Abstract
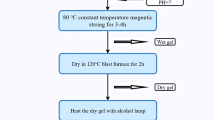
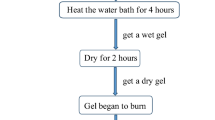
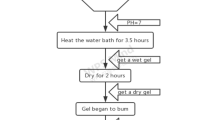
In this study, yttrium ion-doped nickel–magnesium–cobalt ferrite powder was prepared by the sol–gel auto combustions method. The chemical formula is Ni0.2Mg0.1Co0.7Fe2–xYxO4 (where x = 0.00, 0.02, 0.04, 0.06, and 0.08). The structure and magnetic properties were studied by X-ray diffractometer (XRD), Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). XRD measurements show that Ni–Mg–Co ferrite has a good phase formations, and all samples have single-phase cubic spinel structure. As the do** amount of yttrium ions increases, the lattice constant of the samples increases first and then decreases. FTIR measurements also confirm the formations of the cubic spinel structure of ferrite. The UV–Vis optical analysis shows that the bandgap value of optical energy decreases after do** Y3+ ions. SEM confirmed that the sample was spherical spinel with a particle size of 54–60 nm. The saturation magnetizations (Ms) and remanent magnetizations (Mr) increase first and then decrease with the increase of Y3+ ions content at room temperature. This shows that the small amount of Y3+ ions-doped nickel–magnesium–cobalt nanoferrite can optimize the magnetic properties of the ferrite. The coercivity of the samples also showed a downward trend. The comprehensive measurement data show that the sample has the best magnetic properties when x = 0.02. This is also confirmed that the ferrite can be used as magnetic storage material.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Bozadgiev, T. Dimova, T. Mitev, Classifications of ferrospinel structures and textures. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. (1985). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1985.tb15250.x
M. Rostami, M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.R. Ganjali et al., Facile synthesis and characterizations of TiO2–graphene–ZnFe2−xTbxO4 ternary nano-hybrids. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 7008–7016 (2017)
B. Geller, A. Coville, Magnetism and magnetic materials. Phys. Today 11, 48–48 (1958)
A.T. Raghavendar, D. Pajic, K. Zadro, T. Milekovic, P.V. Rao, K.M. Jadhav, D. Ravinder, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, 1–7 (2007)
C. Venkataraju, G. Sathishkumar, K. Sivakumar, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 1817–1822 (2011)
L. Zhao, H. Yang, L. Yu, Y. Cui, X. Zhao, B. Zou, S. Feng, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 301, 445–451 (2006)
S. Uday Bhasker et al., Preparations and characterizations of cobalt magnesium nano ferrites using auto-combustions method. Adv. Mater. Res. 584, 280–284 (2012)
N. Ranvah, Y. Melikhov, I.C. Nlebedim, D.C. Jiles, J.E. Snyder, A.J. Moses, P.I. Williams, Temperature dependence of magnetic anisotropy of germanium/cobalt cosubstituted cobalt ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 5181–5183 (2009)
S.U. Bhasker, Reddy MR Effect of chromium substitutions on structural, magnetic and electrical properties of magneto ceramic cobalt ferrite nano-particles. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 73, 396–402 (2015)
J.A. Paulsen, C.C.H. Lo, J.E. Snyder, A.P. Ring, L.L. Jones, D.C. Jiles, Study of the curie temperature of cobalt ferrite based composites for stress sensor applications. IEEE. Trans. Magn. 39, 3316–3318 (2003)
K.K. Bharathi, J.A. Chelvane, Markandeyulu G Magneto electric properties of Gd and Nd-doped nickel ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 3677–3680 (2009)
M. R ahimi-Nasrabadi, M. Behpour, A. Sobhani-Nasab, S. MostafaHosseinpour-Mashkani, ZnFe2−xLaxO4 nanostructure: synthesis, characterizations, and its magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 9776–9781 (2015)
M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M. Behpour, A. Sobhani-Nasab, Nanocrystalline Ce-doped copper ferrite: synthesis, characterizations, and its photocatalyst applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 11691–11697 (2016)
M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M. Rostami, F. Ahmadi, Synthesis and characterizations of ZnFe(2−x)YbxO4−xgraphene nanocomposites by sol–gel method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 11940–11945 (2016)
S.M. Peymani-Motlagh, N. Moeinian, M. Rostami et al., Effect of Gd3+-, Pr3+- or Sm3+-substituted cobalt–zinc ferrite on photodegradations of methyl orange and cytotoxicity tests. J. Rare Earths 37, 1288–1295 (2019)
X. Pan, A. Sun, Y. Han, Structural and magnetic properties of Bi3+ ions doped Ni–Cu–Co nano ferrites prepared by sol–gel auto combustions method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 4644–4657 (2019)
K. Chen, H. Yang, F. Liang et al., Microwave-irradiations-assisted combustions toward modified graphite as lithium ions battery anode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 909–914 (2017)
K. Chen, H. Yang, F. Liang, D. Xue, A.C.S. Appl, Mater. Interfaces 10, 909–914 (2018)
A. Gholizadeh, E. Jafari, Effects of sintering atmosphere and temperature on structural and magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Zn ferrite nano-particles: Magnetic enhancement by a reducing atmosphere. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 422, 328–336 (2017)
Z. Liu, Z. Peng, C. Lv et al., Do** effect of Sm3+ on magnetic and dielectric properties of Ni–Zn ferrites. Ceram. Int. 43, 1449–1454 (2017)
U. Kurtan, R. Topkaya, S. Esir, A. Baykal, Sol–gel auto combustions synthesis of CoFe2O4/1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone nanocomposite: its magnetic characterizations. Ceram. Int. 39, 6407–6413 (2013)
M.A. Ahmed, S.F. Mansour, M. Afifi, Structural and electrical properties of nanometric Ni–Cu ferrites synthesized by citrate precursor method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 4–10 (2012)
B.R. Babu, M.S.R. Prasad et al., Structural and magnetic properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5AlxFe2−xO4 nano ferrite system. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 148, 585–591 (2014)
M. Kaiser, Effect of nickel substitutions on some properties of Cu–Zn ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 468, 15–21 (2009)
C. Sujatha, K.V. Reddy, K.S. Babu, A.R. Reddy, Rao KH Effect of sintering temperature on electromagnetic properties of NiCuZn ferrite. Ceram. Int. 39, 3077–3086 (2013)
D. Cullity, S.R. Stock, Elements of X-ray diffractions: Pearson new international editions. Fuel 102, 716–723 (2012)
K. Siraj, M. Khaleeq-ur-Rahman, S.I. Hussain, M.S. Rafique, S. Anjum, Effect of depositions temperature on structural, surface, optical and magnetic properties of pulsed laser deposited Al doped CdO thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 6756–6762 (2011)
V.J. Angadi, B. Rudraswamy, K. Sadhana, S.R. Murthy, K. Praveena, Effect of Sm3+–Gd3+ on structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrites synthesized via combustions route. J. Alloys Compd. 656, 5–12 (2016)
K. Krieble, T. Schaeffer, J.A. Paulsen, A.P. Ring, C.C.H. Lo, J.E. Snyder, Mössbauer spectroscopy investigations of Mn-substituted Co-ferrite (Co MnxFe2−xO4). J. Appl. Phys. 97, 98–101 (2005)
J.M. Hastzngs, L.M. Corliss, Neutron diffractions studies of zinc ferrite and nickel ferrite. Rev. Mod. Phys. 25, 114–119 (1953)
G.A. Sawatzky, F.V.D. Woude, A.H. Morrish, Mossbauer study of several ferrimagnetic spinels. Phys. Rev. 187, 747–757 (1969)
M.M. Eltabey, K.M. El-Shokrofy, S.A. Gharbia, Enhancement of the magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Zn ferrites by the non-magnetic Al3+-ions substitutions. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 2473–2477 (2011)
M. Ashokkumar, Zn0.96−xCu0.04FexO (0 ≤ x ≤ 004) alloys—optical and structural studies. Superlattices Microstruct. 69, 53–64 (2014)
P.A. Shaikh, R.C. Kambale, A.V. Rao, Y.D. Kolekar, Effect of Ni do** on structural and magnetsic properties of Co1–xNixFe1.9Mn0.1O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 718–726 (2010)
M.W. Mushtaq et al., Synthesis, structural and biological studies of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 48, 3–565 (2015)
S. Patil, H.B. Naik, G. Nagaraju, R. Viswanath, S. Rashmi, Synthesis of visible light active Gd3+-substituted ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles for photocatalytic and anti-bacterial activities. Eur. Phys. J. 132, 320–328 (2017)
R.C. Kambale, P.A. Shaikh, S.S. Kamble, Y.D. Kolekar, Effect of cobalt substitutions on structural, magnetic and electric proper ties of nickel ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 478, 599–603 (2009)
D. Fritsch, C. Ederer, Epitaxial strain effects in the spinel ferrites CoFe2O4 and NiFe2O4 from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 82, 104–117 (2010)
C.N. Chervin, B.J. Clapsaddle, H.W. Chiu et al., Role of cyclic ether and solvent in a non-alkoxide sol–gel synthesis of yttria-stabilized zirconia nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 18, 4865–4874 (2006)
V. Chaudhari, S.E. Shirsath, M.L. Mane, R.H. Kadam, S.B. Shelke, Mane DR Crystallographic, magnetic and electrical properties of Ni0.5Cu0.25Zn0.25LaxFe2−xO4 nanoparticles fabricated by sol–gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 549, 213–220 (2013)
I.P. Muthuselvam, R.N. Bhowmik, Mechanical alloyed Ho~(3+) do** in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite and understanding of magnetic nanodomains. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 767–776 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that the manuscript complies with the ethical rules applicable to this journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Sun, A., Suo, N. et al. Enhancement of magnetic properties of Ni–Mg–Co ferrites by Y3+ ions do**. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 14961–14976 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04059-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04059-2