Abstract
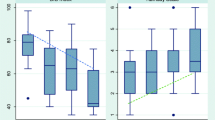
Prior studies have examined the static effect of intravenous ketamine on the BIS Index for sedation but it remains unknown if the BIS Index is a reliable method to track sedation levels in the presence of ketamine. The major objective of the current investigation was to compare the BIS Vista Index ability to track varying depths of sedation as determined by OASS scores in a standardized anesthetic regimen with and without ketamine. The study was a randomized, double blinded clinical trial. Patients undergoing breast surgery under sedation with propofol were randomized to receive ketamine (1.5 μg kg min−1) or saline. Infusion data was used to estimate propofol plasma concentrations (Cp). The main outcome of interest was the correlation between the BIS Vista Index with the OASS score. Twenty subjects were recruited and fifteen completed the study. Four hundred fifty-five paired data points were included in the analysis. Model performance (Nagelkerke R2) of the multinomial logistic regression model was 0.57 with the c-statistic of 0.87 (95 % CI 0.82–0.91). Compared to awake the odds ratio for BIS values predicting moderate sedation in the saline/propofol group 1.19 (95 % CI 1.12–1.25) but only 1.06 (95 % CI 1.02–1.1) in the ketamine/propofol group (P = 0.001). There was no difference in the odds for BIS values to predict deep sedation between groups (P = 0.14). The BIS monitor can be used to monitor sedation level even when ketamine is used with propofol as part of the sedation regimen. However, ketamine reduces the value of the BIS in predicting moderate sedation levels.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gharaei B, Jafari A, Aghamohammadi H, Kamranmanesh M, Poorzamani M, Elyassi H, Rostamian B, Salimi A. Opioid-sparing effect of preemptive bolus low-dose ketamine for moderate sedation in opioid abusers undergoing extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy: a randomized clinical trial. Anesth Analg. 2013;116:75–80.
Smith MC, Williamson J, Yaster M, Boyd GJ, Heitmiller ES. Off-label use of medications in children undergoing sedation and anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2012;115:1148–54.
Webb ST, Hunter DN II. Is sedation by non-anaesthetists really safe? Br J Anaesth. 2013;111:136–8.
Robbertze R, Posner KL, Domino KB. Closed claims review of anesthesia for procedures outside the operating room. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2006;19:436–42.
Radtke FM, Franck M, Lendner J, Krüger S, Wernecke KD, Spies CD. Monitoring depth of anaesthesia in a randomized trial decreases the rate of postoperative delirium but not postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110:i98–105.
Adams R, Brown GT, Davidson M, Fisher E, Mathisen J, Thomson G, Webster NR. Efficacy of dexmedetomidine compared with midazolam for sedation in adult intensive care patients: a systematic review. Br J Anaesth. 2013;111:703–10.
Kertai MD, Whitlock EL, Avidan MS. Brain monitoring with electroencephalography and the electroencephalogram-derived bispectral index during cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 2012;114:533–46.
Yang KS, Habib AS, Lu M, Branch MS, Muir H, Manberg P, Sigl JC, Gan TJ. A prospective evaluation of the incidence of adverse events in nurse-administered moderate sedation guided by sedation scores or bispectral index. Anesth Analg. 2014;119:43–8.
Villafranca A, Thomson IA, Grocott HP, Avidan MS, Kahn S, Jacobsohn E. The impact of bispectral index versus end-tidal anesthetic concentration-guided anesthesia on time to tracheal extubation in fast-track cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 2013;116:541–8.
Möller Petrun A, Kamenik M. Bispectral index-guided induction of general anaesthesia in patients undergoing major abdominal surgery using propofol or etomidate: a double-blind, randomized, clinical trial. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110:388–96.
Choi WJ, Kim SH, Koh WU, Hwang DI, Cho SK, Park PH, Han SM, Shin JW. Effect of pre-exposure to sevoflurane on the bispectral index in women undergoing Caesarean delivery under general anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2012;108:990–7.
Vereecke HE, Struys MM, Mortier EP. A comparison of bispectral index and ARX derived auditory evoked potential index in measuring the clinical interaction between ketamine and propofol anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2003;58:957–61.
Baxter I. Mortality, BIS and the ketamine conundrum. Anaesthesia. 2012;67:800–1.
Hans P, Dewandre PY, Brichant JF, Bonhomme V. Comparative effects of ketamine on Bispectral Index and spectral entropy of the electroencephalogram under sevoflurane anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2005;94:336–40.
Corssen G, Domino EF, Bree RL. Electroencephalographic effects of ketamine anesthesia in children. Anesth Analg. 1969;48:141–7.
Hirota K, Kubota T, Ishihara H, Matsuki A. The effects of nitrous oxide and ketamine on the bispectral index and 95 % spectral edge frequency during propofol–fentanyl anaesthesia. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1999;16:779–83.
Vereecke HE, Struys MM, Mortier EP. A comparison of bispectral index and ARX-derived auditory evoked potential index in measuring the clinical interaction between ketamine and propofol anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 2003;58:957–61.
De Oliveira GS, Fitzgerald PC Jr, Hansen N, Ahmad S, McCarthy RJ. The effect of ketamine on hypoventilation during deep sedation with midazolam and propofol: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2014;31:654–62.
Niesters M, Aarts L, Sarton E, Dahan A. Influence of ketamine and morphine on descending pain modulation in chronic pain patients: a randomized placebo-controlled cross-over proof-of-concept study. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110:1010–6.
Gharaei B, Jafari A, Aghamohammadi H, Kamranmanesh M, Poorzamani M, Elyassi H, Rostamian B, Salimi A. Opioid-sparing effect of preemptive bolus low-dose ketamine for moderate sedation in opioid abusers undergoing extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy: a randomized clinical trial. Anesth Analg. 2013;116:75–80.
Grady MV, Mascha E, Sessler DI, Kurz A. The effect of perioperative intravenous lidocaine and ketamine on recovery after abdominal hysterectomy. Anesth Analg. 2012;115:1078–84.
Rancourt MP, Albert NT, Côté M, Létourneau DR, Bernard PM. Posterior tibial nerve sensory blockade duration prolonged by adding dexmedetomidine to ropivacaine. Anesth Analg. 2012;115:958–62.
Chernik DA, Gillings D, Laine H, Hendler J, Silver JM, Davidson AB, Schwam EM, Siegel JL. Validity and reliability of the Observer’s Assessment of Alertness/Sedation Scale: study with intravenous midazolam. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1990;10:244–51.
Schnider TW, Minto CF, Gambus PL, Andresen C, Goodale DB, Shafer SL, Youngs EJ. The influence of method of administration and covariates on the pharmacokinetics of propofol in adult volunteers. Anesthesiology. 1998;88:1170–82.
DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44:837–45.
Faraoni D, Salengros JC, Engelman E, Ickx B, Barvais L. Ketamine has no effect on bispectral index during stable propofol–remifentanil anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2009;102:336–9.
Kurehara K, Asano N, Iwata T, Yamaguchi A, Kawano Y, Furuya H. The influence of ketamine on the bispectral index, the spectral edge frequency 90 and the frequency bands power during propofol anesthesia. Masui. 1999;48:611–6.
Phillips W, Anderson A, Rosengreen M, Johnson J, Halpin J. Propofol versus propofol/ketamine for brief painful procedures in the emergency department: clinical and bispectral index scale comparison. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2010;24:349–55.
Morse Z, Kaizu M, Sano K, Kanri T. BIS monitoring during midazolam and midazolam–ketamine conscious intravenous sedation for oral surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;94:420–4.
Acknowledgments
Author receives Grants from “IRB# Northwestern University STU00031783”.
Funding
Department of Anesthesiology, Northwestern University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Financial disclosure
The Department of Anesthesiology at Northwestern University sponsored the research. The authors are employed by the Department of Anesthesiology at Northwestern University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Oliveira, G.S., Kendall, M.C., Marcus, RJ. et al. The relationship between the Bispectral Index (BIS) and the Observer Alertness of Sedation Scale (OASS) scores during propofol sedation with and without ketamine: a randomized, double blinded, placebo controlled clinical trial. J Clin Monit Comput 30, 495–501 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-015-9745-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-015-9745-0