IGF-I, IGFBP-1, -2 and -3 and risk of endometrial cancer. Int J Cancer. 2004;108 2:262–8. doi:10.1002/ijc.11544.
Wang HS, Wang TH. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), insulin resistance and insulin-like growth factors (IGfs)/IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs). Chang Gung Med J. 2003;26 8:540–53.
Belfiore A, Pandini G, Vella V, Squatrito S, Vigneri R. Insulin/IGF-I hybrid receptors play a major role in IGF-I signaling in thyroid cancer. Biochimie 1999;81 4:403–7. doi:10.1016/S0300-9084(99)80088-1.
Garrouste FL, Remacle-Bonnet MM, Lehmann MM, Marvaldi JL, Pommier GJ. Up-regulation of insulin/insulin-like growth factor-I hybrid receptors during differentiation of HT29-D4 human colonic carcinoma cells. Endocrinology 1997;138 5:2021–32. doi:10.1210/en.138.5.2021.
Papa V, Pezzino V, Costantino A, Belfiore A, Giuffrida D, Frittitta L, et al. Elevated insulin receptor content in human breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 1990;86 5:1503–10. doi:10.1172/JCI114868.
Mathieu MC, Clark GM, Allred DC, Goldfine ID, Vigneri R. Insulin receptor expression and clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1997;109 6:565–71.
Sciacca L, Costantino A, Pandini G, Mineo R, Frasca F, Scalia P, et al. Insulin receptor activation by IGF-II in breast cancers: evidence for a new autocrine/paracrine mechanism. Oncogene 1999;18 15:2471–9. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202600.
Munshi S, Hall DL, Kornienko M, Darke PL, Kuo LC. Structure of apo, unactivated insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor kinase at 1.5 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2003;59 Pt 10:1725–30. doi:10.1107/S0907444903015415.
Garcia-Echeverria C, Pearson MA, Marti A, Meyer T, Mestan J, Zimmermann J, et al. In vivo antitumor activity of NVP-AEW541-A novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of the IGF-IR kinase. Cancer Cell. 2004;5 3:231–9. doi:10.1016/S1535-6108(04)00051-0.
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades NS, McMullan CJ, Poulaki V, Shringarpure R, Akiyama M, et al. Inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 tyrosine kinase activity as a therapeutic strategy for multiple myeloma, other hematologic malignancies, and solid tumors. Cancer Cell. 2004;5 3:221–30. doi:10.1016/S1535-6108(04)00050-9.
Vasilcanu R, Vasilcanu D, Rosengren L, Natalishvili N, Sehat B, Yin S, et al. Picropodophyllin induces downregulation of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor: potential mechanistic involvement of Mdm2 and beta-arrestin1. Oncogene 2008;27 11:1629–38. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210797.
Haluska P, Carboni JM, Loegering DA, Lee FY, Wittman M, Saulnier MG, et al. In vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of the dual insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin receptor inhibitor, BMS-554417. Cancer Res. 2006;66 1:362–71. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1107.
Karp DD, Paz-Ares LG, Blakely LJ, Kreisman H, Eisenberg PD, Cohen RB, et al. Efficacy of the anti-insulin like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) antibody CP-751871 in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2007;25 18_suppl:7506.
Dunn SE, Hardman RA, Kari FW, Barrett JC. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) alters drug sensitivity of HBL100 human breast cancer cells by inhibition of apoptosis induced by diverse anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 1997;57 13:2687–93.
Gooch JL, Van Den Berg CL, Yee D. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I rescues breast cancer cells from chemotherapy-induced cell death-proliferative and anti-apoptotic effects. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1999;56 1:1–10. doi:10.1023/A:1006208721167.
Lee JY, Han CY, Yang JW, Smith C, Kim SK, Lee EY, et al. Induction of glutathione transferase in insulin-like growth factor type I receptor-overexpressed hepatoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;72 4:1082–93. doi:10.1124/mol.107.038174.
Yee D, Favoni RE, Lebovic GS, Lombana F, Powell DR, Reynolds CP, et al. Insulin-like growth factor I expression by tumors of neuroectodermal origin with the t(11;22) chromosomal translocation. A potential autocrine growth factor. J Clin Invest. 1990;86 6:1806–14. doi:10.1172/JCI114910.
Scotlandi K, Manara MC, Nicoletti G, Lollini PL, Lukas S, Benini S, et al. Antitumor activity of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor kinase inhibitor NVP-AEW541 in musculoskeletal tumors. Cancer Res. 2005;65 9:3868–76. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3192.
Scotlandi K, Avnet S, Benini S, Manara MC, Serra M, Cerisano V, et al. Expression of an IGF-I receptor dominant negative mutant induces apoptosis, inhibits tumorigenesis and enhances chemosensitivity in Ewing's sarcoma cells. Int J Cancer. 2002;101 1:11–6. doi:10.1002/ijc.10537.
Benini S, Manara MC, Baldini N, Cerisano V, Massimo S, Mercuri M, et al. Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor I receptor increases the antitumor activity of doxorubicin and vincristine against Ewing's sarcoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7 6:1790–7.
Martins AS, Mackintosh C, Martin DH, Campos M, Hernandez T, Ordonez JL, et al. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor pathway inhibition by ADW742, alone or in combination with imatinib, doxorubicin, or vincristine, is a novel therapeutic approach in Ewing tumor. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12 11 Pt 1:3532–40. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1778.
Chu KC, Anderson WF, Fritz A, Ries LA, Brawley OW. Frequency distributions of breast cancer characteristics classified by estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status for eight racial/ethnic groups. Cancer 2001;92 1:37–45. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(20010701)92:1<37::AID-CNCR1289>3.0.CO;2-F.
MacGregor JI, Jordan VC. Basic guide to the mechanisms of antiestrogen action. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50 2:151–96.
Nahta R, Esteva FJ. HER2 therapy: molecular mechanisms of trastuzumab resistance. Breast Cancer Res. 2006;8 6:215. doi:10.1186/bcr1612.
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem. 2001;276 13:9817–24. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010840200.
Parisot JP, Hu XF, DeLuise M, Zalcberg JR. Altered expression of the IGF-1 receptor in a tamoxifen-resistant human breast cancer cell line. Br J Cancer. 1999;79 5–6:693–700. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6690112.
Knowlden JM, Hutcheson IR, Barrow D, Gee JM, Nicholson RI. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: a supporting role to the epidermal growth factor receptor. Endocrinology 2005;146 11:4609–18. doi:10.1210/en.2005-0247.
Cohen BD, Baker DA, Soderstrom C, Tkalcevic G, Rossi AM, Miller PE, et al. Combination therapy enhances the inhibition of tumor growth with the fully human anti-type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11 5:2063–73. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1070.
Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Creighton CJ, Qin L, Tsimelzon A, Huang S, et al. Tamoxifen resistance in breast tumors is driven by growth factor receptor signaling with repression of classic estrogen receptor genomic function. Cancer Res. 2008;68 3:826–33. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2707.
Lu Y, Zi X, Zhao Y, Mascarenhas D, Pollak M. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling and resistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin). J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93 24:1852–7. doi:10.1093/jnci/93.24.1852.
Nahta R, Yuan LX, Zhang B, Kobayashi R, Esteva FJ. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 heterodimerization contributes to trastuzumab resistance of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65 23:11118–28. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3841.
Haluska P, Carboni JM, TenEyck C, Attar RM, Hou X, Yu C, et al. HER receptor signaling confers resistance to the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibitor, BMS-536924. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7 9:2589–98. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0493.
Lacy MQ, Alsina M, Fonseca R, Paccagnella ML, Melvin CL, Yin D, et al. Phase I, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the anti-insulinlike growth factor Type 1 receptor monoclonal antibody CP-751,871 in patients with multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26 19:3196–203. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.9319.
Karp DD, Paz-Ares LG, Novello S, Haluska P, Garland L, Cardenal F, et al. High activity of the anti-IGF-IR antibody CP-751,871 in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in squamous NSCLC. ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2008;26 15_suppl:8015.
Gualberto A, Melvin CL, Dean A, Ang AL, Reynolds JM, Lee AV, et al. Characterization of NSCLC patients responding to anti-IGF-IR therapy. ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2008;26 15_suppl:8000.
Higano CS, Yu EY, Whiting SH, Gordon MS, LoRusso P, Fox F, et al. A phase I, first in man study of weekly IMC-A12, a fully human insulin like growth factor-I receptor IgG1 monoclonal antibody, in patients with advanced solid tumors. ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2007;25 18_suppl:3505.
Olmos D, Okuno S, Schuetze SM, Paccagnella ML, Yin D, Gualberto A, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and preliminary activity of the anti-IGF-IR antibody CP-751,871 in patients with sarcoma. ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2008;26 15_suppl:10501.
Sarantopoulos J, Mita AC, Mulay M, Romero O, Lu J, Capilla F, et al. A phase IB study of AMG 479, a type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) antibody, in combination with panitumumab (P) or gemcitabine (G). ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2008;26 15_suppl:3583.
Atzori F, Tabernero J, Cervantes A, Botero M, Hsu K, Brown H, et al. A phase I, pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) study of weekly (qW) MK-0646, an insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) monoclonal antibody (MAb) in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors. ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2008;26 15_suppl:3519.
Hidalgo M, Tirado Gomez M, Lewis N, Vuky JL, Taylor G, Hayburn JL, et al. A phase I study of MK-0646, a humanized monoclonal antibody against the insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 (IGF1R) in advanced solid tumor patients in a q2 wk schedule. ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2008;26 15_suppl:3520.
Rodon J, Patnaik A, Stein M, Tolcher A, Ng C, Dias C, et al. A phase I study of q3W R1507, a human monoclonal antibody IGF-1R antagonist in patients with advsanced cancer. ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2007;25 18_suppl:3590.
Moreau P, Hulin C, Facon T, Boccadoro M, Mery-Mignard D, Deslandes A, et al. Phase I Study of AVE1642 Anti IGF-1R monoclonal antibody in patients with advanced multiple myeloma. Blood 2007;110 11:1166. ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts.
Tolcher AW, Patnaik A, Till E, Takimoto CH, Papadopoulos KP, Massard C, et al. A phase I study of AVE1642, a humanized monoclonal antibody IGF-1R (insulin like growth factor1 receptor) antagonist, in patients(pts) with advanced solid tumor(ST). ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2008;26 15_suppl:3582.
Harzstark AL, Ryan C, Diamond M, Jones J, Zavodovskaya M, Maddux B, et al. A phase I trial of nordihydroguareacetic acid (NDGA) in patients with non-metastatic prostate cancer and rising PSA. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2007;25 18_suppl:15500.
Pollak MN, Lacy MQ, Lipton A, Demers L, Leitzel K, de Bono JS, et al. Pharmacodynamic properties of the anti-IGF-IR monoclonal antibody CP-751,871 in cancer patients. ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2007;25 18_suppl:3587.
Tolcher AW, Rothenberg ML, Rodon J, Delbeke D, Patnaik A, Nguyen L, et al. A phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of AMG 479, a fully human monoclonal antibody against insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor (IGF-1R), in advanced solid tumors. ASCO Meeting Abstracts 2007;25 18_suppl:3002.
Lacy M, Alsina M, Melvin CL, Roberts L, Yin D, Petersen JF, et al. Phase 1 first-in-human dose escalation study of cp-751,871, a specific monoclonal antibody against the insulin like growth factor 1 receptor. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2006;24 18_suppl:7609.
Wittman M, Carboni J, Attar R, Balasubramanian B, Balimane P, Brassil P, et al. Discovery of a (1H-benzoimidazol-2-yl)-1H-pyridin-2-one (BMS-536924) inhibitor of insulin-like growth factor I receptor kinase with in vivo antitumor activity. J Med Chem. 2005;48 18:5639–43. doi:10.1021/jm050392q.
Parrizas M, Gazit A, Levitzki A, Wertheimer E, LeRoith D. Specific inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity and biological function by tyrphostins. Endocrinology 1997;138 4:1427–33. doi:10.1210/en.138.4.1427.
Arteaga CL, Kitten LJ, Coronado EB, Jacobs S, Kull FC Jr, Allred DC, et al. Blockade of the type I somatomedin receptor inhibits growth of human breast cancer cells in athymic mice. J Clin Invest. 1989;84 5:1418–23. doi:10.1172/JCI114315.
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge J. Mark Curry of the Mayo Clinic Section of Illustration & Design for his assistance with the drawings. We thank Barbara Rainville for her help with secretarial support related to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by the Mayo Clinic Breast SPORE (CA116201-01), NIH K12 (CA090628-05) the Fred C. and Katherine B. Andersen Foundation and the Mayo Clinic Cancer Center (CA15083).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weroha, S.J., Haluska, P. IGF-1 Receptor Inhibitors in Clinical Trials—Early Lessons. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 13, 471–483 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-008-9104-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-008-9104-6