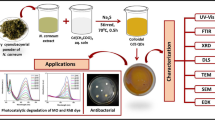
Abstract
In this study, two solvents (deep eutectic and water/deep eutectic solvents) were used for N-doped carbon dots (N-CDs) preparation by microwave irradiation. The solvent can influence surface chemical composition, quantum yield, morphology, and fluorescence of CDs. N-CDs synthesized in water/deep eutectic solvent (DES) had better quantum yield (24.5%) with respect to N-CDs synthesized in deep eutectic solvent (17.4%). These carbon dots were used as a rapid and high sensitive “off–on” fluorescent probe for the determination of Fe3+ ion and cetirizine. Morphology and structure of the N-CDs were characterized by FT-IR, UV–Vis, XRD and TEM. Linear range and detection limit for N-CDs synthesis in deep eutectic solvent for cetirizine were 0.08–48 µM and 15 nM, respectively and for N-CDs synthesis in water/deep eutectic solvent were 0.03–50 µM and 10 nM, respectively. Applicability of this nanoprobe was tested in cetirizine determination in serum sample. Antibacterial activities of the two synthesized N-CDs were also investigated using agar disk diffusion method.





Similar content being viewed by others
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Li H, Kang Z, Liu Y, Lee ST (2012) Carbon nanodots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem 22:24230–24253
Wang Q, Zheng H, Long Y, Zhang L, Gao M, Bai W (2011) Microwave–hydrothermal synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from graphite oxide. Carbon 49:3134–3140
Zuo P, Lu X, Sun Z, Guo Y, He H (2016) A review on syntheses, properties, characterization and bioanalytical applications of fluorescent carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183:519–542
Fan J, Chu PK (2010) Group IV nanoparticles: synthesis, properties, and biological applications. Small 6:2080–2098
Qu D, Zheng M, Zhang L, Zhao H, **e Z, **g X et al (2014) Formation mechanism and optimization of highly luminescent N-doped graphene quantum dots. Sci Rep 4:5294
Lim S, Shen W, Gao Z (2015) Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:362–381
Wang H, Lu Q, Hou Y, Liu Y, Zhang Y (2016) High fluorescence S, N co-doped carbon dots as an ultra-sensitive fluorescent probe for the determination of uric acid. Talanta 155:62–69
Li H, Sun C, Vijayaraghavan R, Zhou F, Zhang X, MacFarlane D (2016) Long lifetime photoluminescence in N, S co-doped carbon quantum dots from an ionic liquid and their applications in ultrasensitive detection of pesticides. Carbon 104:33–39
Zhang Y, Cui P, Zhang F, Feng X, Wang Y, Yang Y et al (2016) Fluorescent probes for “off–on” highly sensitive detection of Hg2+ and L-cysteine based on nitrogen-doped carbon dots. Talanta 152:288–300
Gao Z, Li X, Shi L, Yang Y (2019) Deep eutectic solvents-derived carbon dots for detection of mercury (II), photocatalytic antifungal activity and fluorescent labeling for C. albicans. Spectrochim Acta A 220:117080
Yang J, Zhang X, Ma Y, Gao G, Chen X, Jia HR (2016) Carbon dot-based platform for simultaneous bacterial distinguishment and antibacterial applications. ACS Appl Mater Inter 8:32170–32181
Travlou N, Giannakoudakis D, Algarra M, Labella A (2018) S-and N-doped carbon quantum dots: Surface chemistry dependent antibacterial activity. Carbon 135:104–111
Zhao Y, Tian Y, Cui Y, Liu W, Ma W, Jiang X (2010) Small molecule-capped gold nanoparticles as potent antibacterial agents that target Gram-negative bacteria. J Am Chem Soc 132:12349–12356
Liu J, Lu S, Tang Q, Zhang K, Yu W (2017) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of photoluminescent carbon nanodots with selective antibacterial activity against Porphyromonas gingivalis. Nanoscale 9:7135–7142
Shetti NP, Maloje SJ, Nayak DS, Aminabhavi TM (2019) Nanostructured silver doped Ti02/CNTs hybrid as an efficient electrochemical drug, cetirizine. Microchem J 150:104124
Çalhan SD, Alaş M, Aşık M, Kaya F (2018) One-pot synthesis of hydrophilic and hydrophobic fluorescent carbon dots using deep eutectic solvents as designer reaction media. J Mater Sci 53:15362–15375
Tereshatov EE, Boltoeva MY, Folden CM (2016) First evidence of metal transfer into hydrophobic deep eutectic and low-transition-temperature mixtures: indium extraction from hydrochloric and oxalic acids. Green Chem 18:4616–4622
Jiang X, Huang J, Chen T, Zhao Q (2020) Synthesis of hemicellulose/deep eutectic solvent based carbon quantum dots for ultrasensitive detection of Ag+ and L-cysteine with “off-on” pattern. Int J Boil Macromol 153:412–420
Yin Q, Wang M, Fang D, Zhu Y (2021) Novel N, Cl-doped deep eutectic solvents-based carbon dots as a selective fluorescent probe for determination of morphine in food. RSC Adv 11:16805–16811
Li L, Huang Y, Zhao P, Miao H, Zhao T (2020) Deep eutectic solvent-assisted synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for cell imaging. Chem Res Chinese U 36:955–961
Nazari F, Tabaraki R (2020) Sensitive fluorescence detection of atorvastatin by doped carbon dots synthesized in deep eutetic media. Spectrochim Acta A 236:118341
Grabolle M, Spieles M, Lesnyak V, Gaponik N, Eychmuüller A, Resch-Genger U (2009) Determination of the fluorescence quantum yield of quantum dots: suitable procedures and achievable uncertainties. Anal Chem 81:6285–6294
Liu L, Feng F, Paau MC, Hu Q, Liu Y, Chen Z et al (2015) Sensitive determination of kaempferol using carbon dots as a fluorescence probe. Talanta 144:390–397
Boonmee C, Promarak V, Tuntulani T, Ngeontae W (2018) Cysteamine-capped copper nanoclusters as a highly selective turn-on fluorescent assay for the detection of aluminum ions. Talanta 178:796–804
Lee JK, Lee S, Kim YI, Kim JG, Min BK, Lee KI et al (2015) The seeded growth of graphene. Sci Rep 4:5682
Liao S, Zhao X, Zhu F, Chen M, Wu Z, Yang H et al (2018) Novel S, N-doped carbon quantum dot-based off-on" fluorescent sensor for silver ion and cysteine. Talanta 180:300–308
Gao G, Jiang YW, Jia HR, Yang J, Wu FG (2018) On-off-on fluorescent nanosensor for Fe3+ detection and cancer/normal cell differentiation via silicon-doped carbon quantum dots. Carbon 134:232–243
Lee CBTL, Wu TY, Ting CH, Tan JK, Siow LF, Cheng CK et al (2019) One-pot furfural production using choline chloride-dicarboxylic acid based deep eutectic solvents under mild conditions. Bioresour Technol 278:486–489
Culkova E, Chomistekova ZL, Bellova R, Melichercíkova D, Durdiak J, Timko J et al (2018) Boron-doped diamond film electrode as voltammetric sensor for cetirizine. Int J Electrochem 13:6358–6372
Pushpanjali PA, Manjunatha JG, Hareesha N, D'Souza ES, Charithra MM, Prinith NS (2021) Voltammetric analysis of antihistamine drug cetirizine and paracetamol at poly (L-Leucine) layered carbon nanotube paste electrode. Surf Inter 24:101154
Kalambate PK, Srivastava AK (2016) Simultaneous voltammetric determination of paracetamol, cetirizine and phenylephrine using a multiwalled carbon nanotube-platinum nanoparticles nanocomposite modified carbon paste electrode. Sens Actuat B-Chem 233:237–248
Karakaya S, Dilgin DG (2019) Low-cost determination of cetirizine by square wave voltammetry in a disposable electrode. Monatsh Chem 150:1003–1010
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fereshteh Nazari: Carried out the experiment, wrote—original draft. Reza Tabaraki: Supervision, Project administration, Resources, Writing—Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabaraki, R., Nazari, F. Comparison of Carbon Dots Prepared in Deep Eutectic Solvent and Water/Deep Eutectic Solvent: Study of Fluorescent Detection of Fe3+ and Cetirizine and their Photocatalytic Antibacterial Activity. J Fluoresc 32, 549–558 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-021-02875-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-021-02875-1